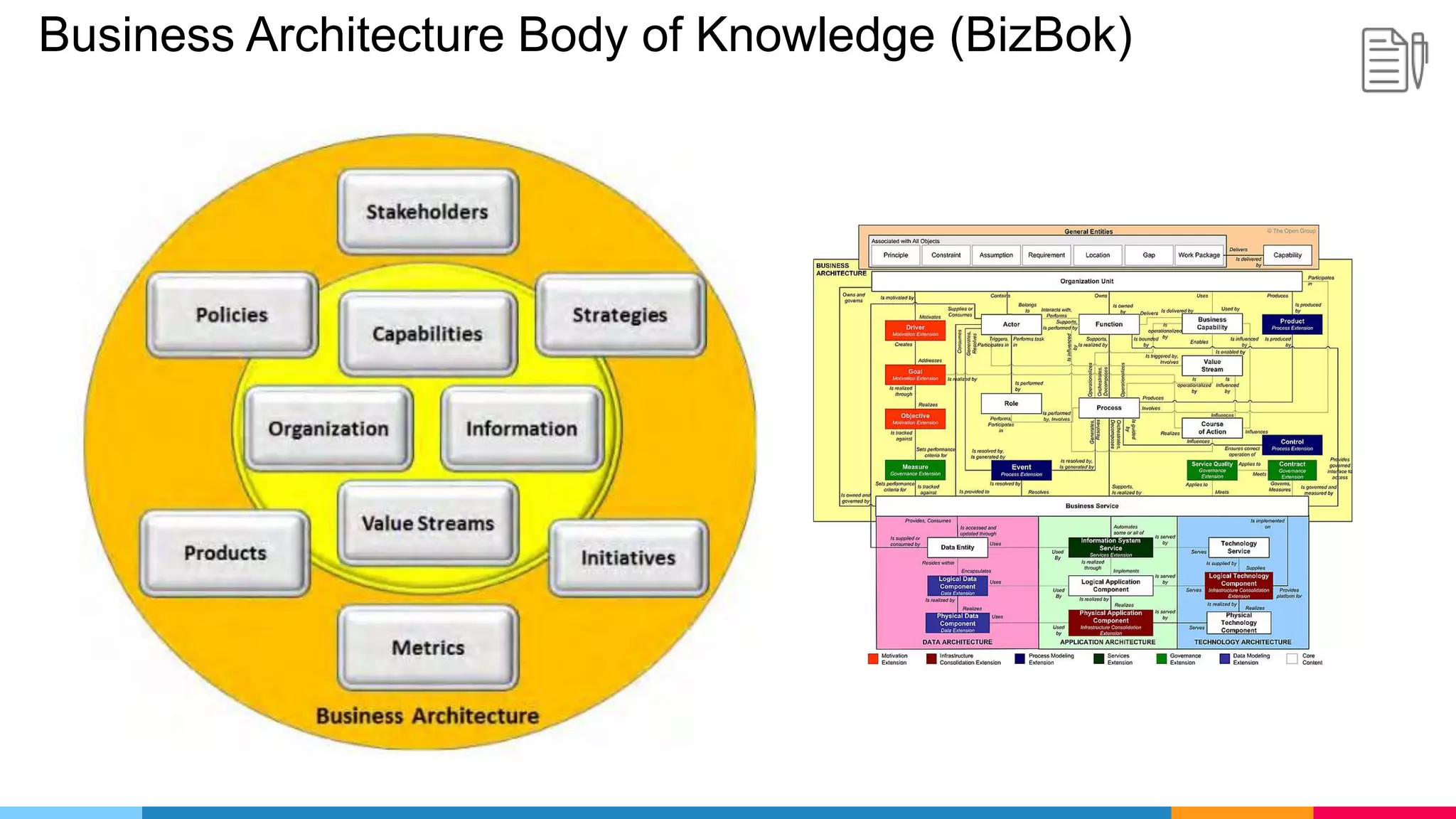
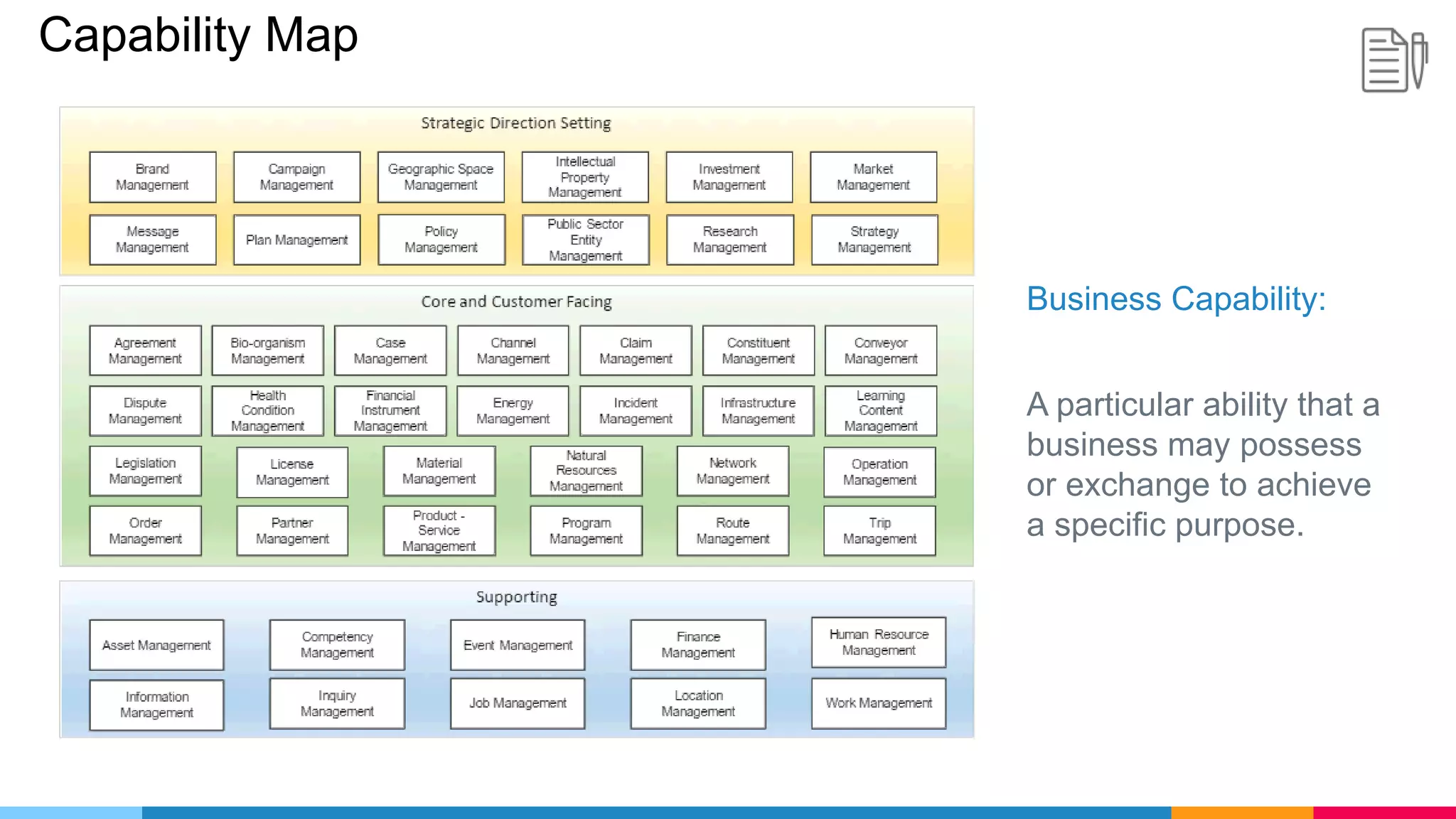
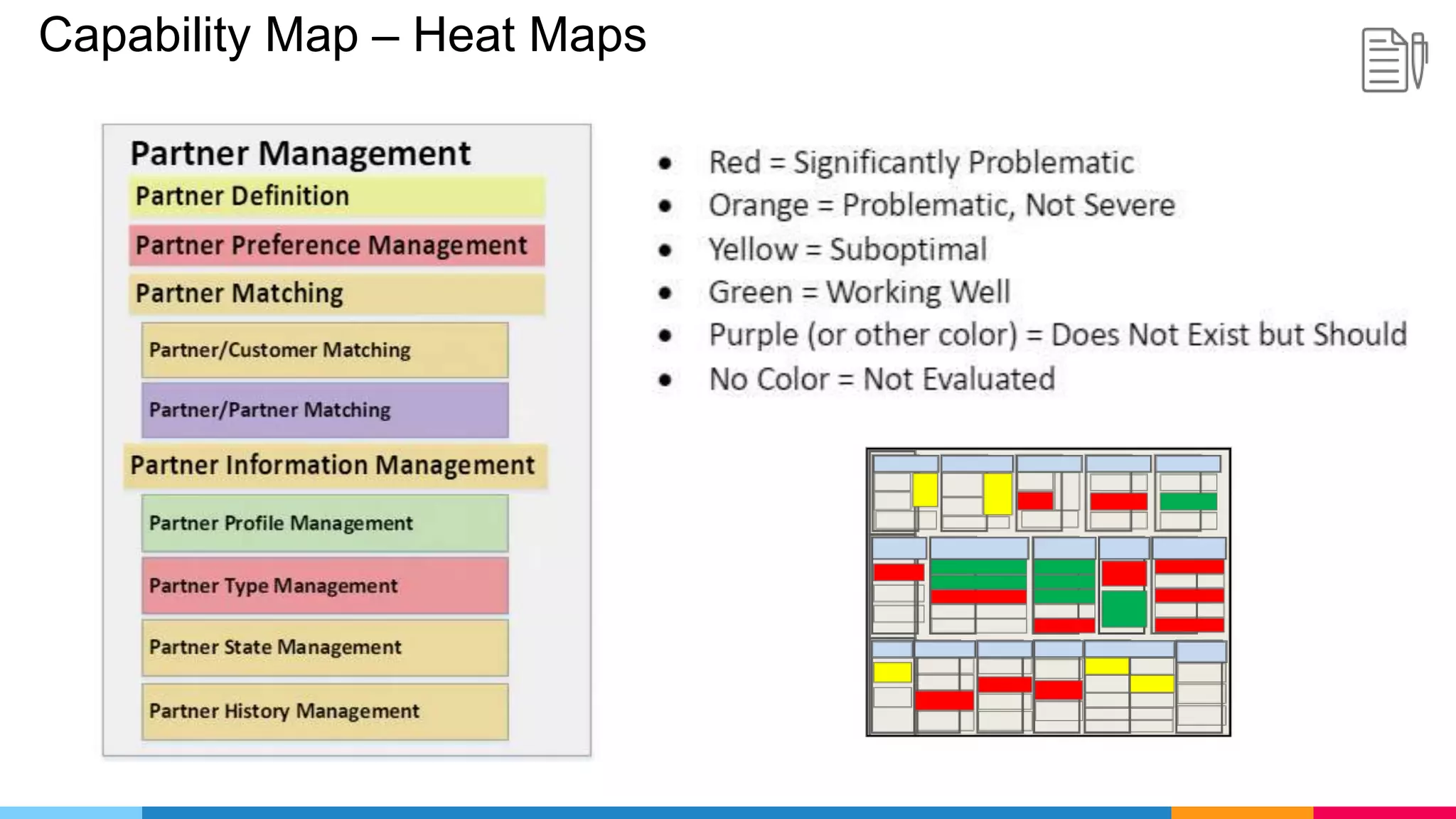
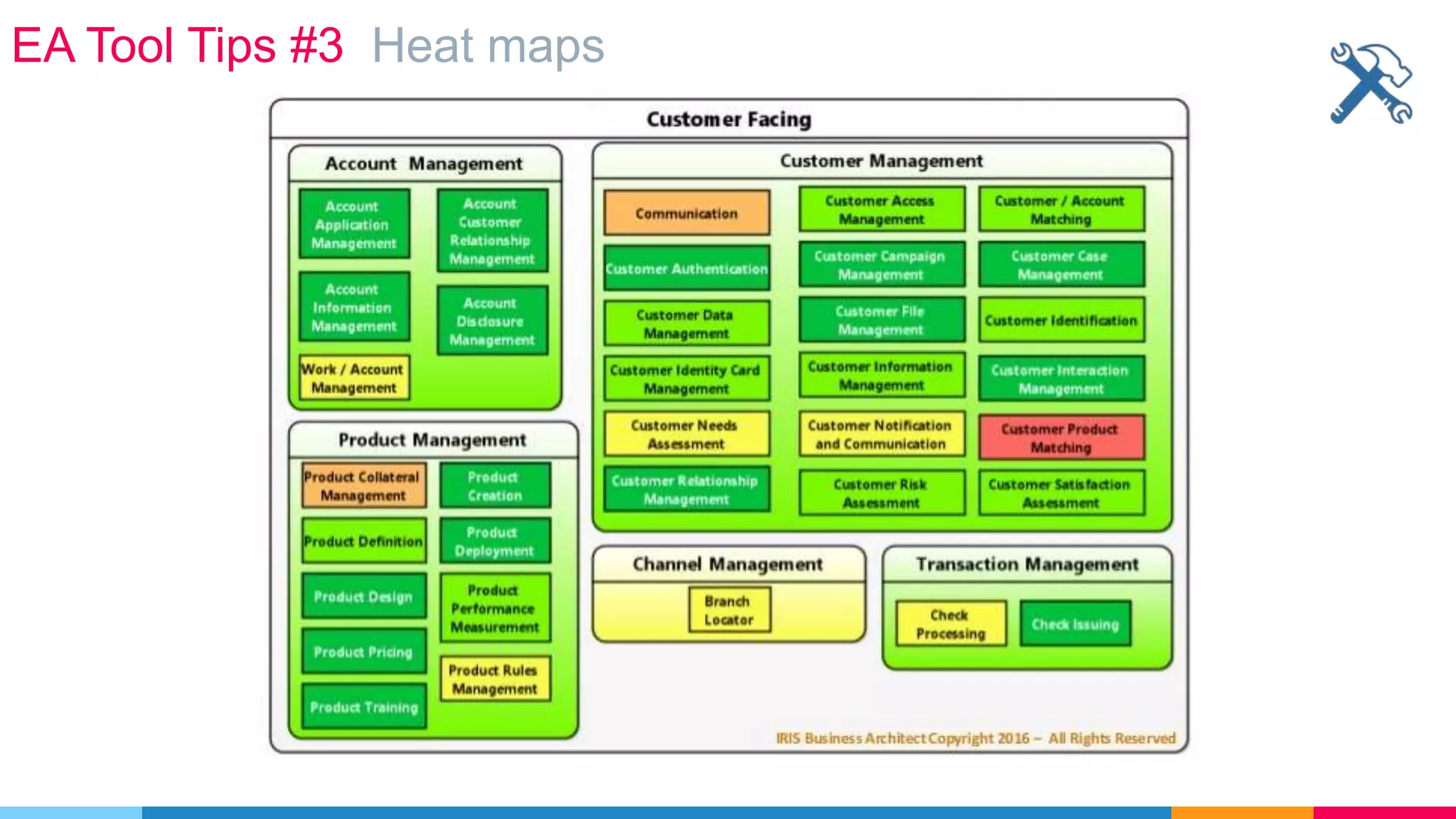
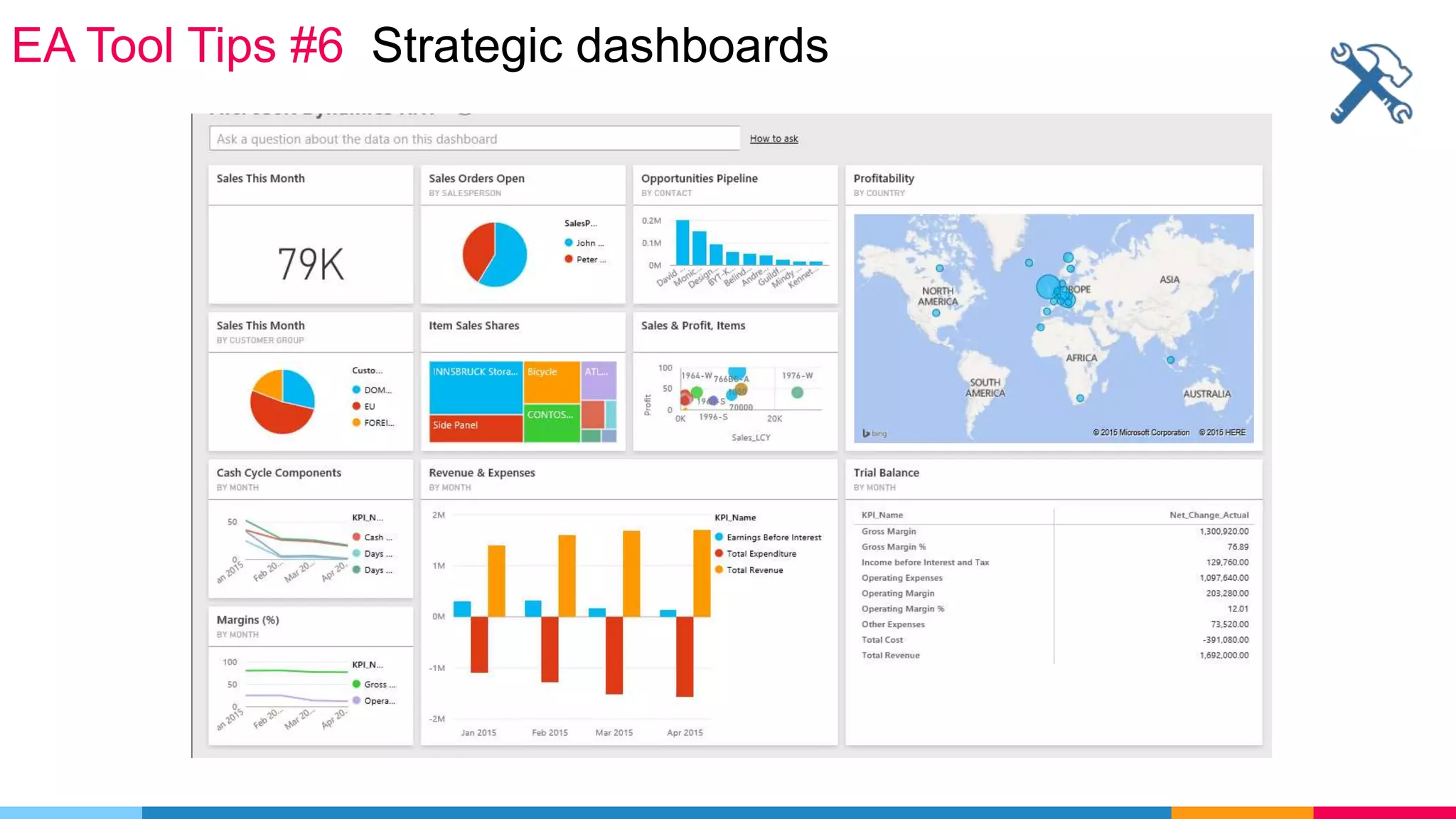
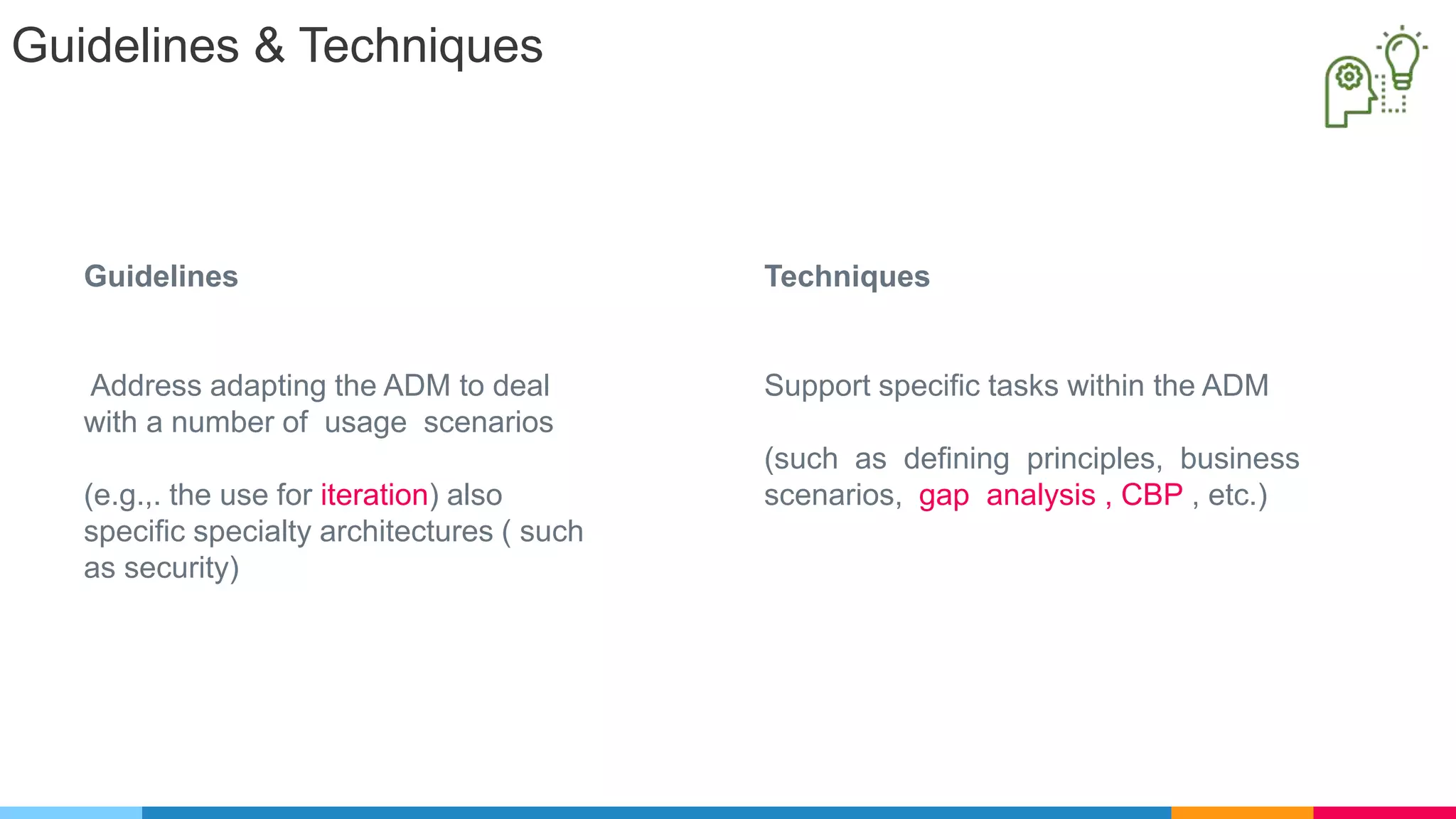
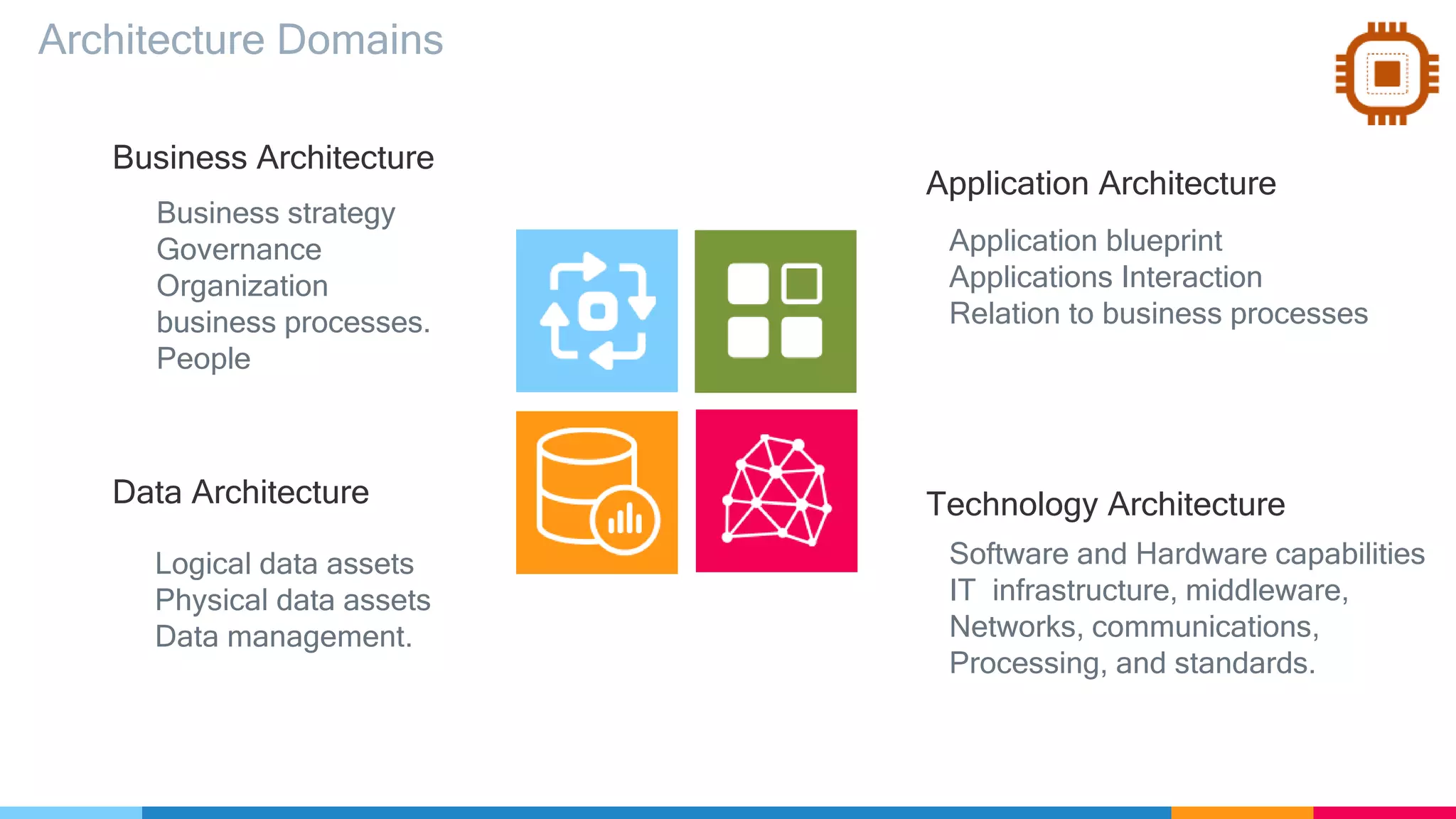
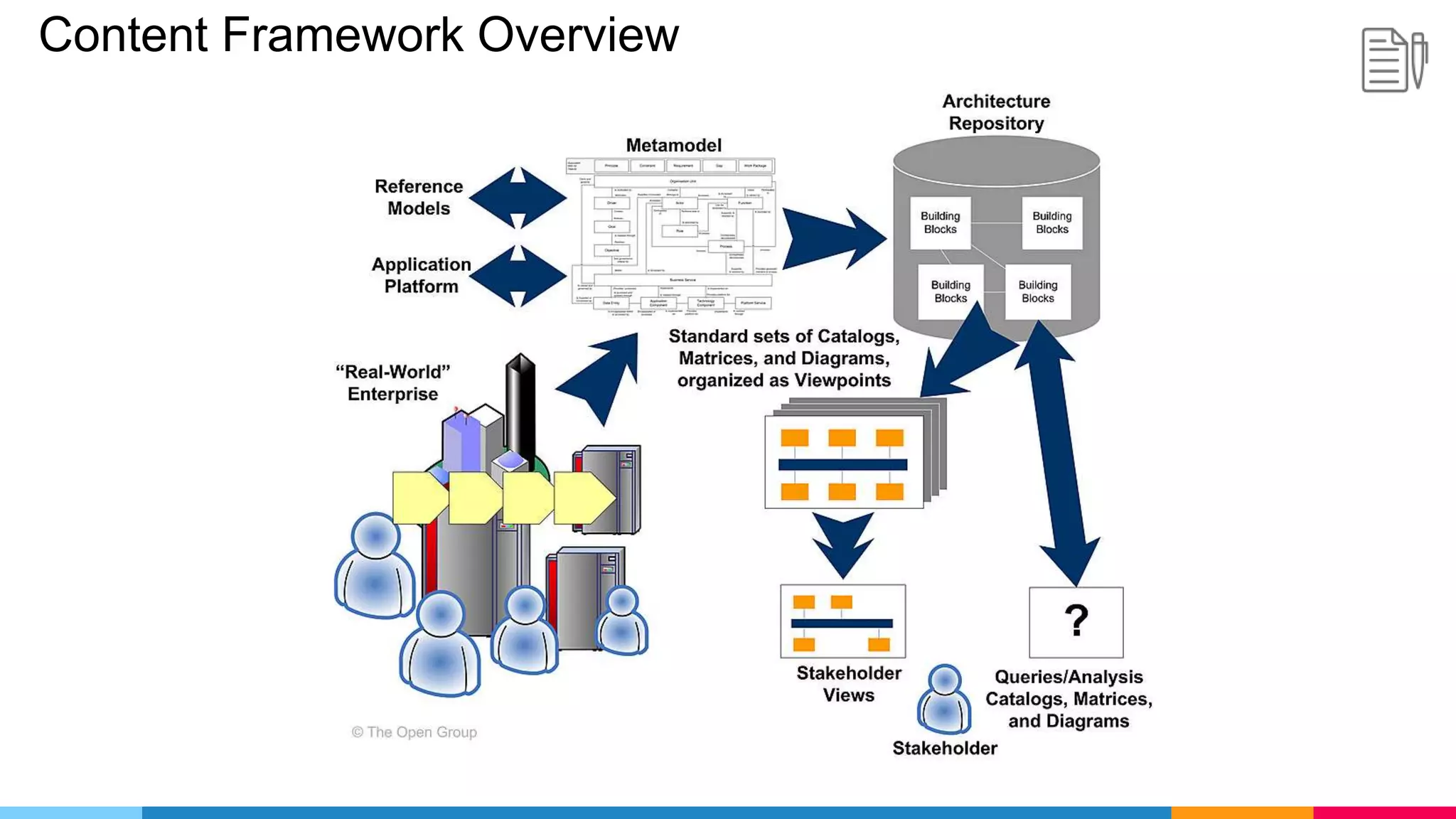
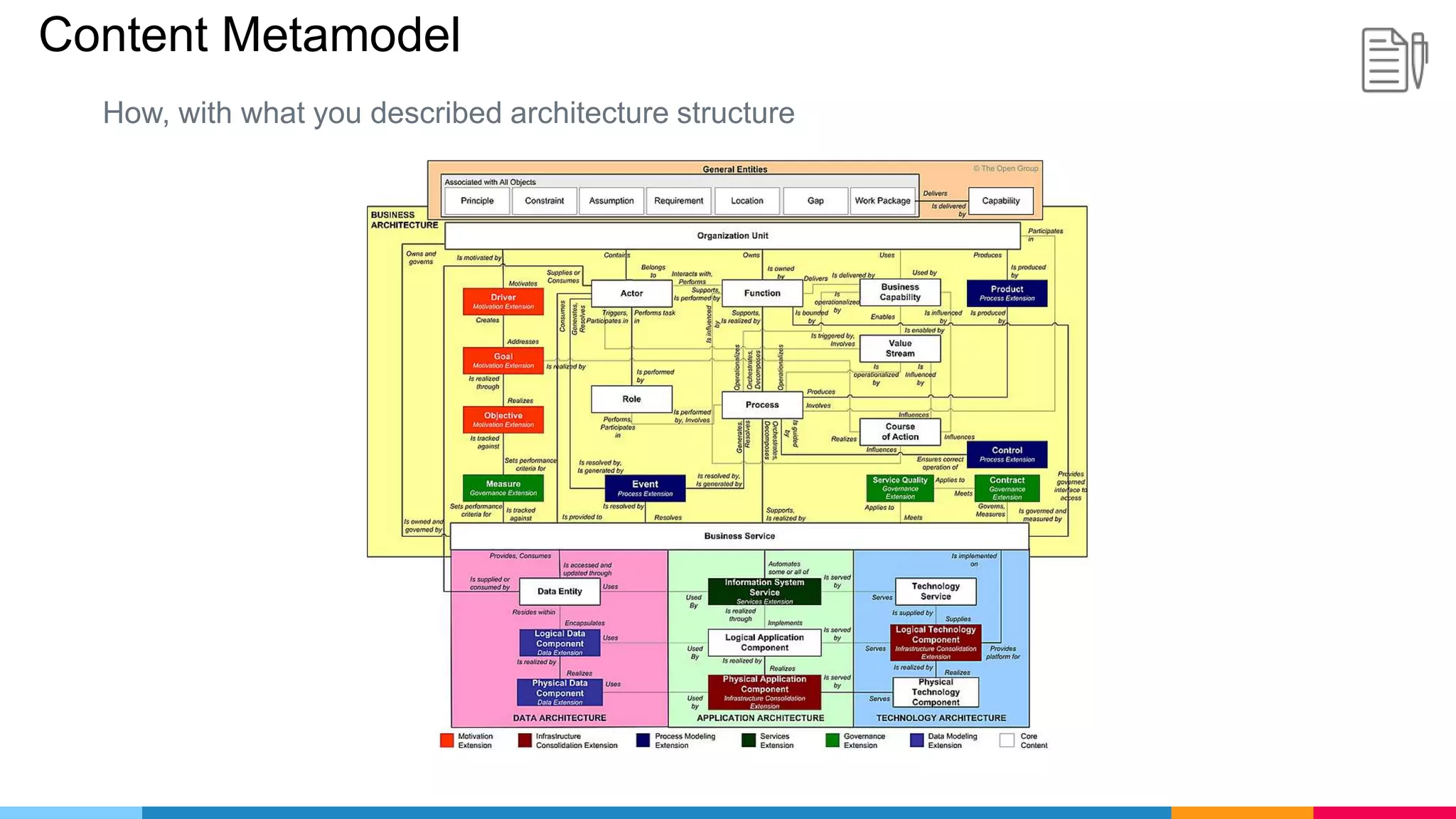
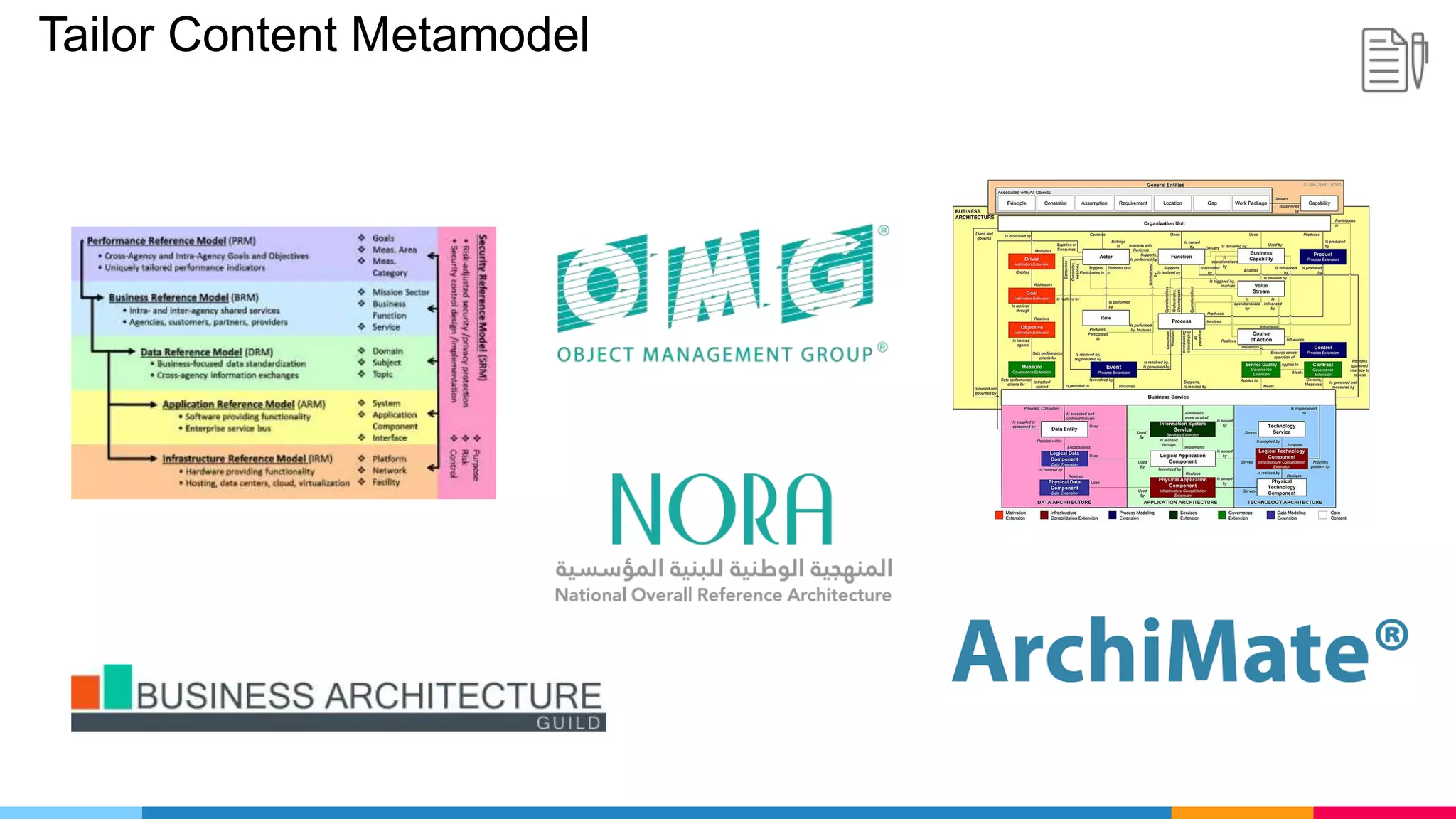
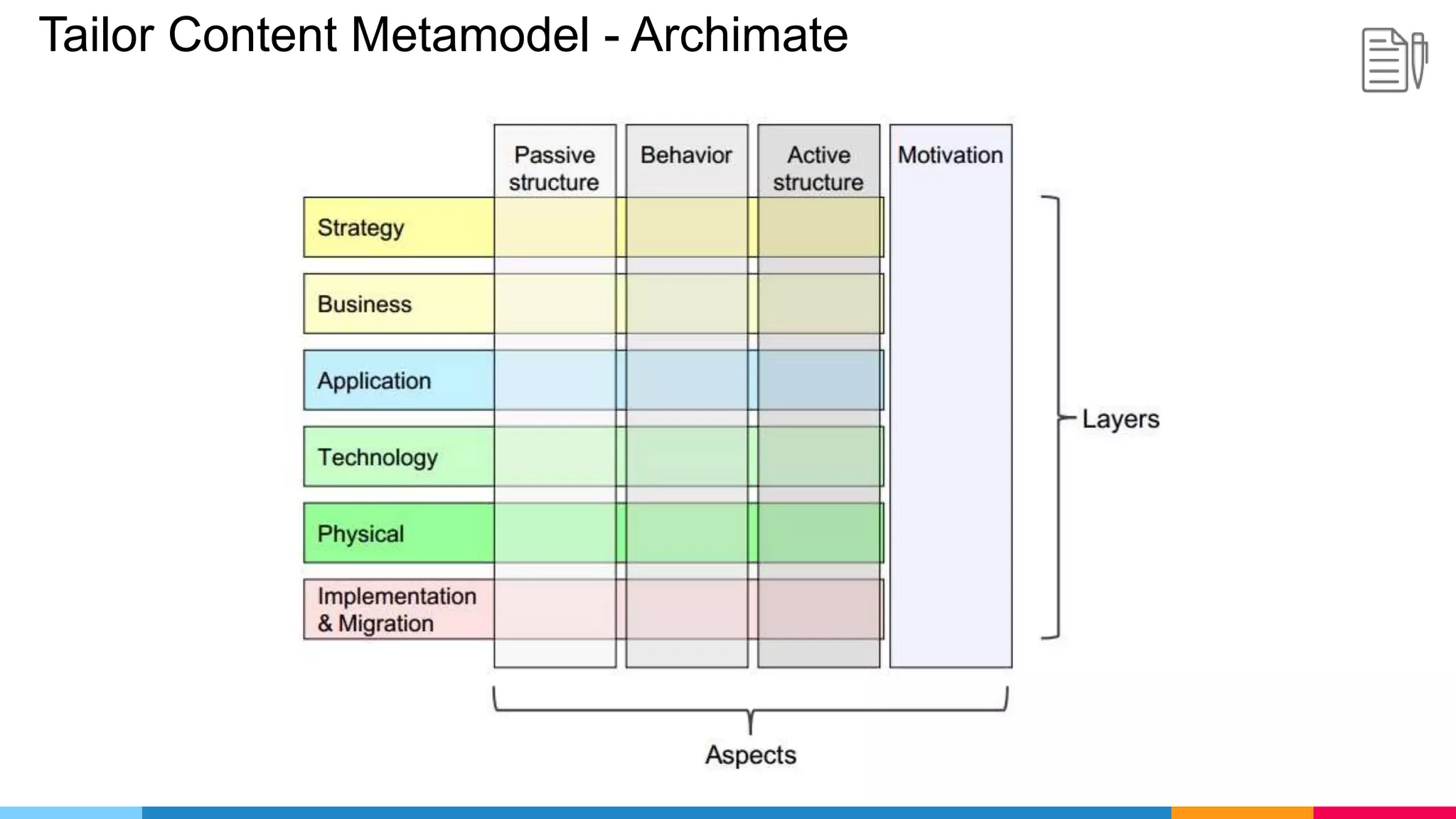
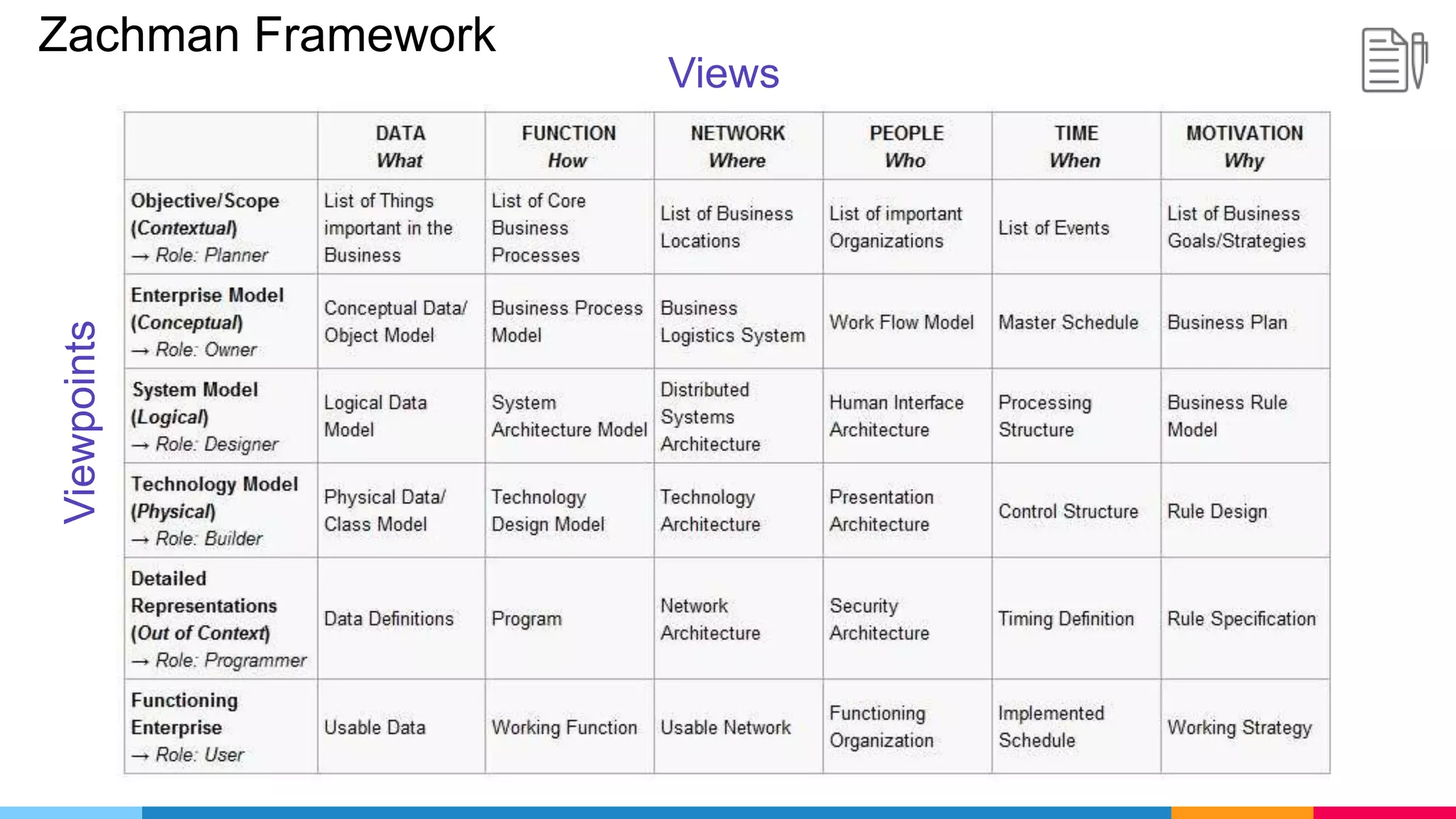
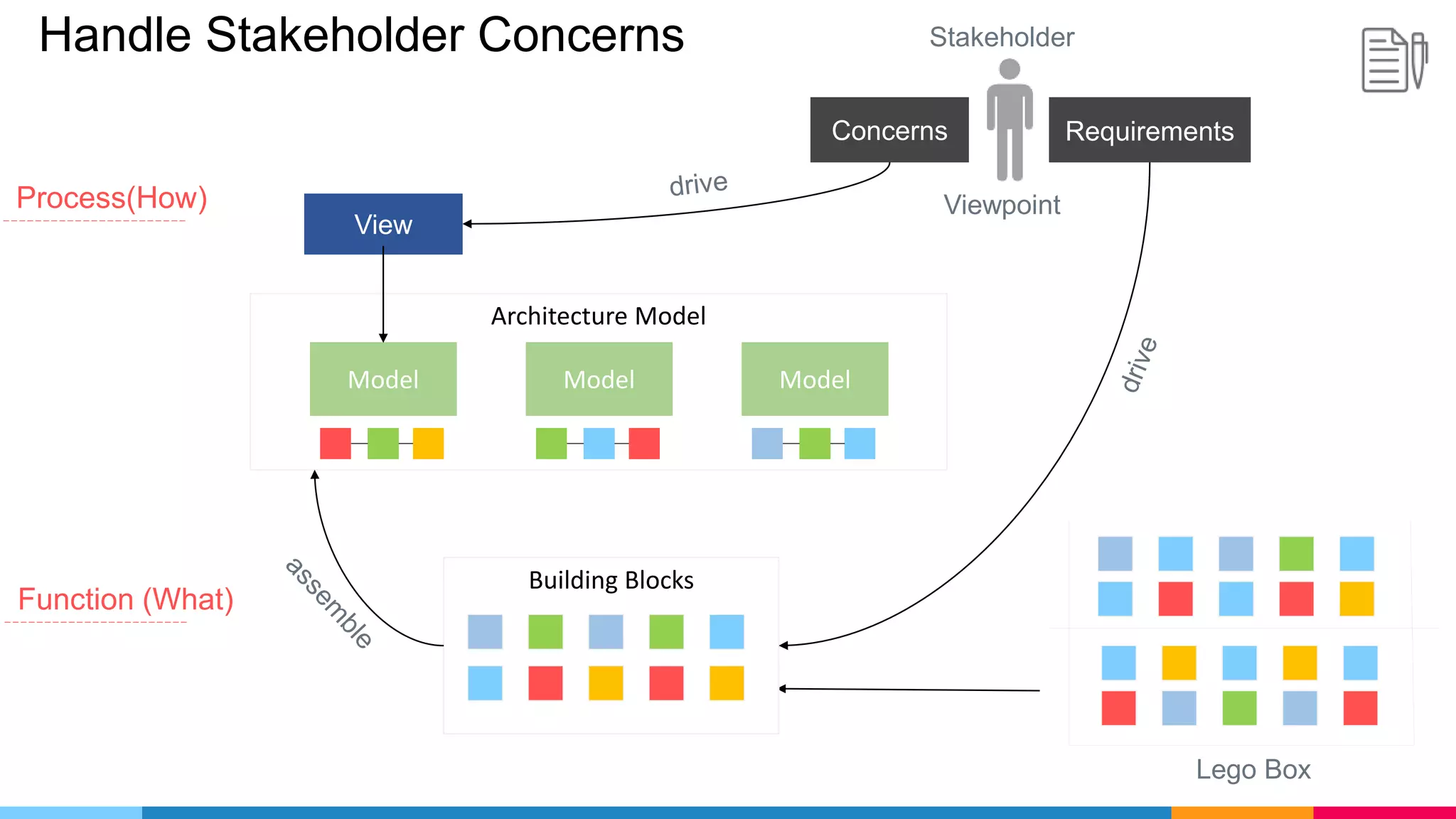
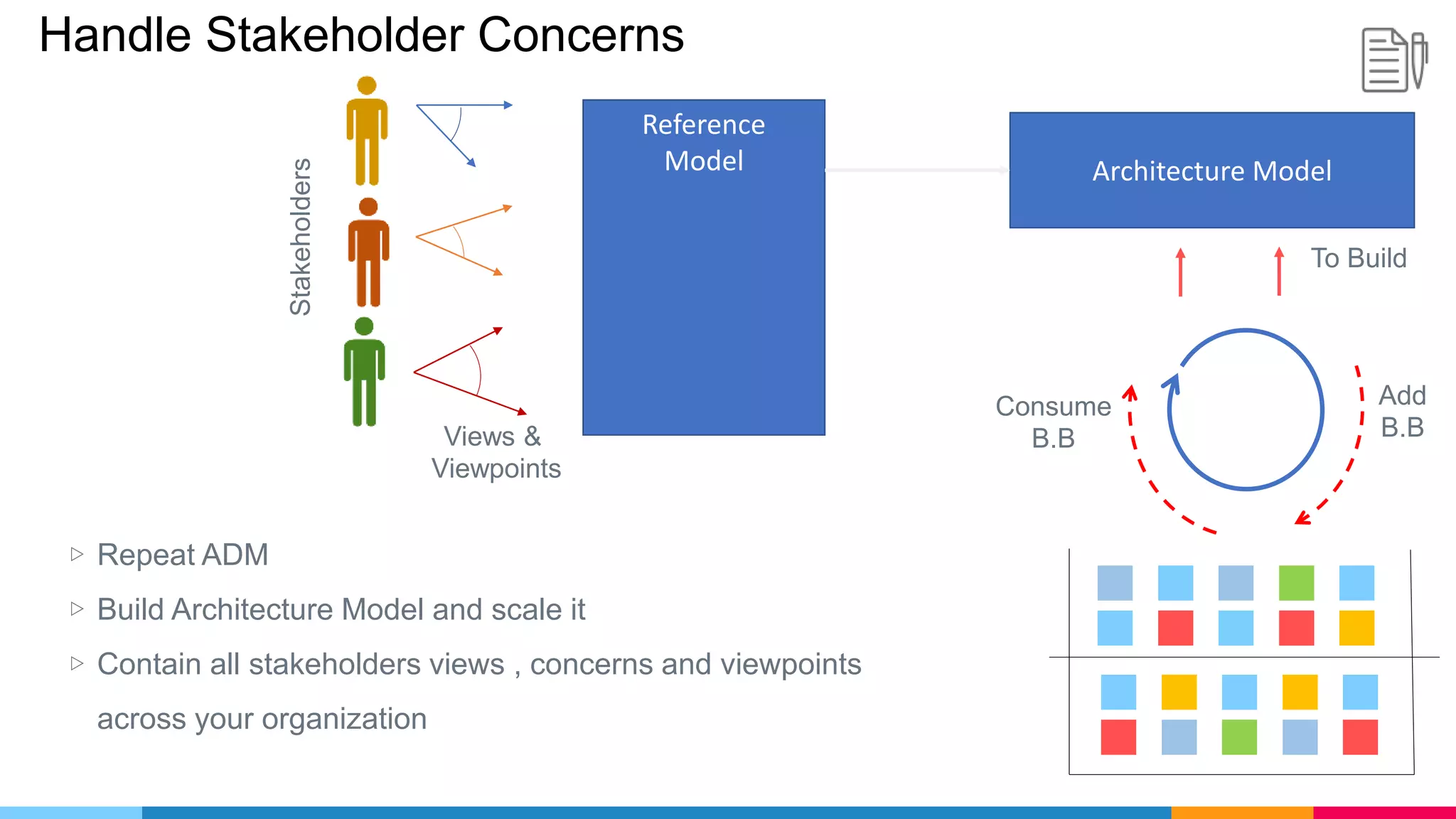
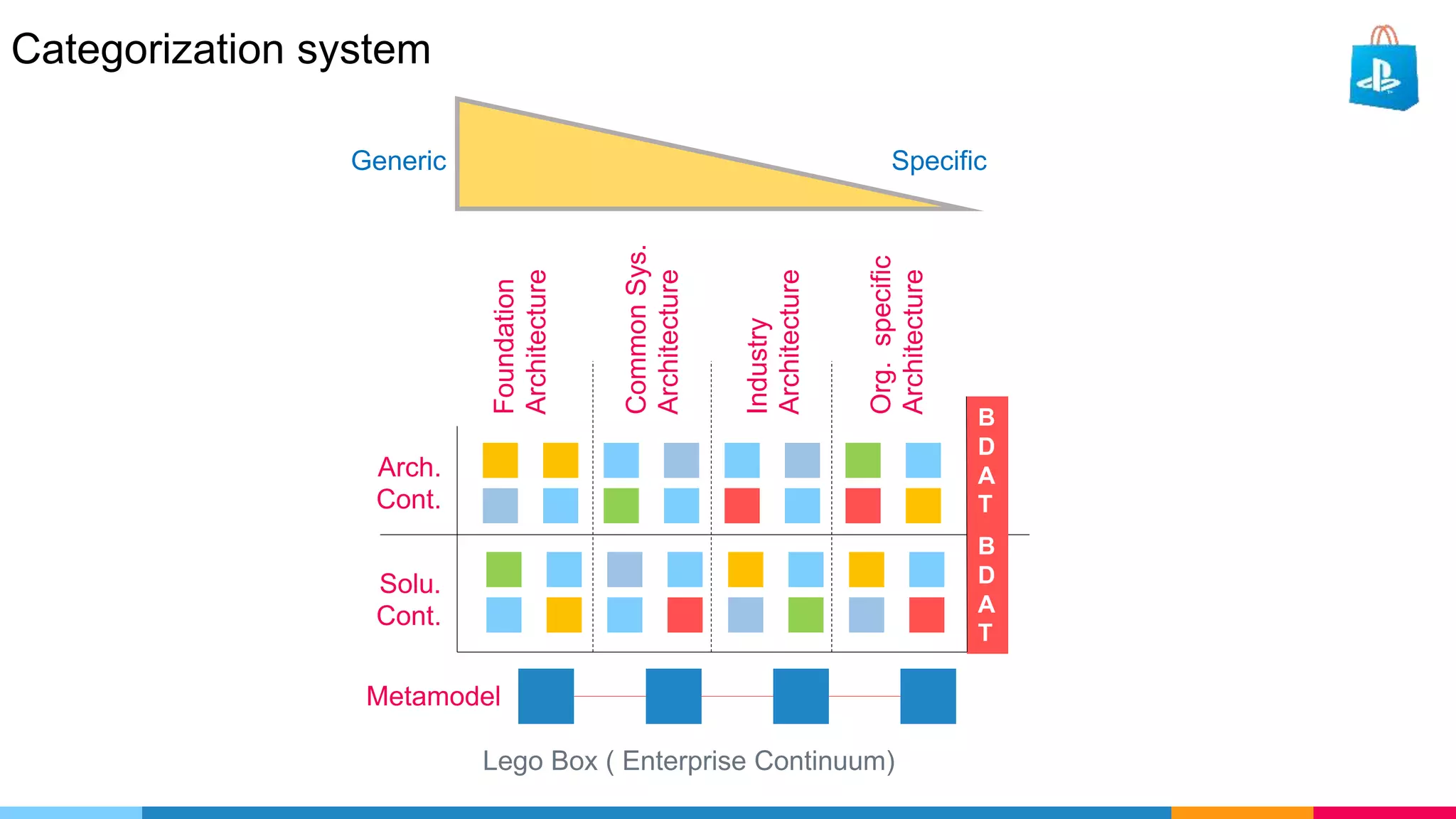
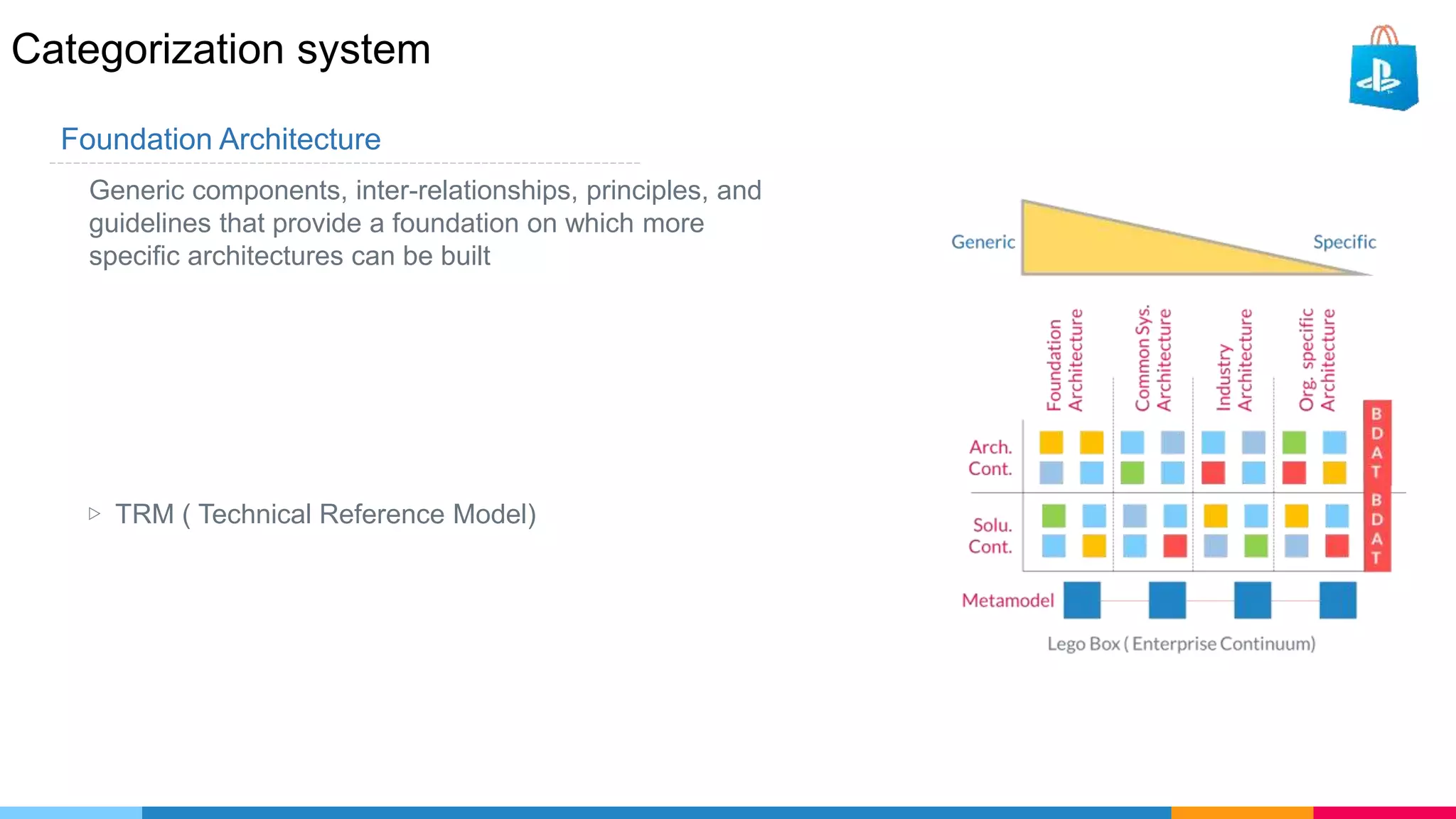
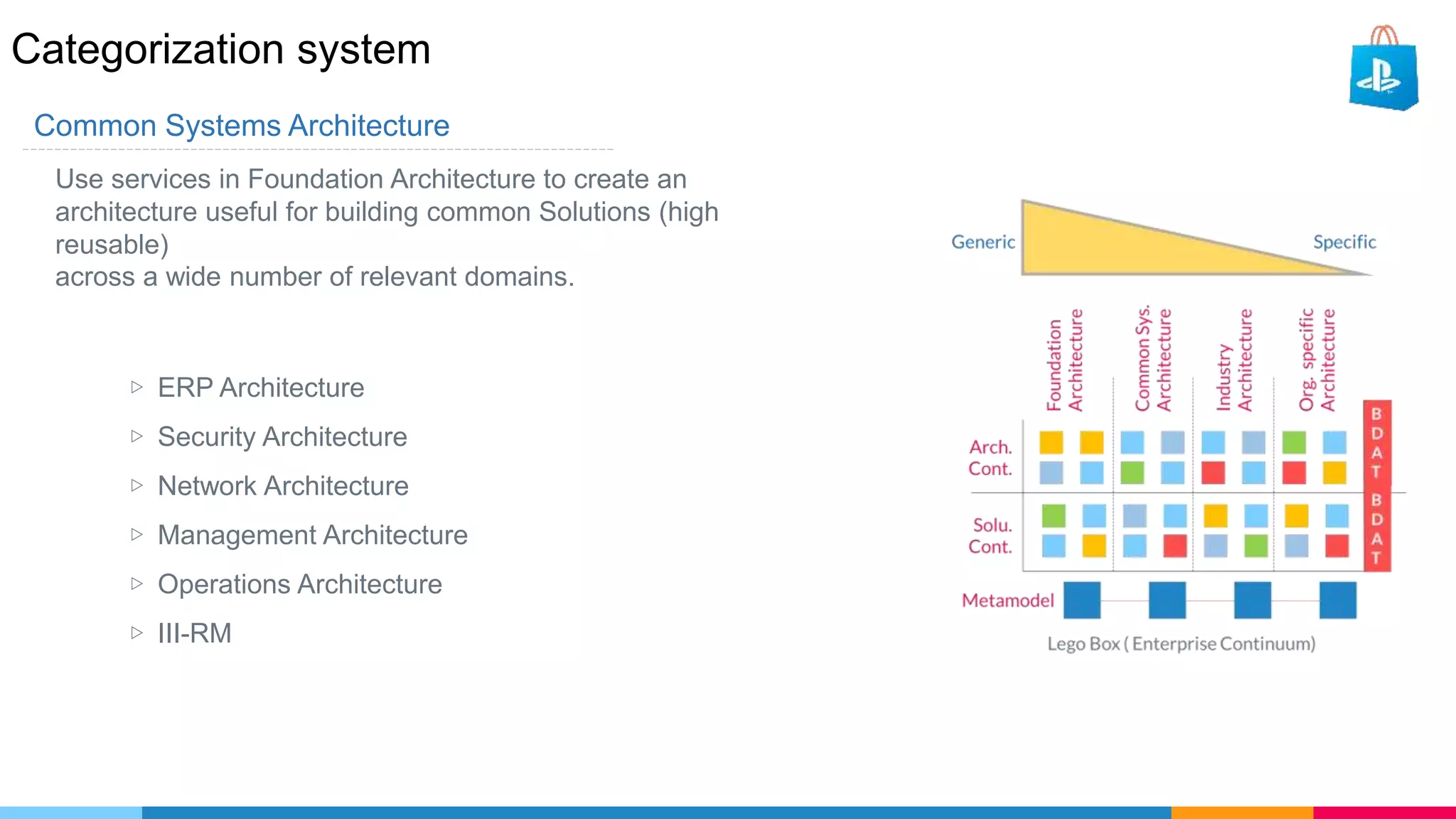
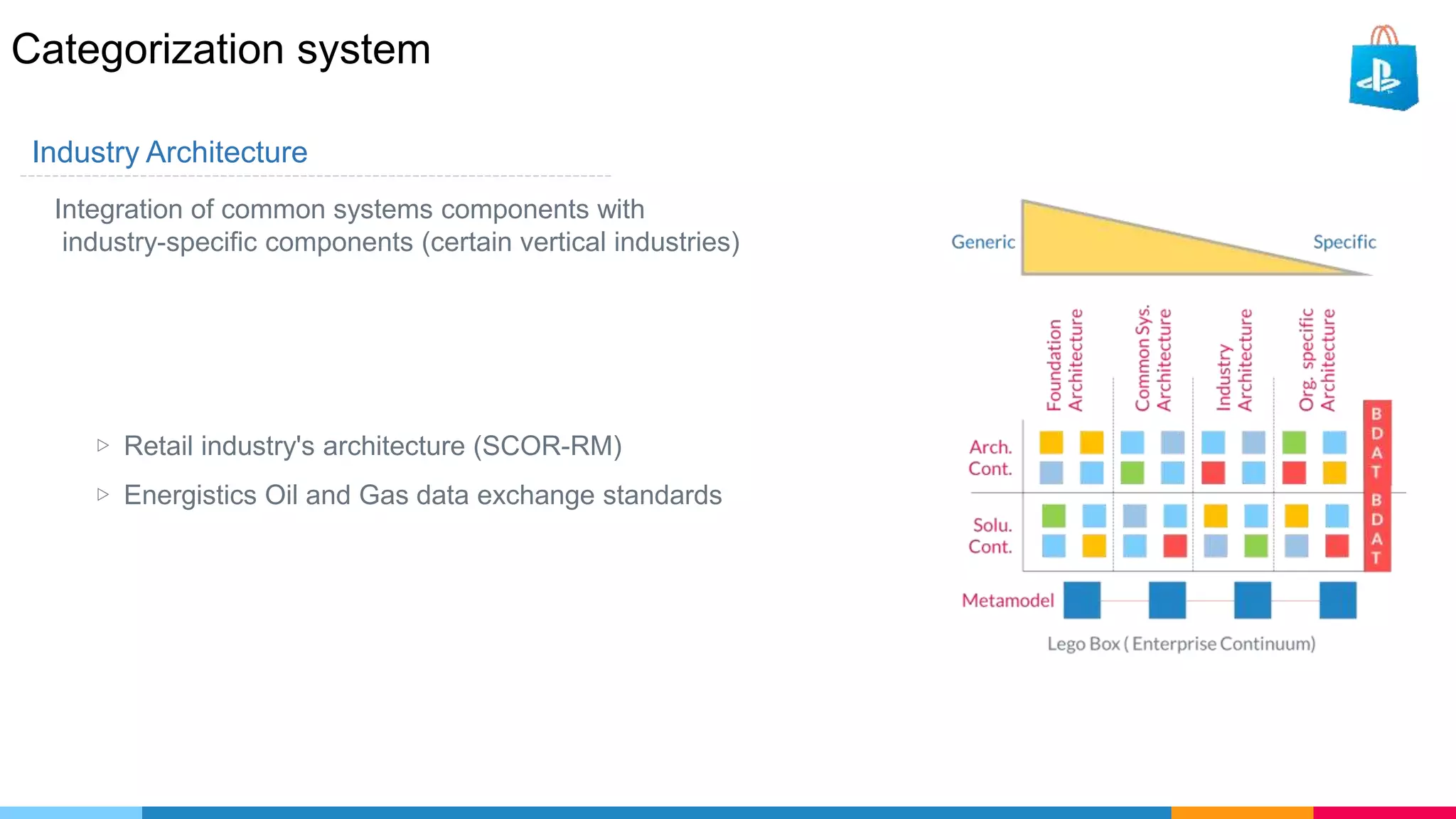
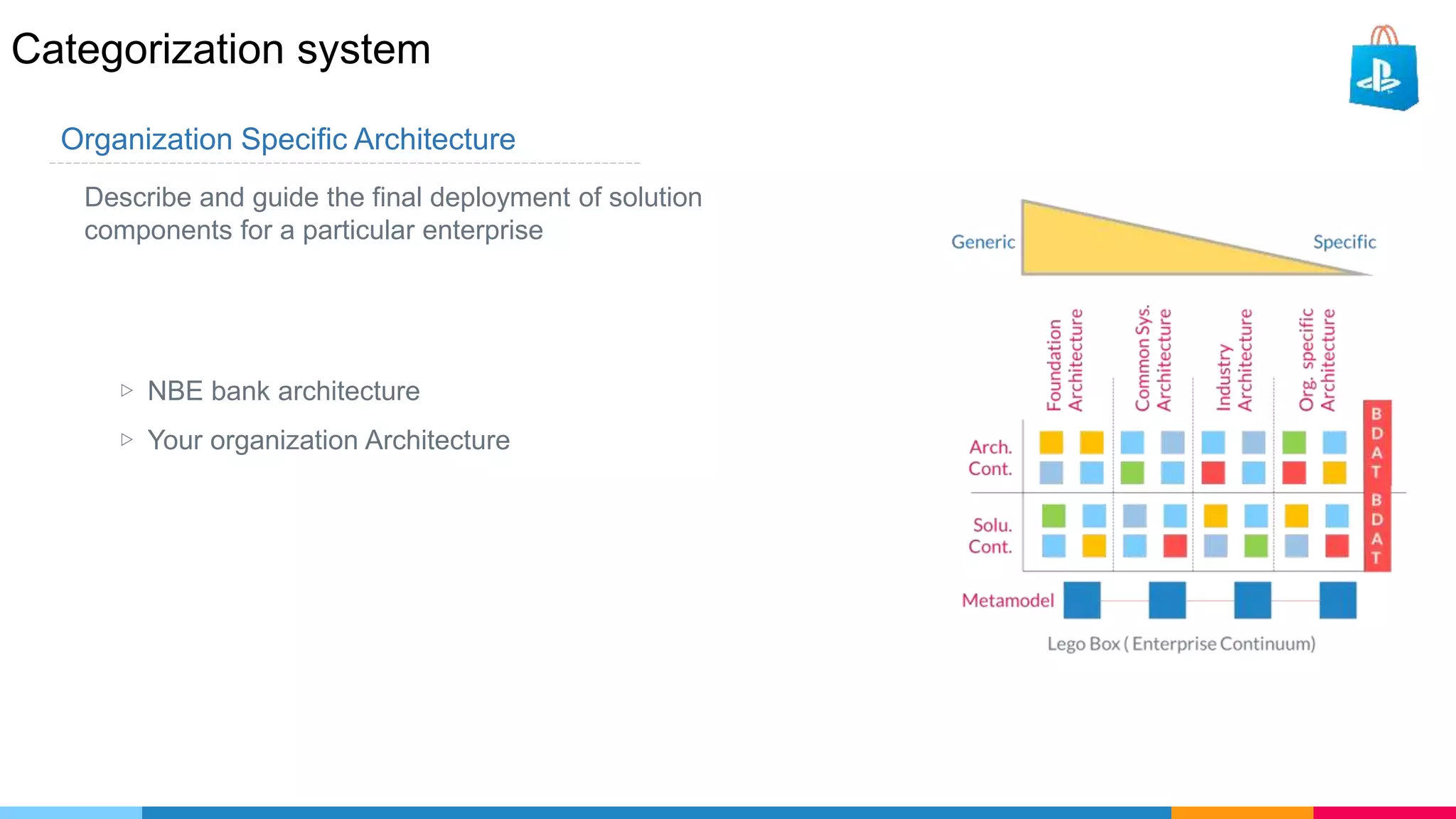
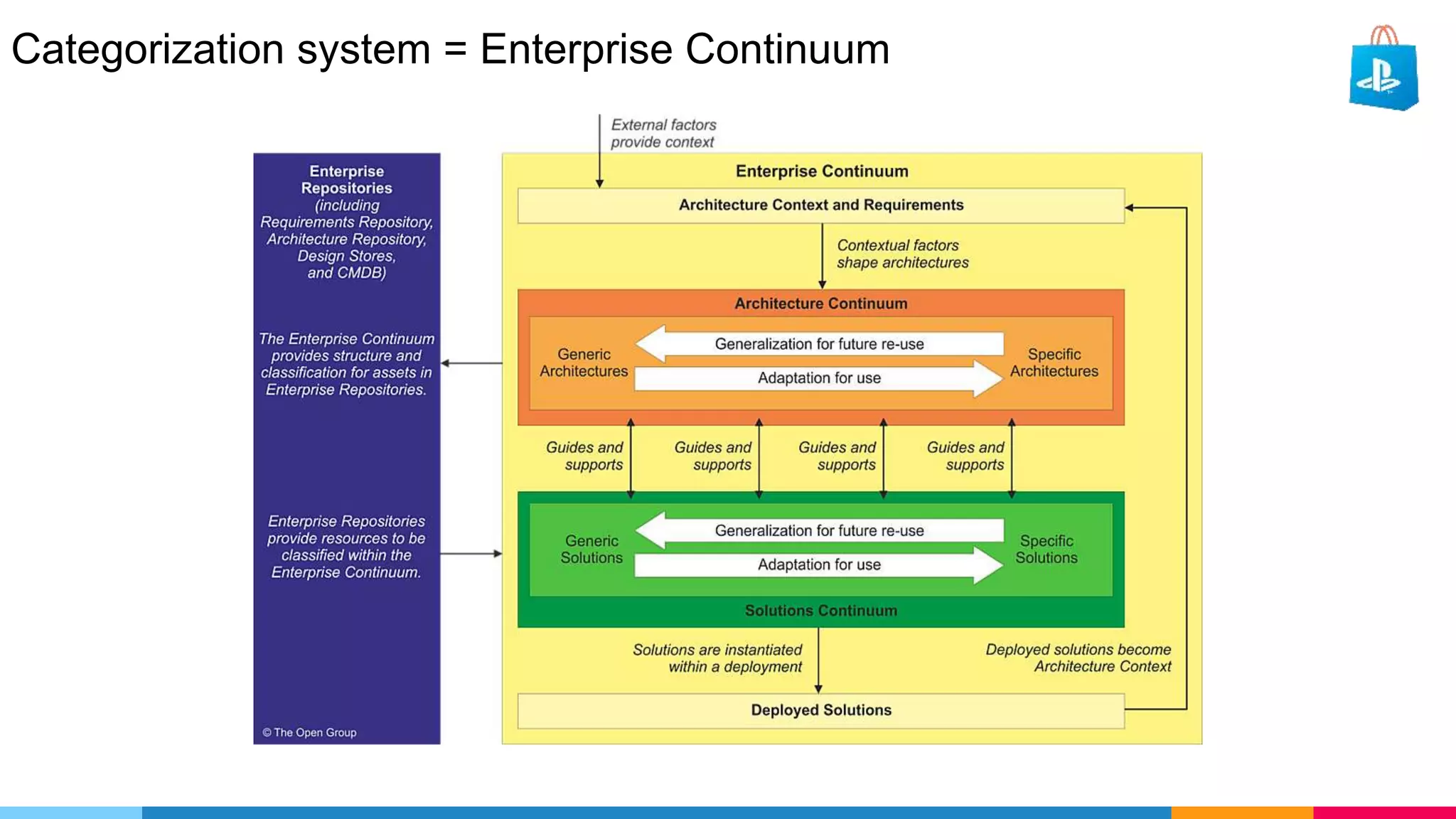
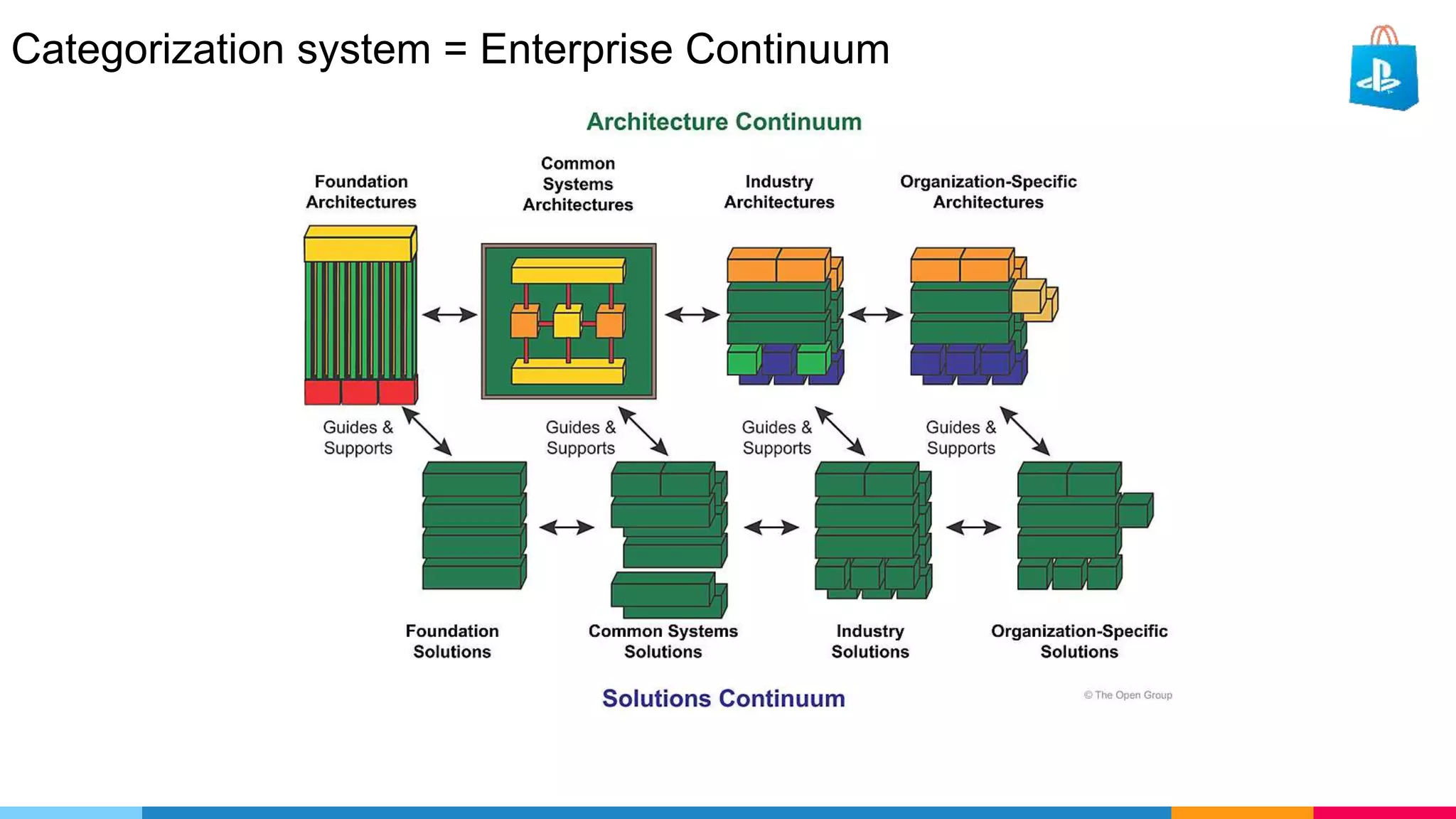
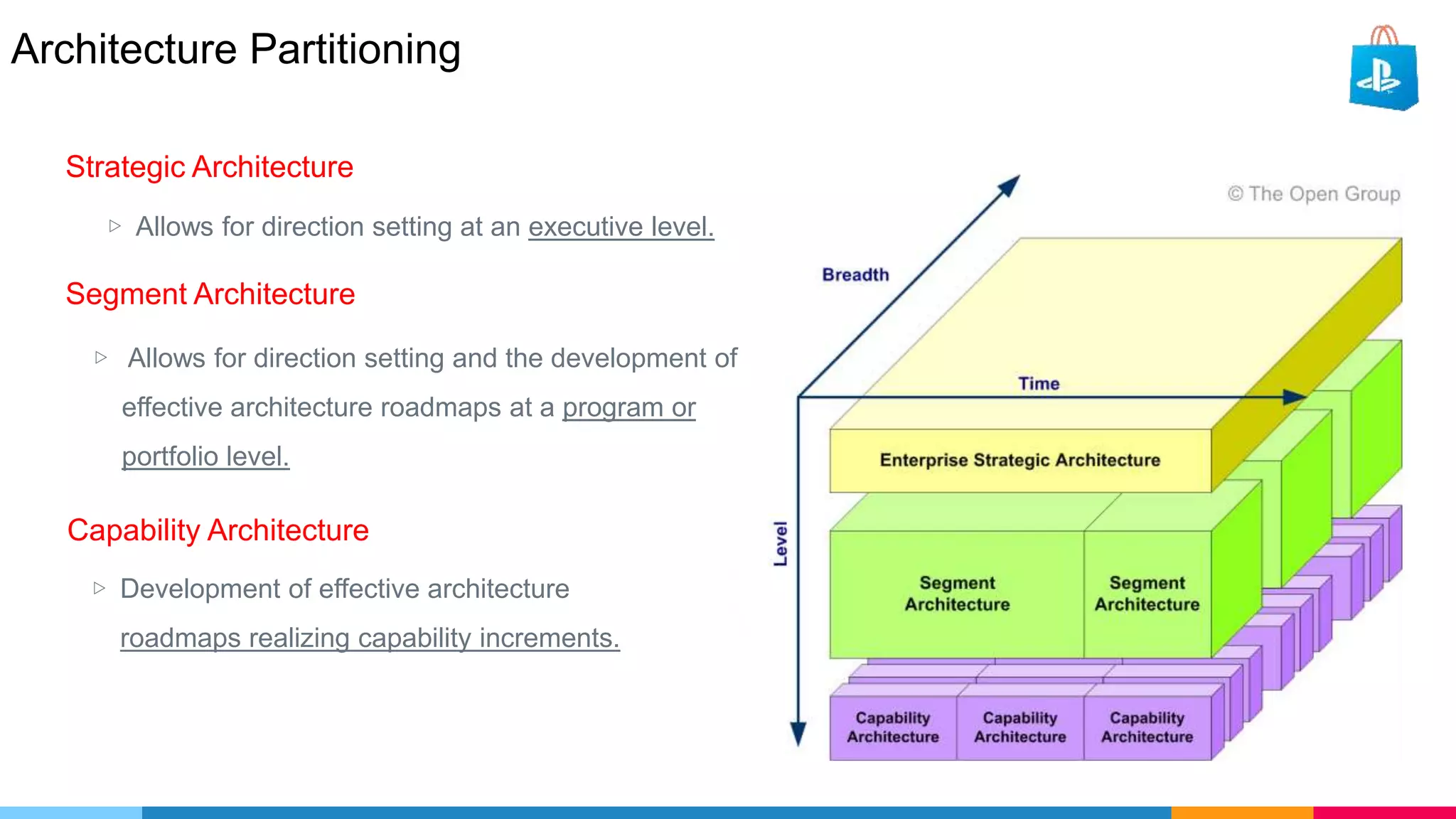
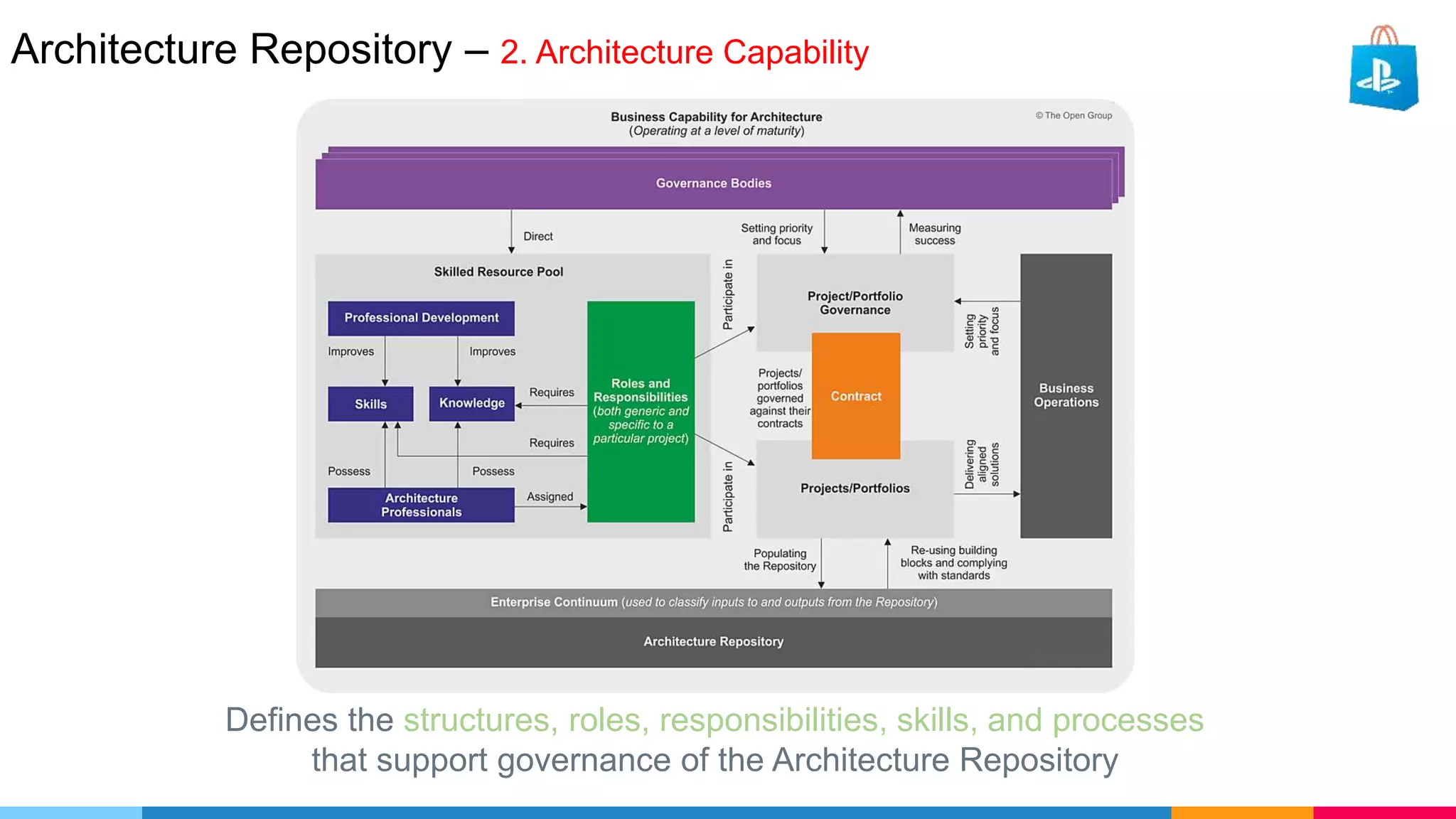
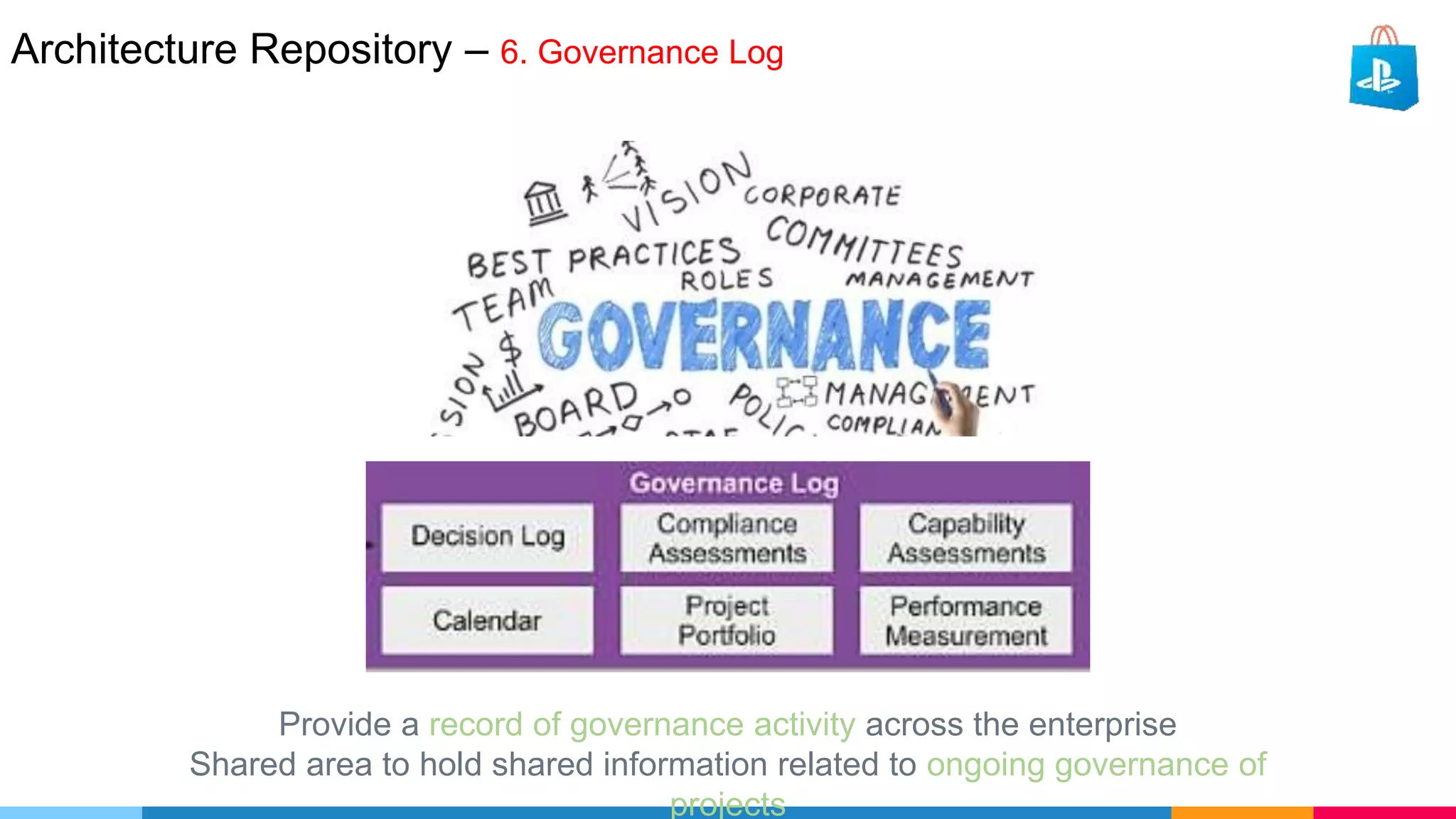
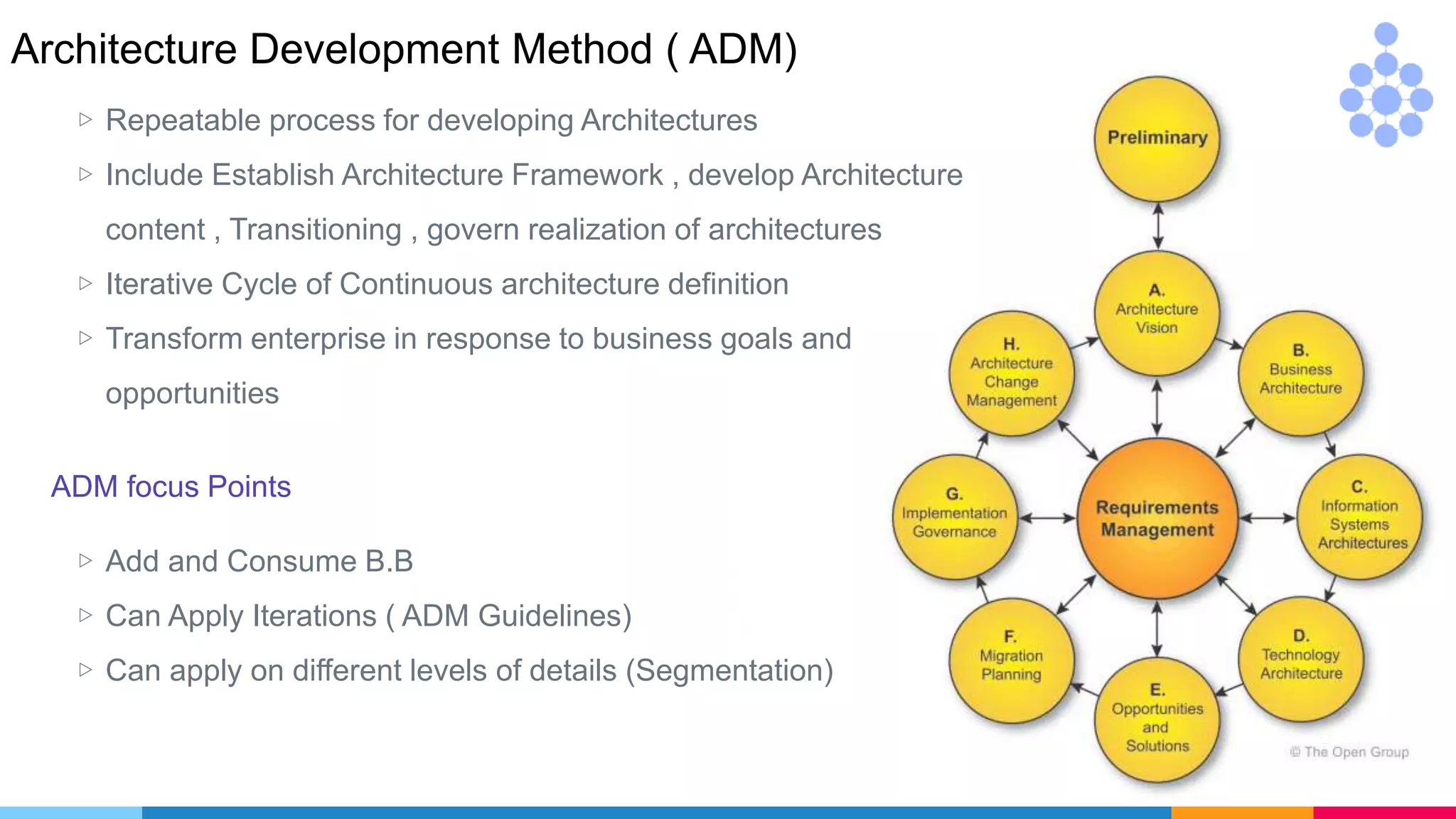
The document provides an agenda for an enterprise architecture presentation covering topics such as EA introductions, frameworks, content modeling, repositories, development methods, and updates to business architecture and EA tools. It includes diagrams to illustrate EA concepts such as relating EA to Lego blocks, architecture domains, and the enterprise continuum for categorizing architecture. The presentation aims to provide an overview of enterprise architecture and discuss best practices.

















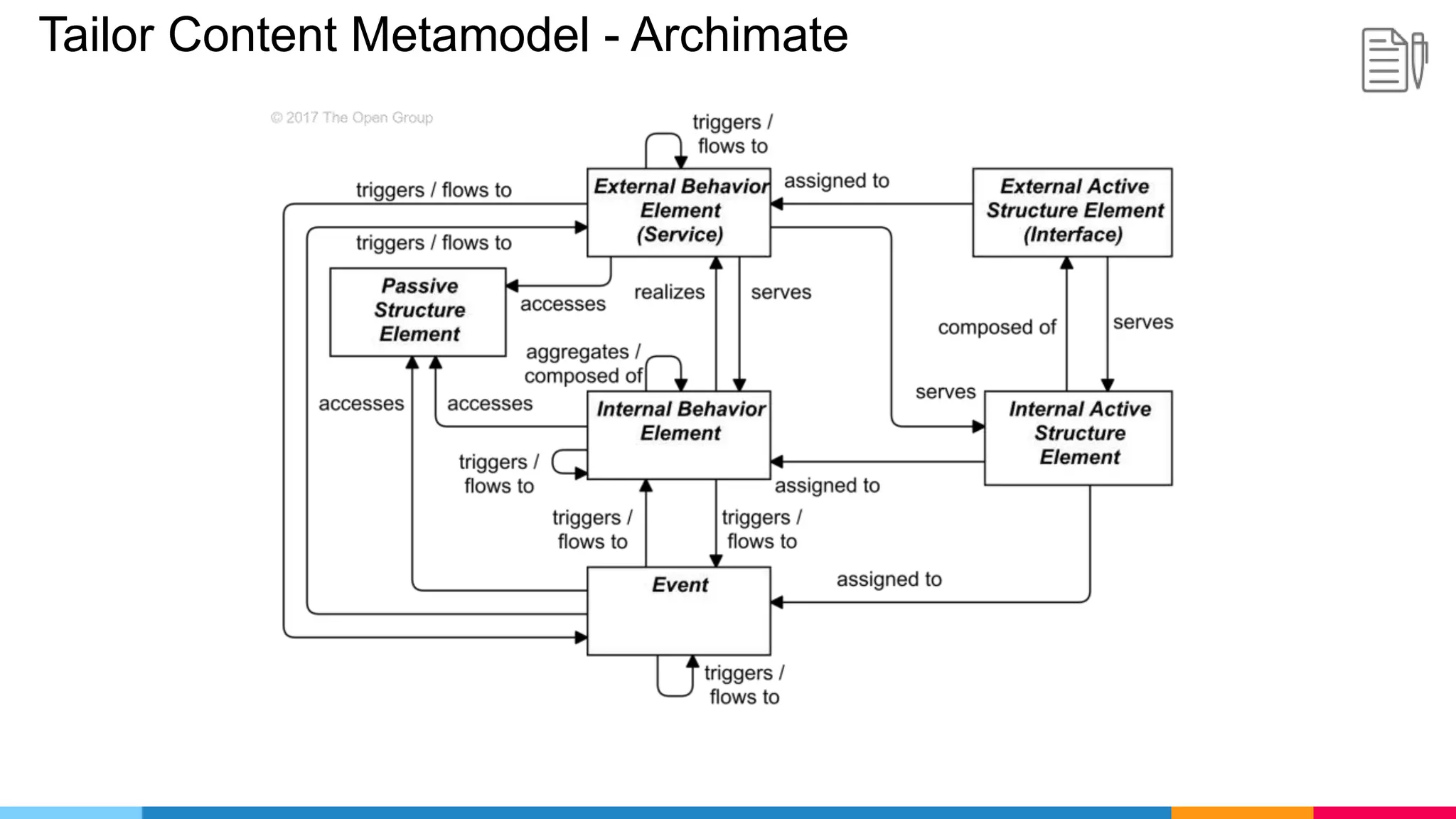
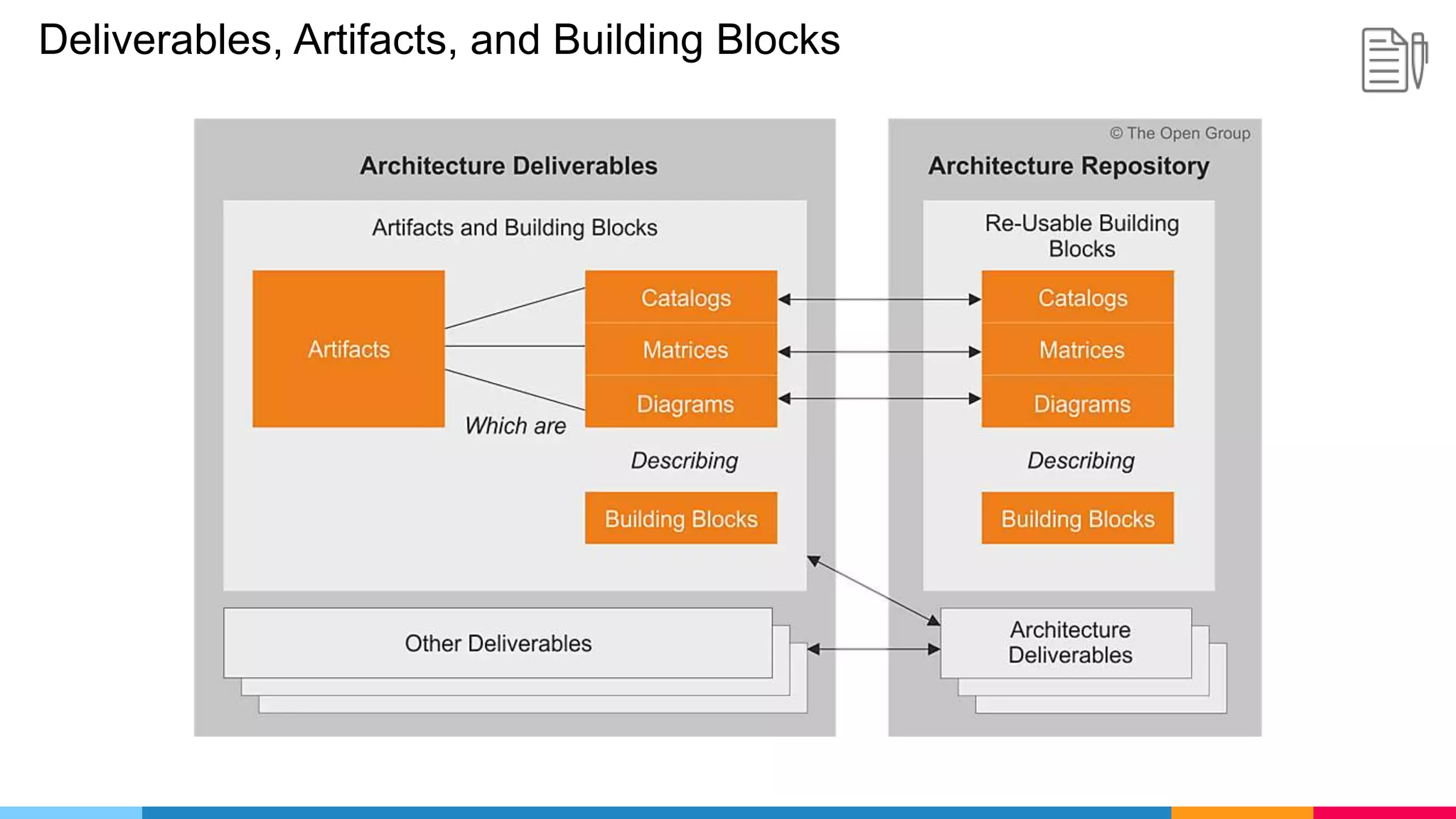
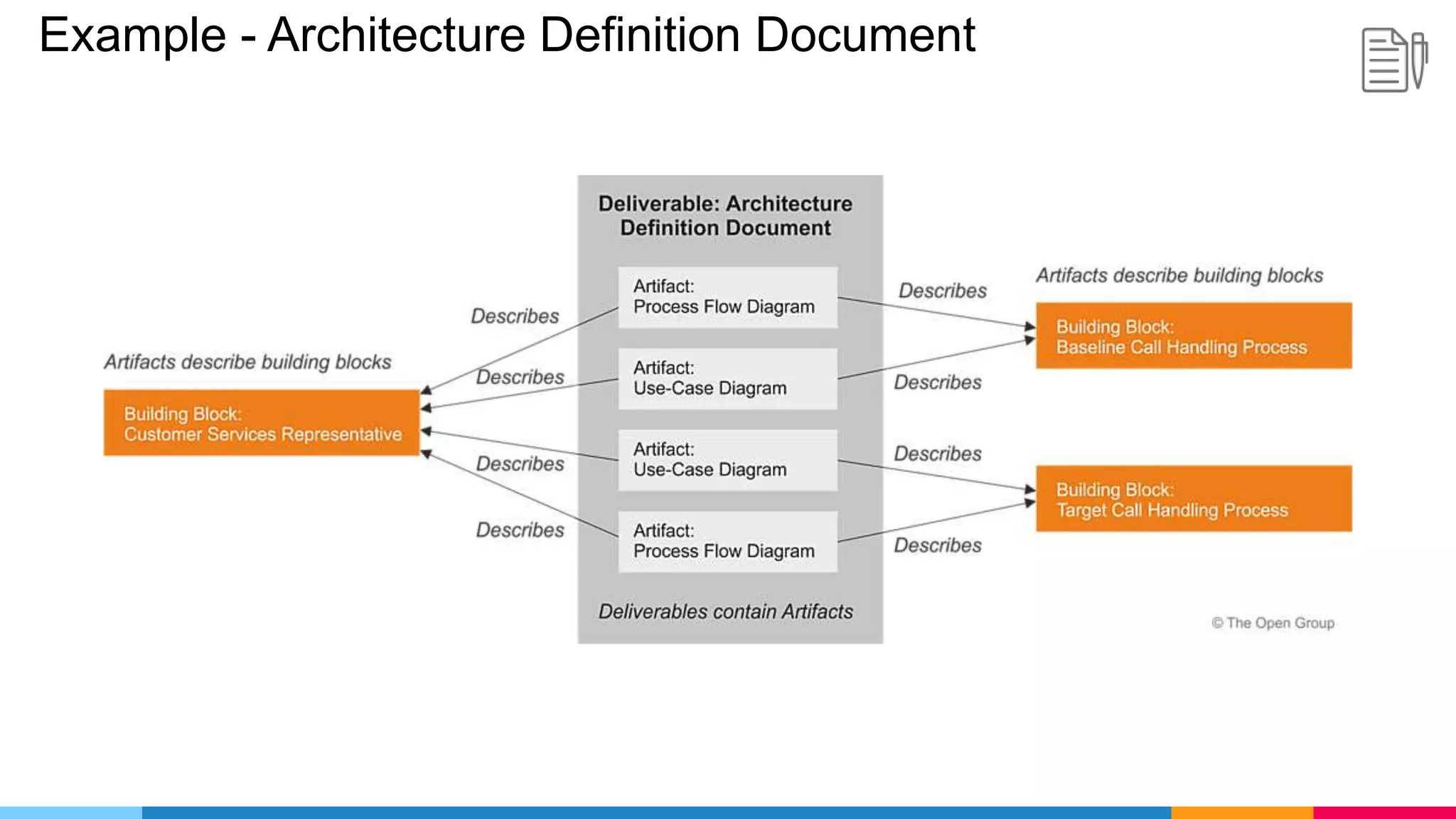
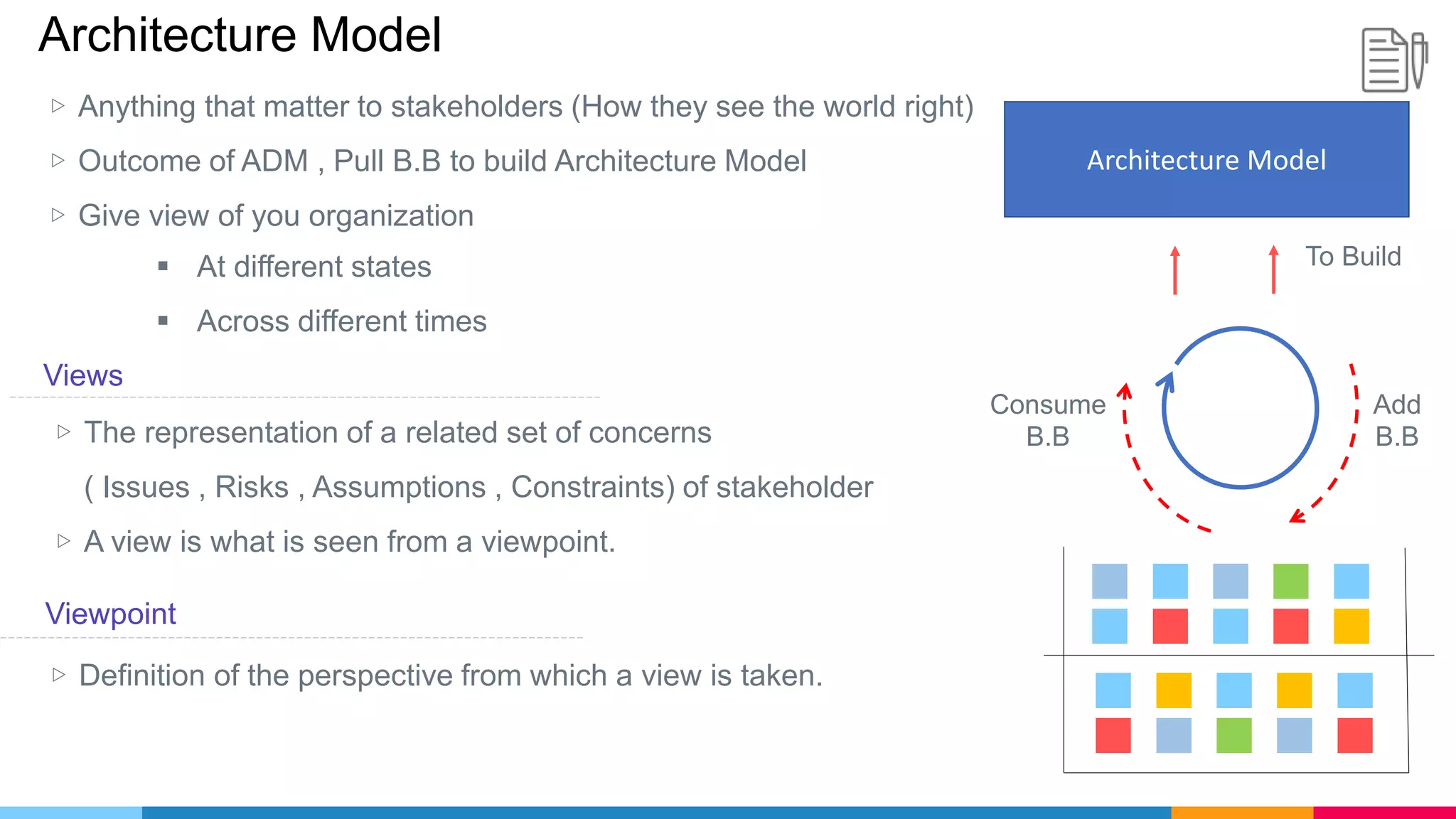








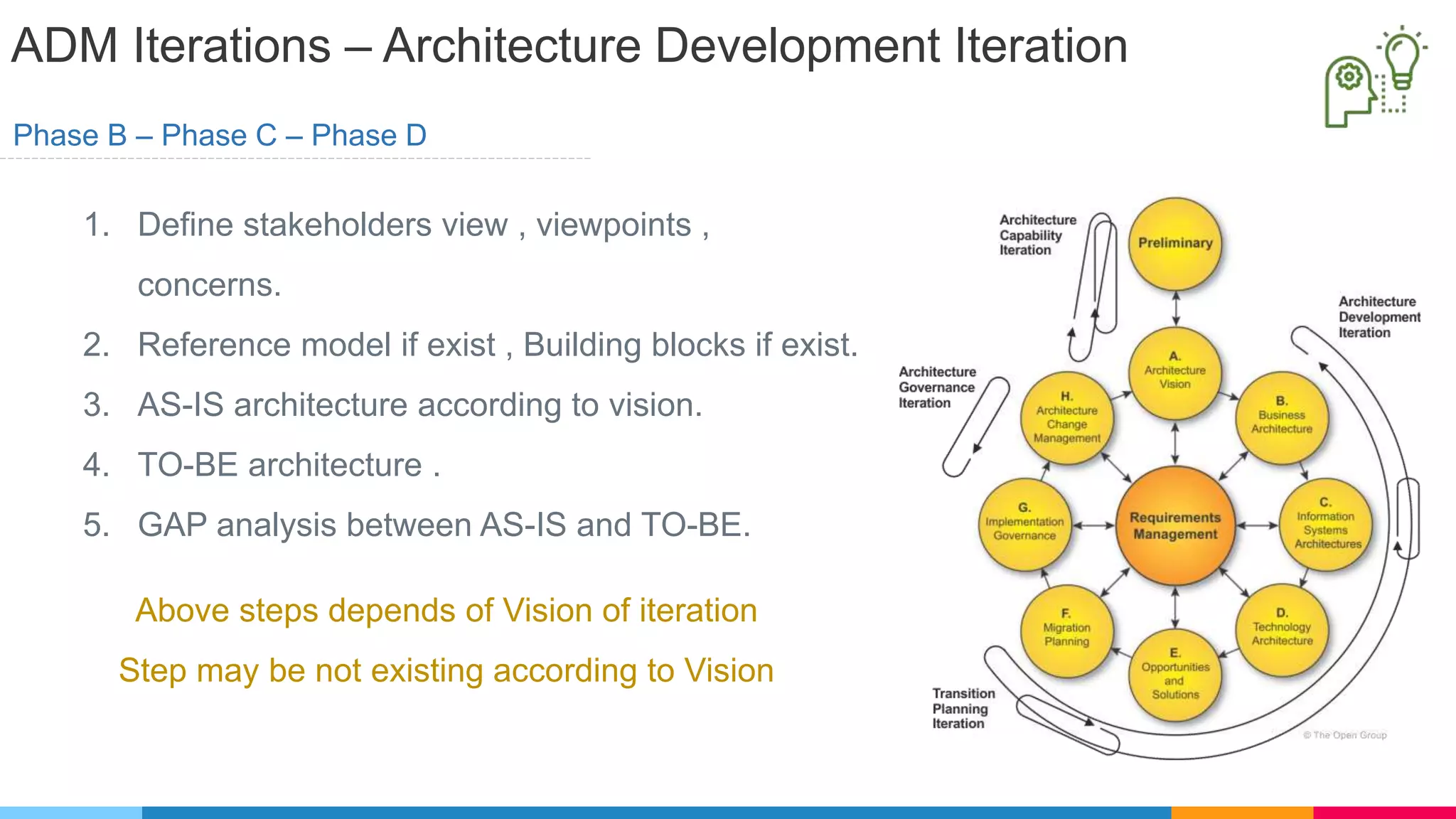
![ADM Phases
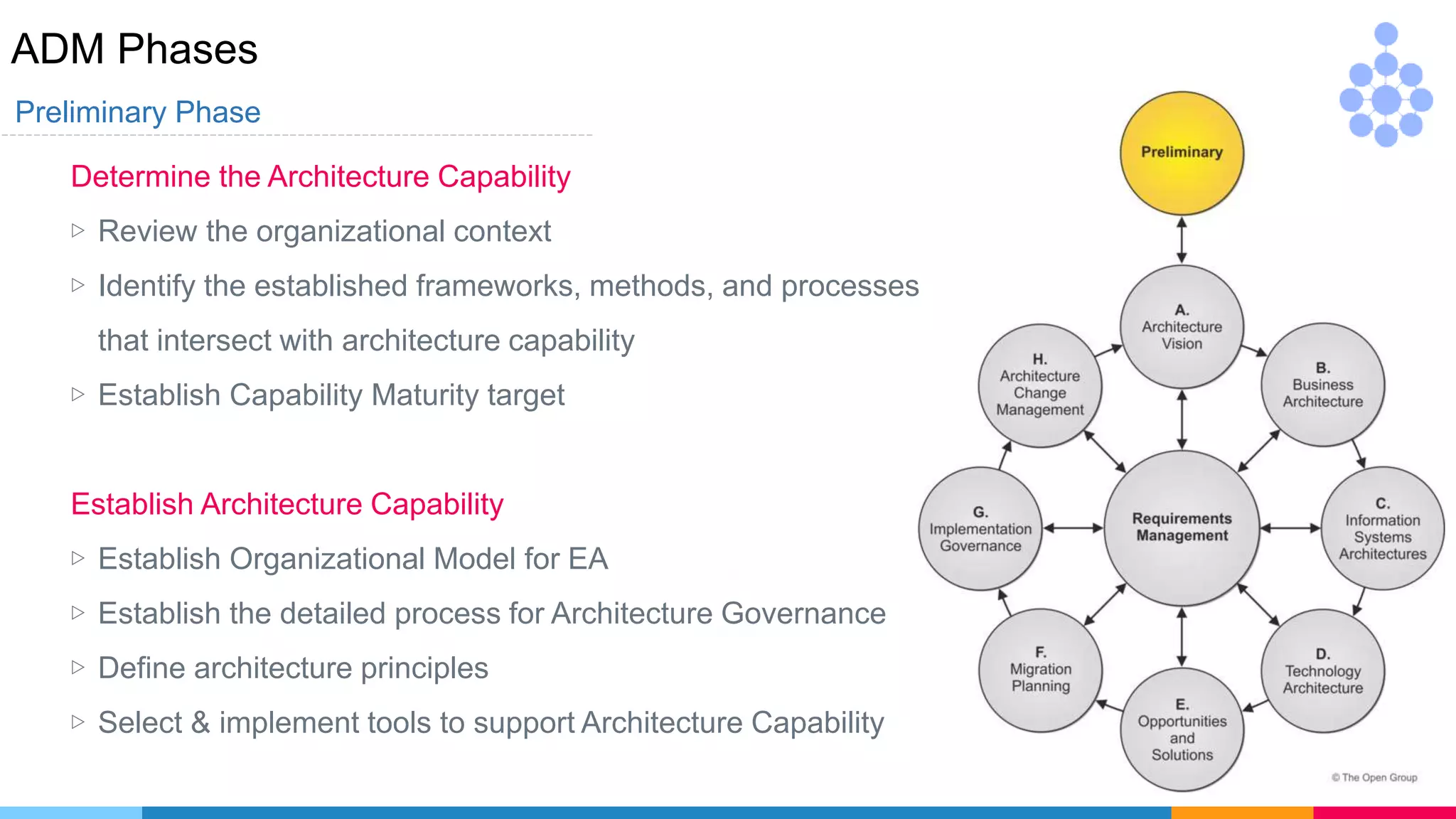
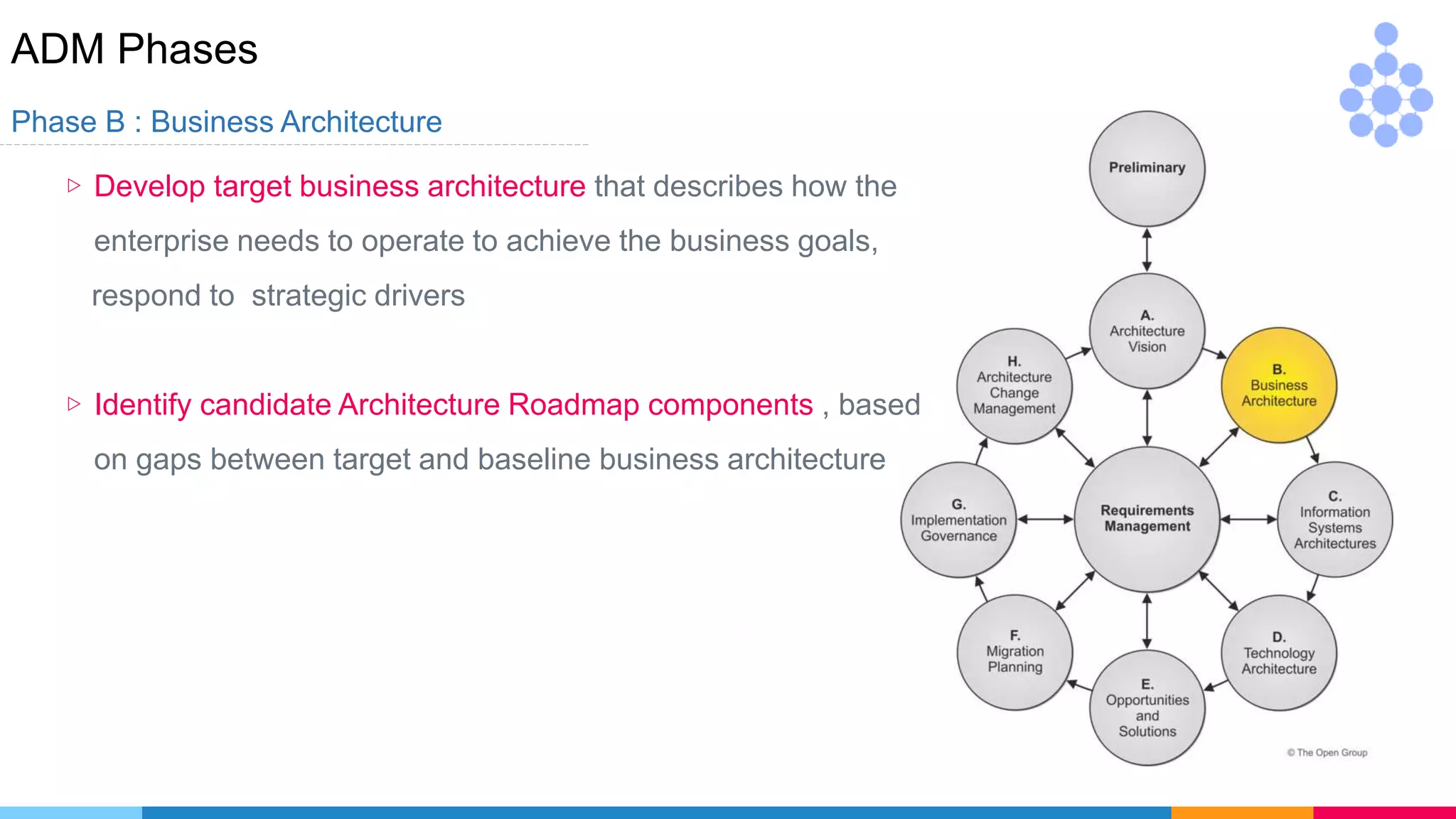
Phase A : Architecture Vision
▷ Develop Vision of the capabilities and business value to be
