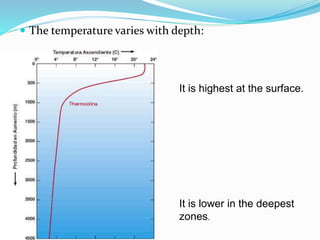
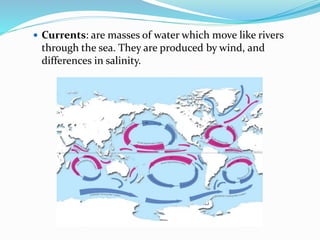
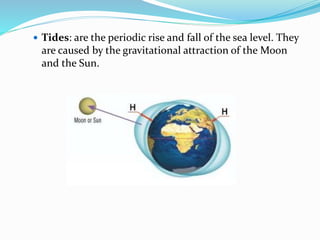
Water is found in oceans, ice/snow, underground, in the atmosphere, and within living things. Sea water is salty due to dissolved gases, while fresh water is found in streams, glaciers, rivers, lakes, and underground. The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface through processes like evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff.