Embed presentation
Download to read offline

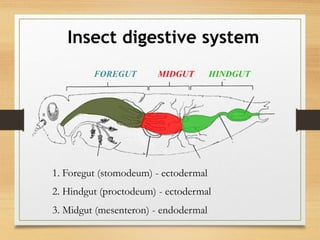

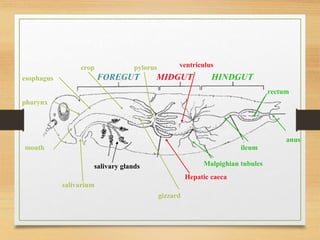
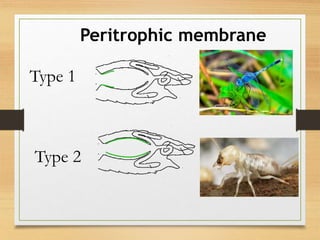

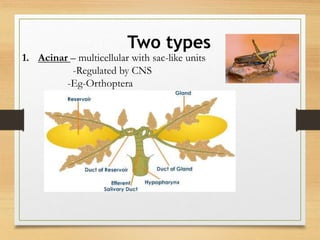





The document details the insect digestive system, which consists of three main parts: the foregut, midgut, and hindgut, and includes the structure and function of salivary glands. It discusses the composition of saliva, types of salivary glands, and their roles in digestion, such as enzyme secretion and food lubrication. Additionally, it explains the regulation of these processes by the nervous system and neurohormones.