delivered for [iteration , partitioning ]
▷ Define scope , identify stakeholders , obtain approvals
▷ Evaluate Capabilities
Prelim
VisionVisionVision](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewintogaf9-191004111311/75/Togaf-9-2-Introduction-61-2048.jpg)
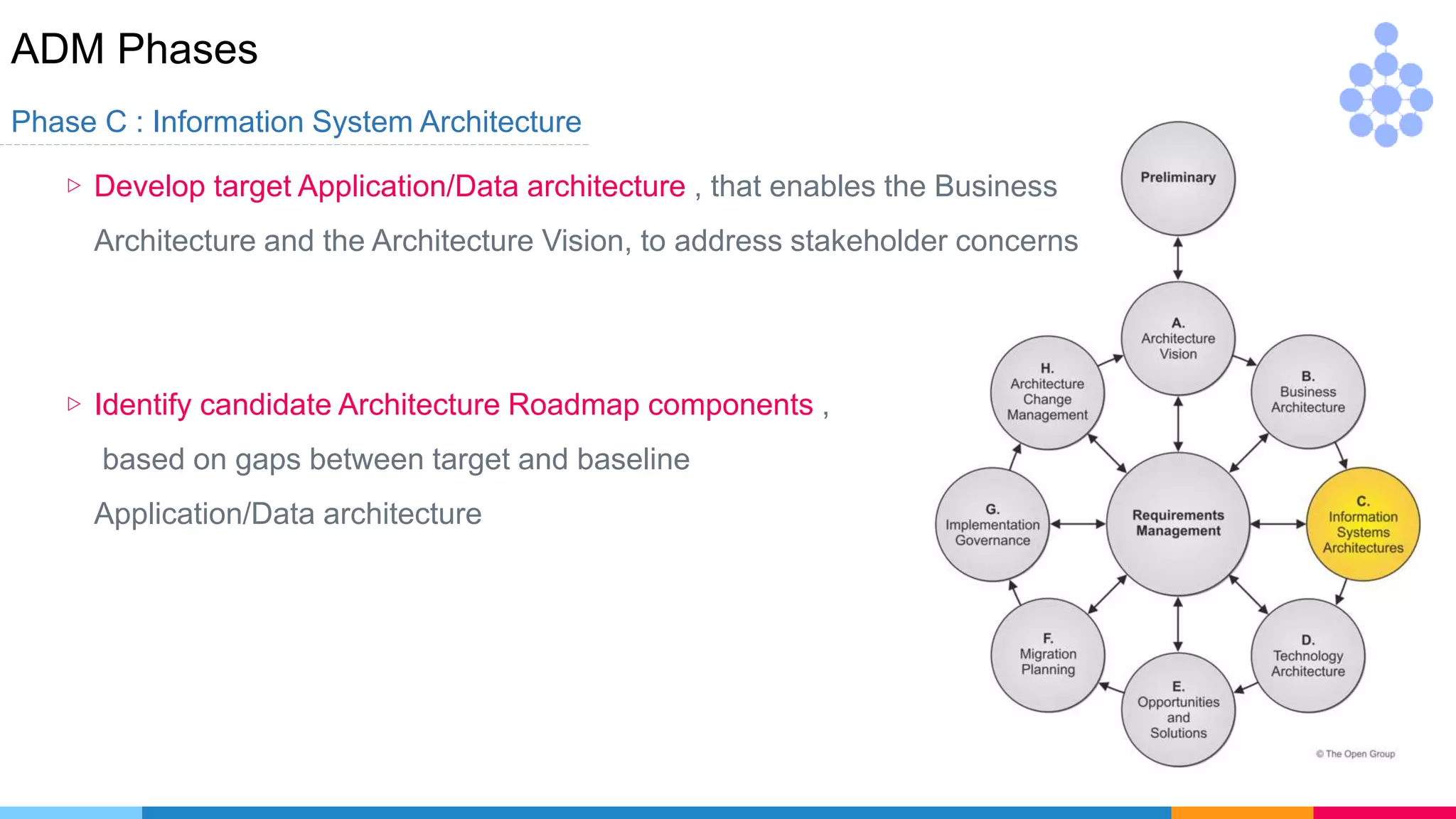
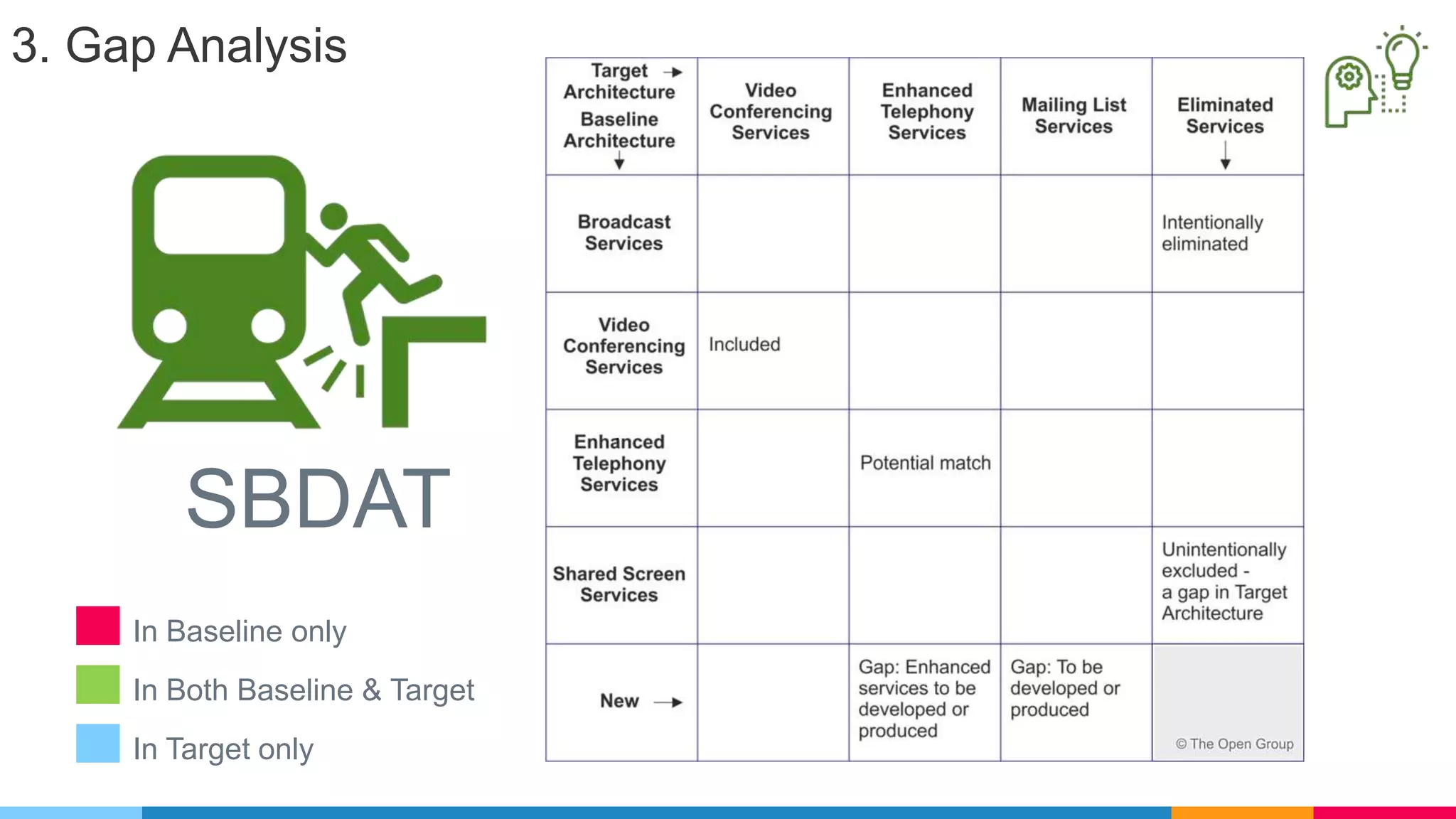
![ADM Phases
