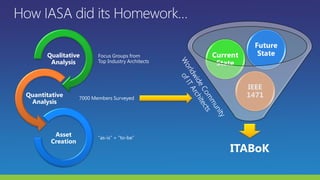
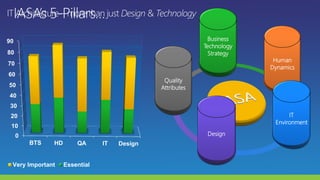
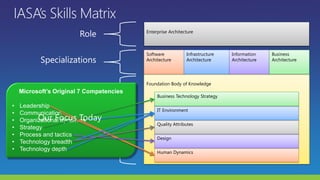
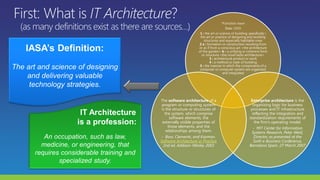
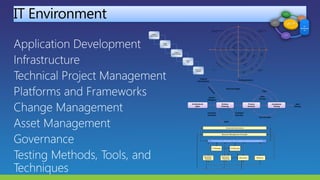
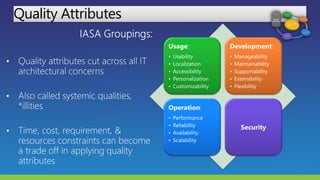
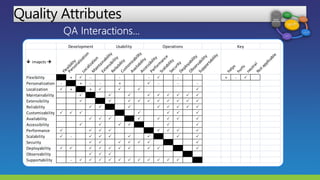
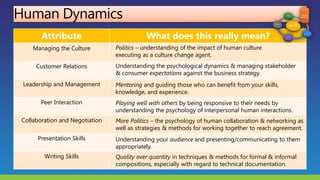
The document lists several distinguished fellows and their affiliations in enterprise architecture. It then discusses the development of the IT Architecture Body of Knowledge (ITABoK) which was informed by focus groups, a 7000 member survey, and asset creation. The document outlines the ITABoK framework which includes 5 pillars (human dynamics, design, quality attributes, IT environment, business technology strategy) and several specializations.