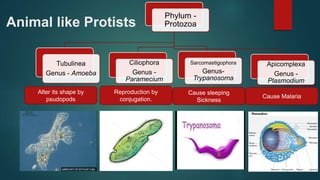
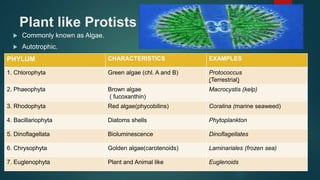
Protists constitute a kingdom within the five-kingdom classification, made up of mainly unicellular eukaryotic organisms that can be autotrophic or heterotrophic. Key types include animal-like, plant-like, and fungus-like protists, with significant roles in ecosystems, industry, and human health. They can reproduce both asexually and sexually, with several health-related impacts stemming from animal-like protists such as malaria and sleeping sickness.