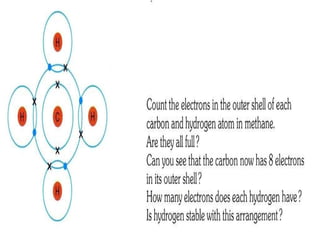
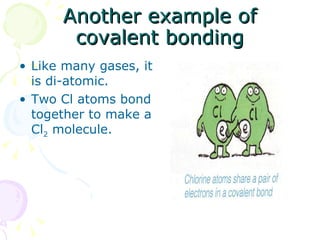
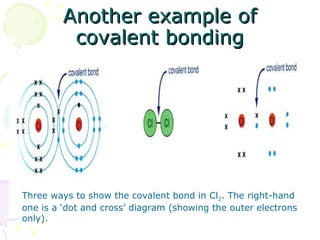
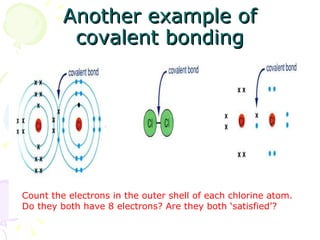
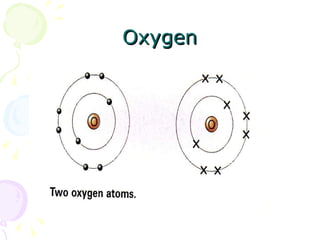
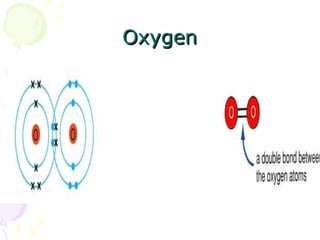
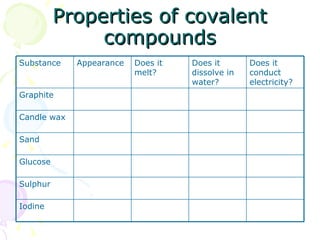
Covalent bonding occurs when two non-metal atoms share electrons in their outer shells to gain a stable electron configuration. Chlorine exists as Cl2 molecules where each chlorine atom shares one electron with the other to fill its outer shell. Oxygen also exists as O2 molecules where each oxygen atom shares two electrons in a double bond to fill its outer shell. Covalent compounds have strong bonds within their molecules but weak intermolecular forces, which explains their low melting points and why many exist as gases.