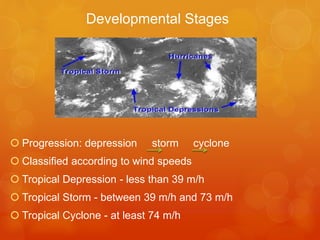
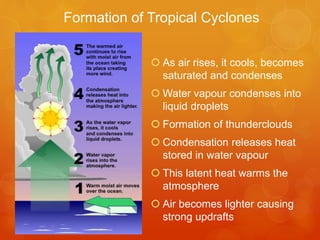
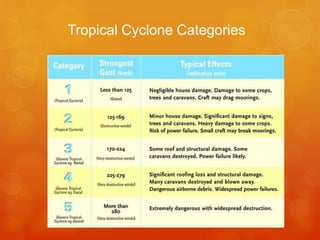
Tropical cyclones develop over warm tropical oceans and are low pressure storm systems characterized by strong winds and heavy rainfall. They form when moist air rises rapidly over warm ocean waters, condenses to form thunderstorms, and the Coriolis effect causes the storms to rotate. Tropical cyclones are categorized based on their wind speeds and can cause extensive damage through high winds, storm surges, and flooding. A notable example is the devastating 1970 Bhola cyclone in Bangladesh, which had wind speeds up to 115 mph and a 33 foot storm surge, resulting in 300,000 to 500,000 fatalities.