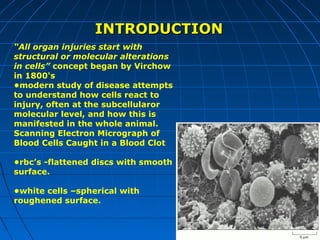
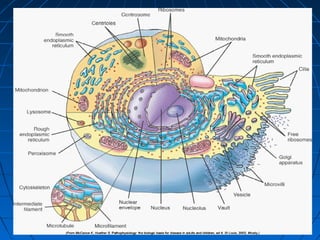
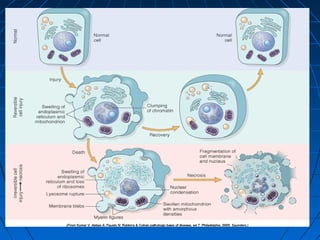
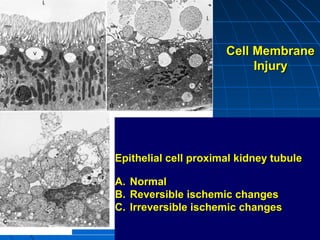
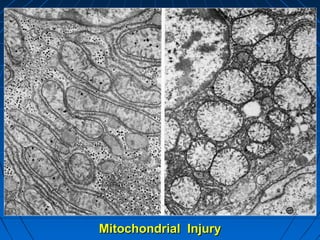
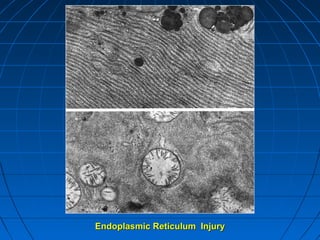
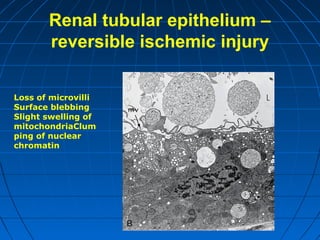
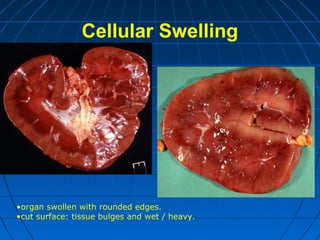
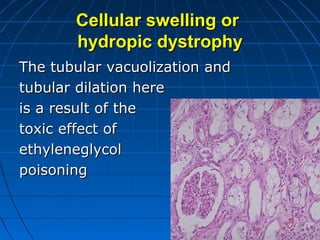
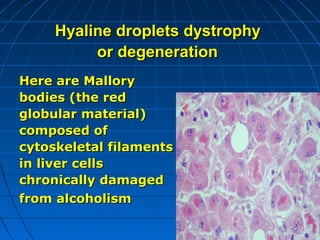
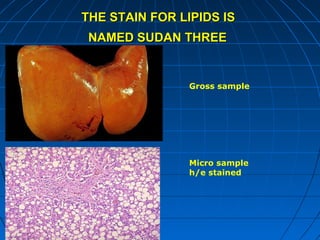
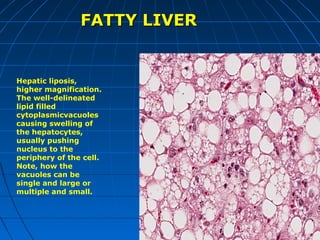
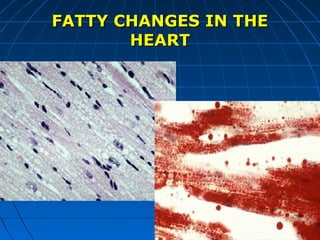
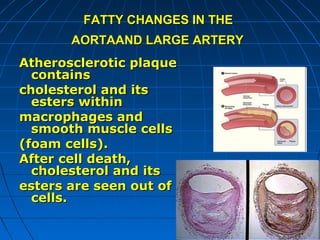
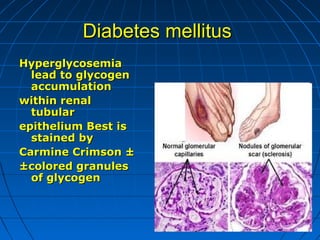
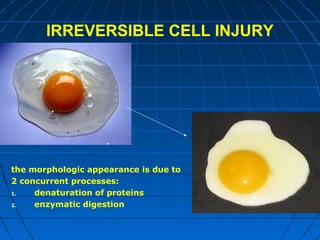
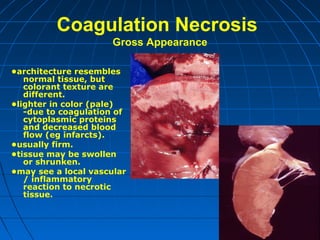
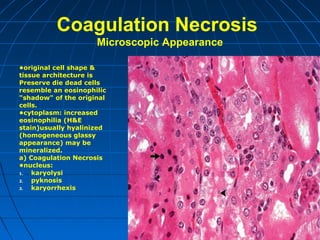
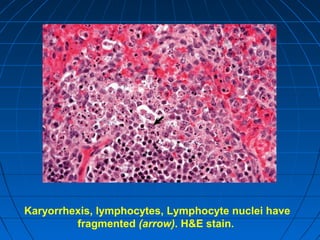
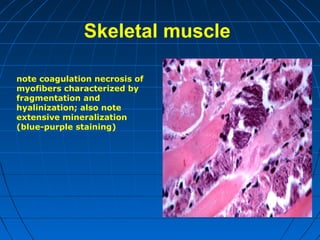
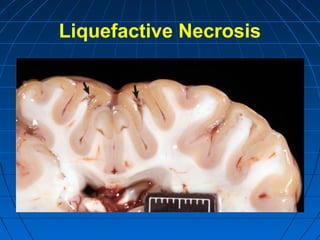
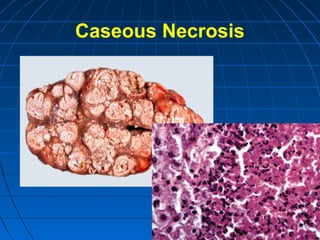
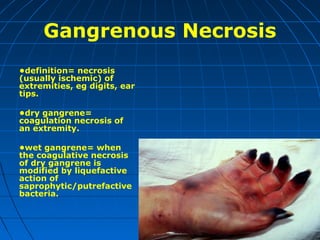
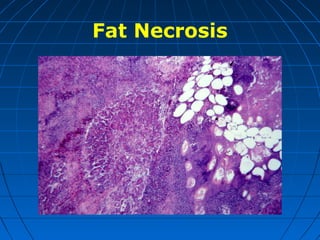
This document discusses cellular injury and cell death. It begins by introducing the hierarchical structure of the human body from cells to organs to systems. It then describes the different types of tissues and cellular adaptations and injuries. The main types of cellular injury discussed are reversible and irreversible injuries. Reversible injuries include changes like swelling while irreversible injuries involve cell death through necrosis or apoptosis. The document closes by defining different patterns of necrosis like coagulation, liquefactive, and caseous necrosis.