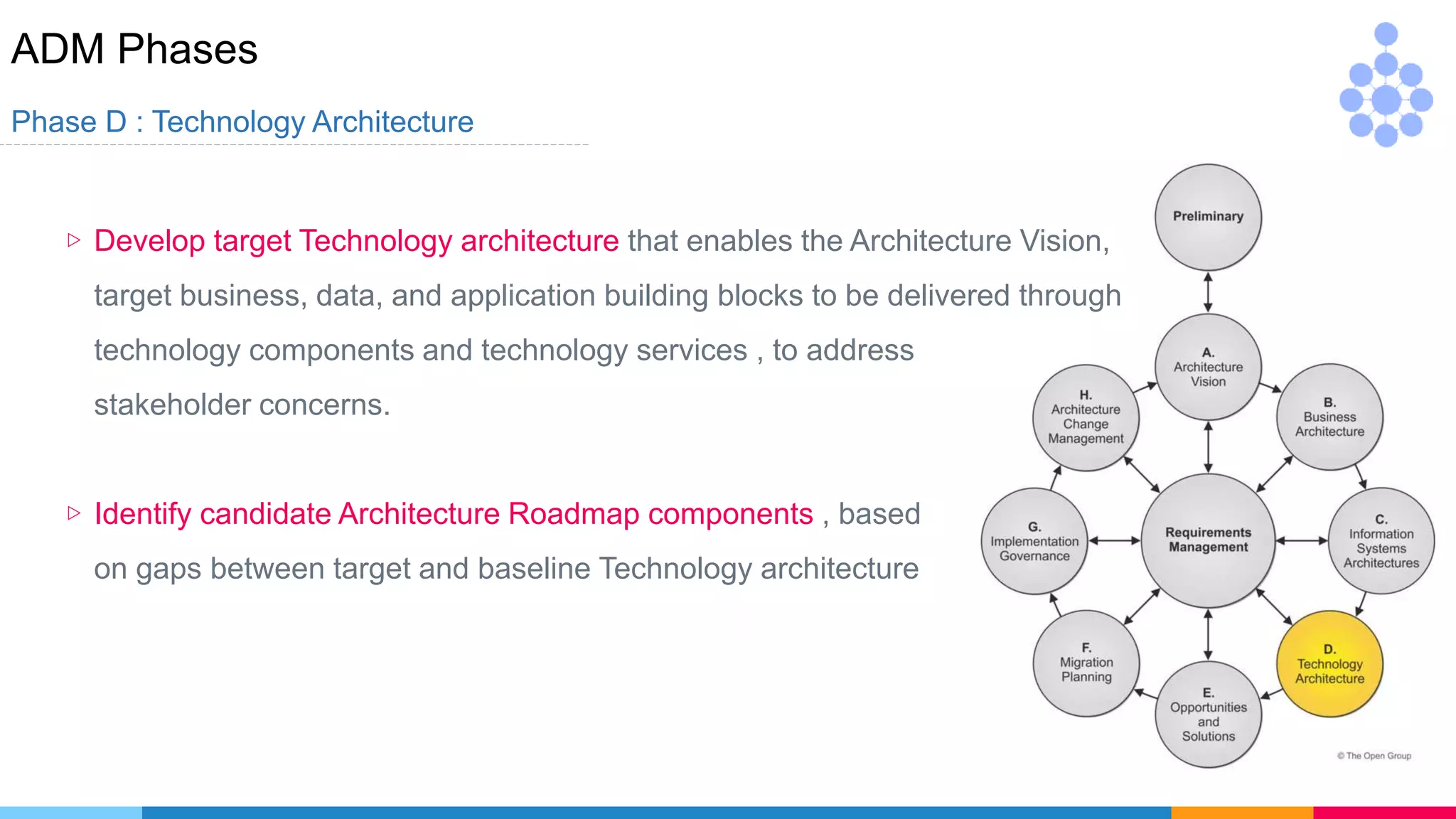
Phase F : Migration Planning
▷ Detailed implementation and migration plan by PMO
▷ Include [ cost , time , effort , resources ,
critical projects and align other projects
(strategic , segmented , capability)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewintogaf9-191004111311/75/Togaf-9-2-Introduction-66-2048.jpg)
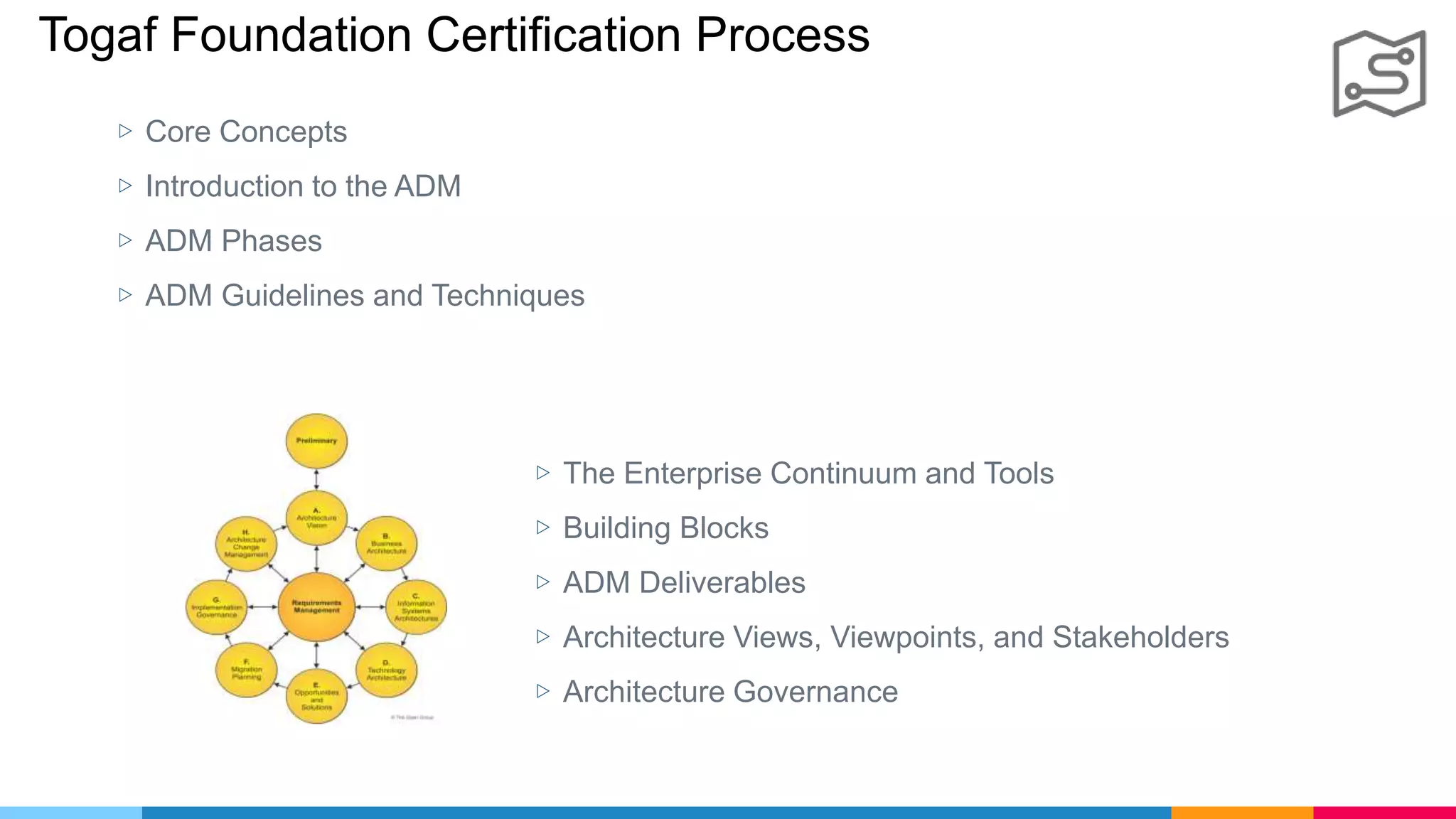
