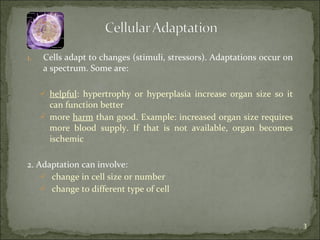
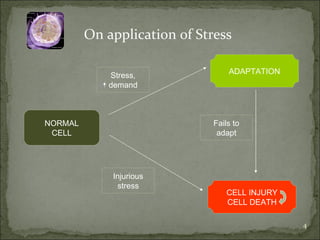
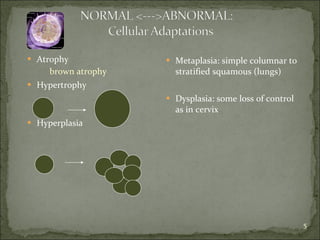
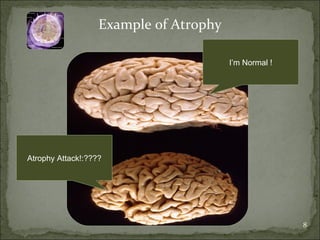
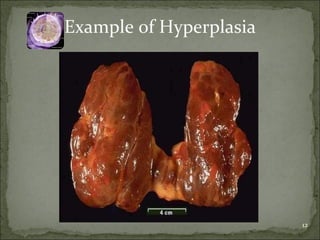
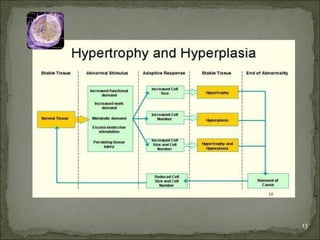
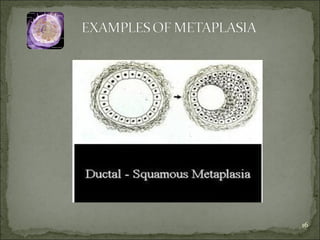
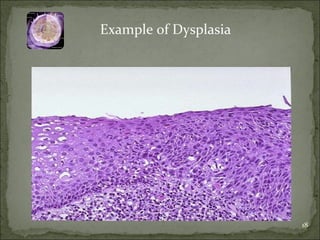
Homeostasis refers to the steady state that cells exist in normally, with an equilibrium between the cells and their environment to allow for adequate functioning. When this balance is disturbed, it can predispose cells to pathology. Cells can adapt to changes through processes along a spectrum, including helpful adaptations like hypertrophy (increase in cell size) and hyperplasia (increase in cell number), or more harmful adaptations that can lead to cell injury or death if the stress cannot be adapted to. Adaptations may involve changes in cell size or number, or changes to a different cell type through metaplasia. Dysplasia refers to some loss of cellular control, as seen in conditions like cervical dysplasia, and can progress