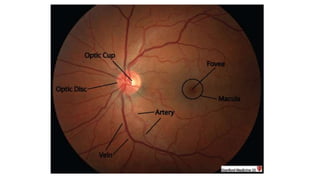
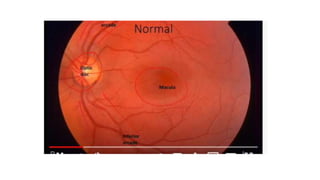
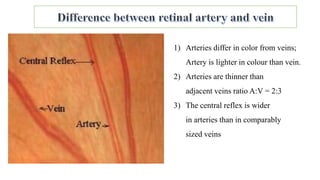
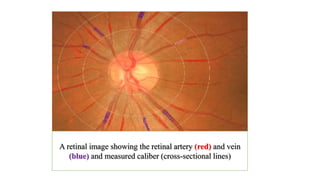
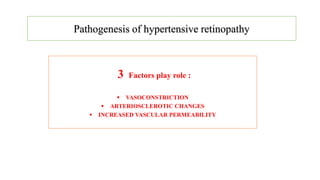
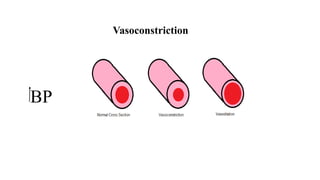
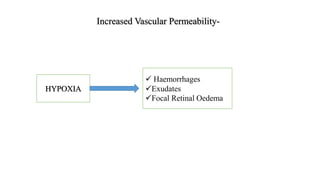
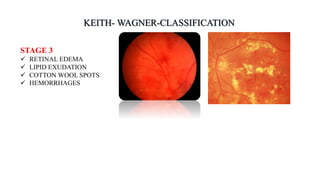
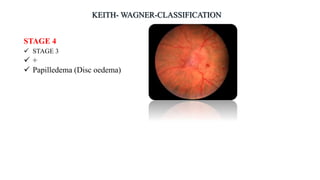
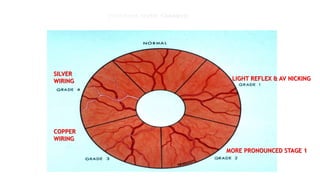
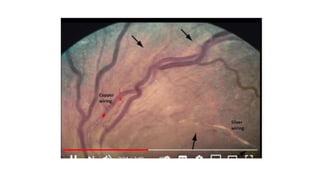
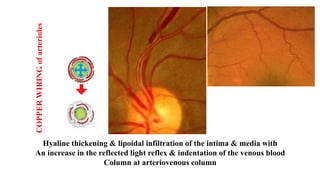
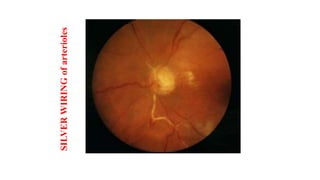
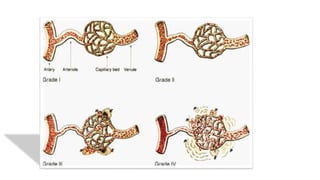
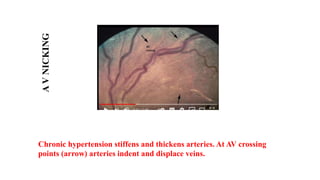
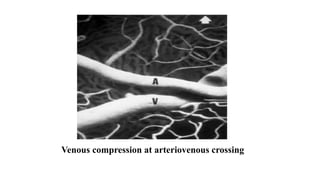
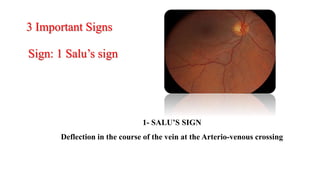
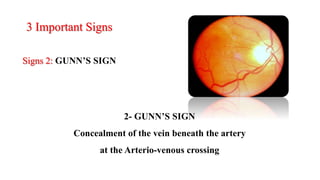
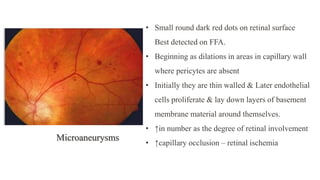
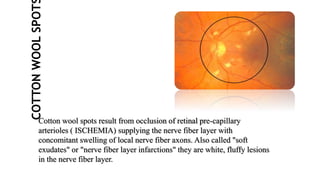
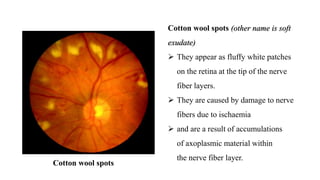
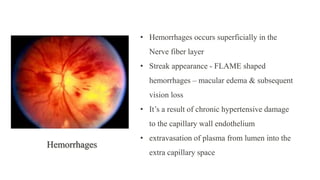
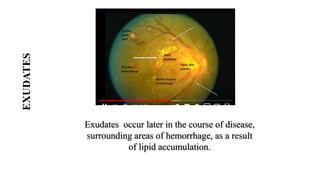
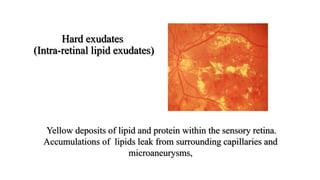
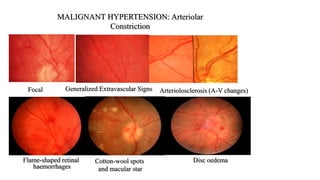
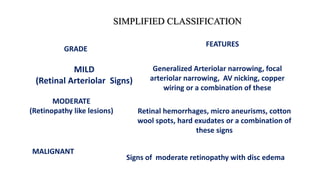
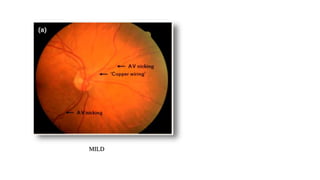
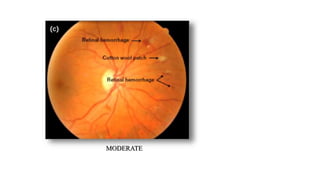
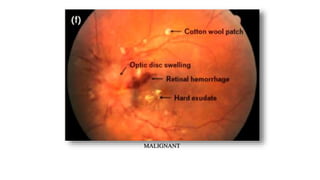
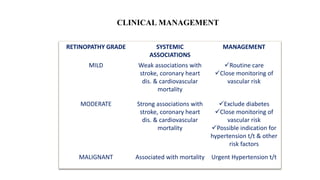
The document discusses the relationship between hypertension and ocular changes, particularly focusing on hypertensive retinopathy and its classification stages. Key indicators include vascular changes observed through ophthalmoscopy such as narrowing, exudates, and hemorrhages in the retina. It also highlights important signs and the management of varying degrees of retinopathy, linking them to systemic health risks.