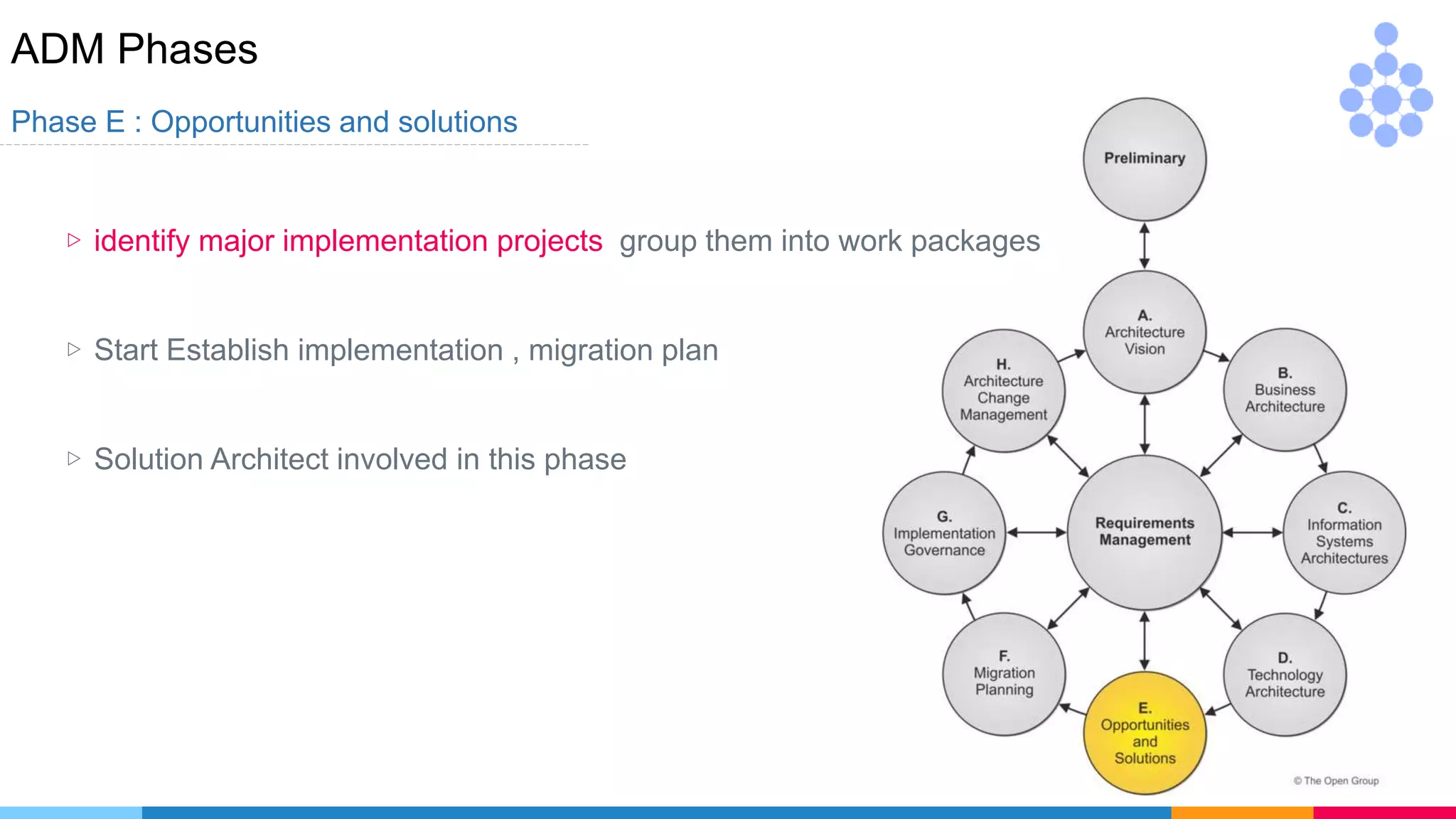
![ADM Phases
Phase G : Implementation Governance
▷ Handover your projects to be implemented by
[ internal dev team , vendor , outsource]
▷ Compliance architecture to our business
[I Give you this / You deliver this / What is the gaps]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewintogaf9-191004111311/75/Togaf-9-2-Introduction-67-2048.jpg)