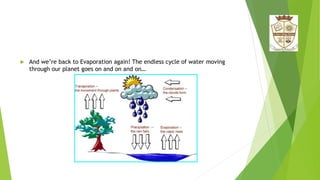
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface. Water evaporates from oceans, lakes, rivers, and soil and transpiration from plants. It rises into the atmosphere and condenses into clouds. Precipitation falls as rain or snow and either runs off into rivers and lakes or infiltrates into soils where it becomes groundwater or is absorbed by plants. Groundwater flows toward springs, rivers, lakes, and oceans, completing the cycle as water evaporates or transpires again into the air. This constant cycling is essential for sustaining life on Earth.