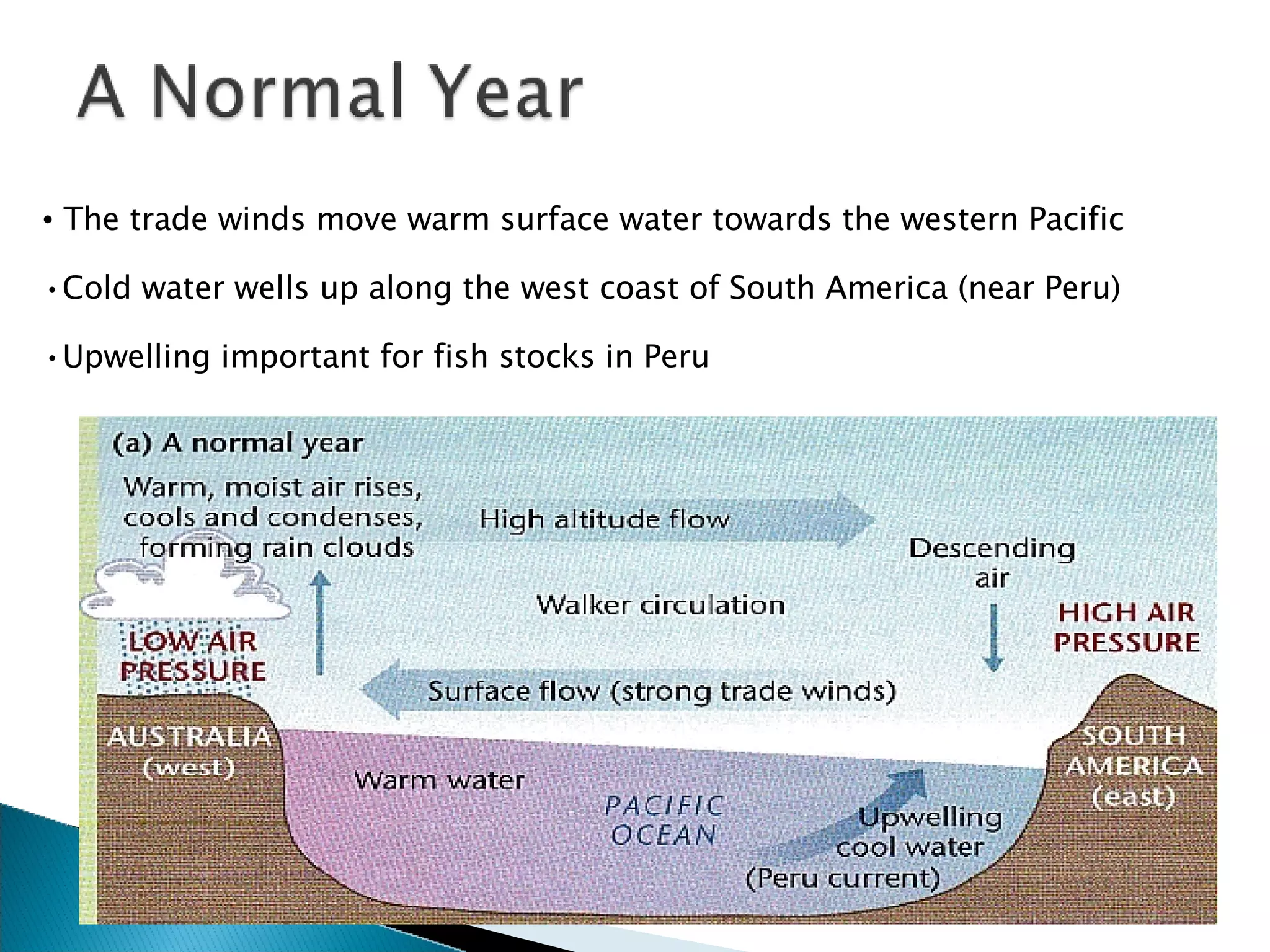
The document discusses the phenomenon of El Niño, a climate pattern in the tropical Pacific that alters weather globally every 3 to 7 years, caused by changing ocean currents and trade winds. El Niño disrupts upwelling, impacting marine life and leading to various weather anomalies, such as increased natural disasters and altered precipitation patterns. La Niña, an intensified version of normal conditions, results in opposite effects, including heavy rains and rising sea levels in certain regions, highlighting the complex interplay between these climate phenomena and broader climate change.