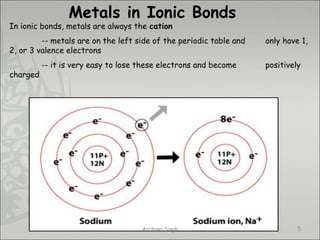
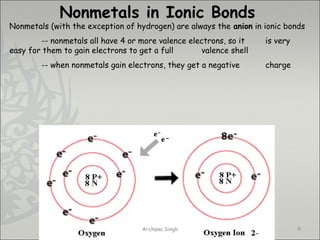
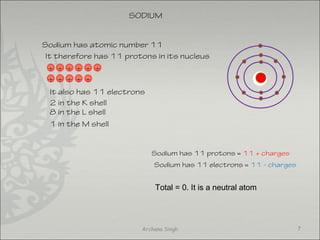
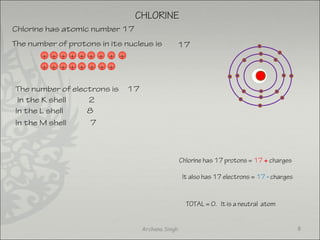
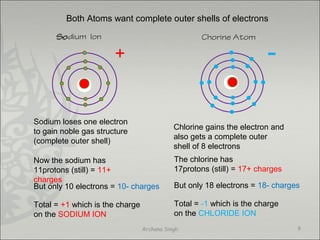
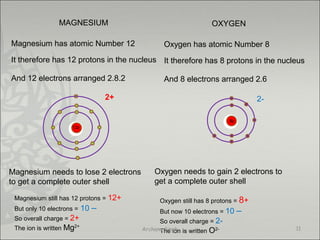
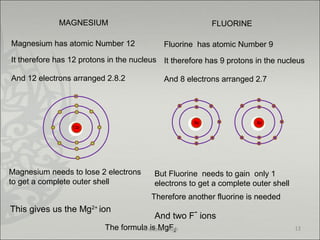
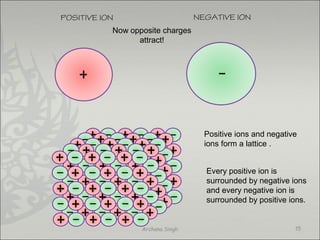
The document discusses ionic bonding between metals and non-metals. Ionic bonding occurs when metals give up electrons to form positive ions and non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions. The positive and negative ions are then attracted to each other, forming an ionic compound. Metals are usually found on the left side of the periodic table and easily give up valence electrons. Non-metals are usually on the right side and readily gain electrons to achieve a full valence shell. When ions form, they arrange in a crystalline lattice structure with positive and negative ions alternating. Ionic compounds have properties like being crystalline solids, having high melting points, and being able to conduct electricity when melted or