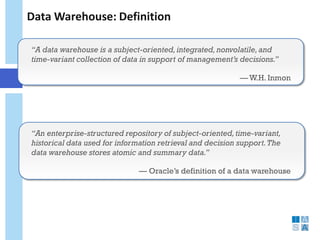
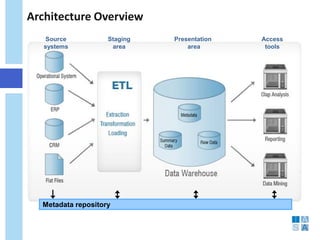
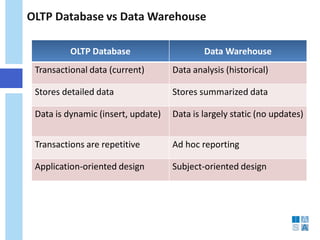
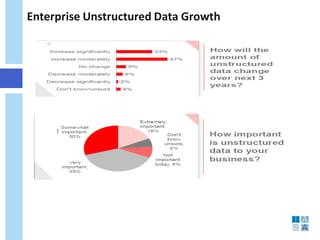
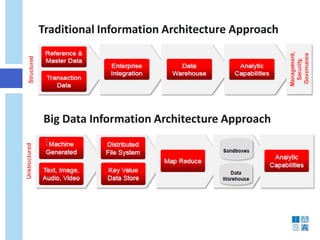
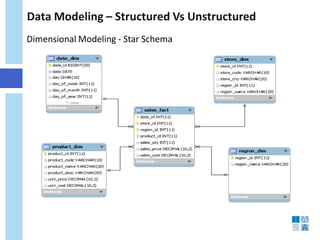
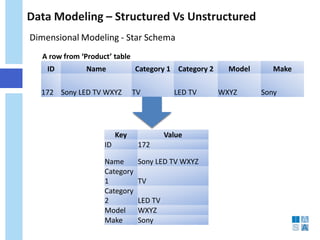
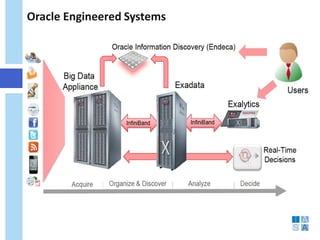
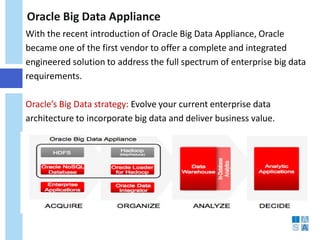
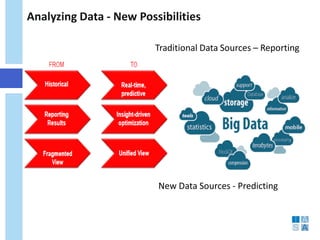
This document discusses the evolution of data warehousing and its relationship to big data. It provides definitions of data warehousing, describing it as a subject-oriented collection of integrated and non-volatile data used for decision making. Key concepts like facts, dimensions, and data marts are introduced. The document then contrasts online transaction processing databases with data warehouses. Challenges of data warehousing are mentioned. The remainder covers big data characteristics, information architectures for structured and unstructured data, Oracle tools for big data, and how data analytics is shifting from reporting to prediction.