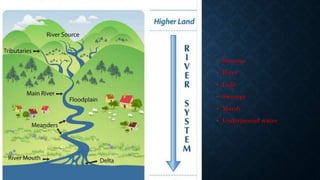
The document discusses the hydrosphere and the distribution of water on Earth. It describes the water cycle by which water evaporates from oceans and transpiration from plants, condenses to form clouds, and precipitates as rain or snow back to Earth's surface and subsurface. It outlines the major types of water found on Earth's surface, including streams, rivers, lakes, swamps, marshes, and underground water, as well as Earth's ice and oceans which hold the vast majority of the planet's water supply.