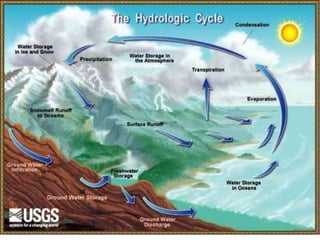
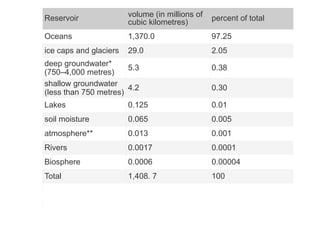
The hydrosphere includes all water on Earth's surface and subsurface in liquid or frozen form, such as oceans, seas, lakes, rivers and groundwater. It covers 70% of Earth's surface, primarily as oceans, and provides habitat for many organisms. Water cycles between reservoirs in the hydrosphere, atmosphere and geosphere through evaporation, condensation and precipitation in a continuous circular motion.