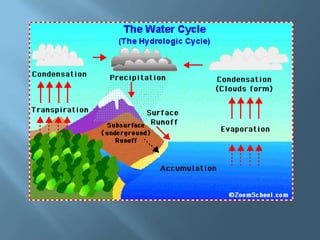
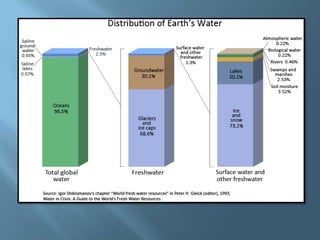
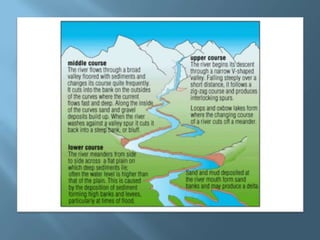
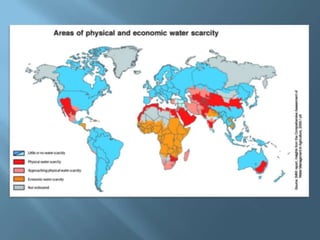
The document explains the four interconnected spheres of the Earth: lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere, focusing on the hydrosphere, which encompasses all water on Earth. It discusses the water cycle, types of water (saltwater and freshwater), and various water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and glaciers, as well as the importance of water for life and its uneven distribution. Additionally, it mentions environmental issues like floods and droughts, emphasizing the necessity for water recycling.