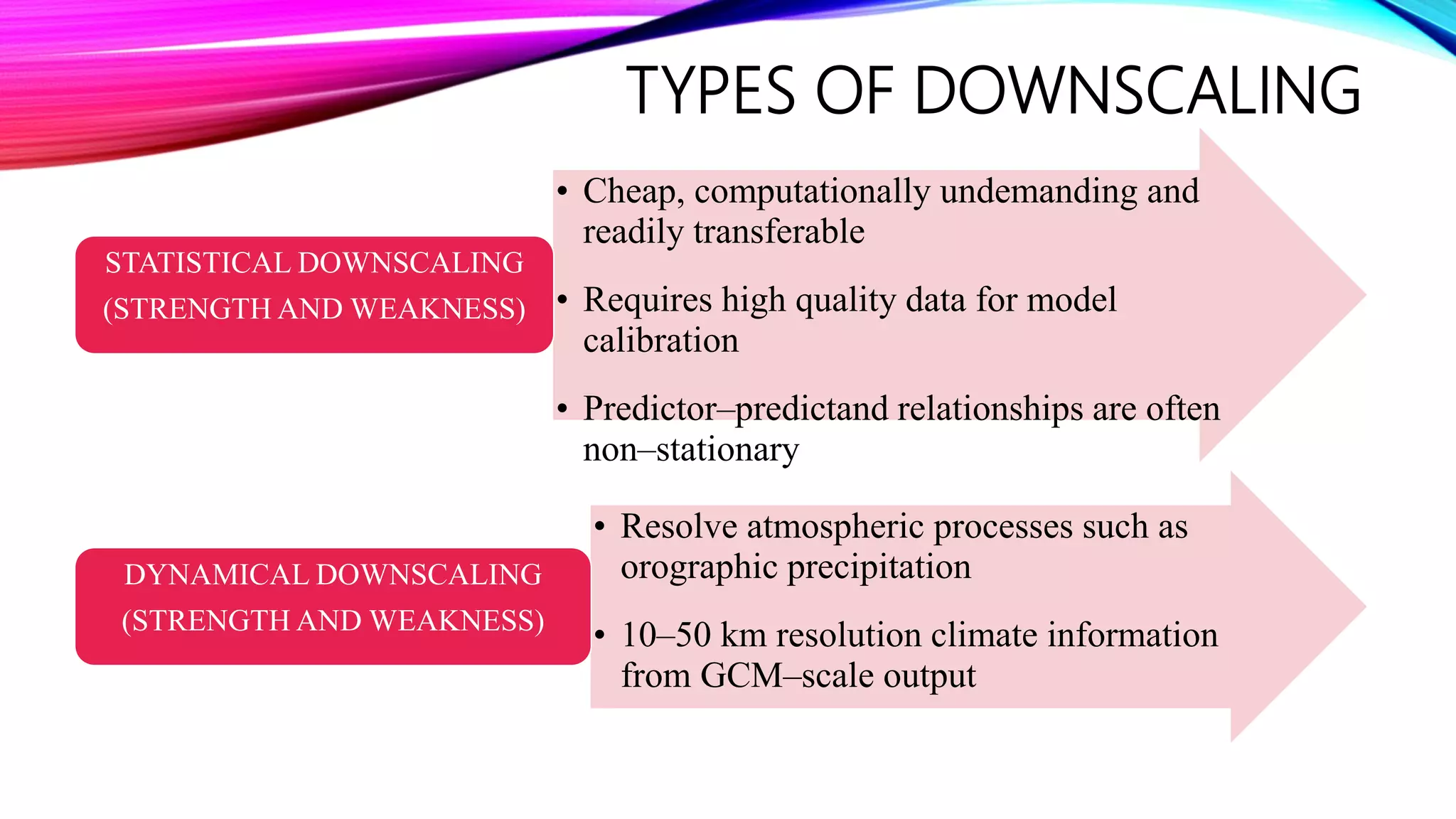
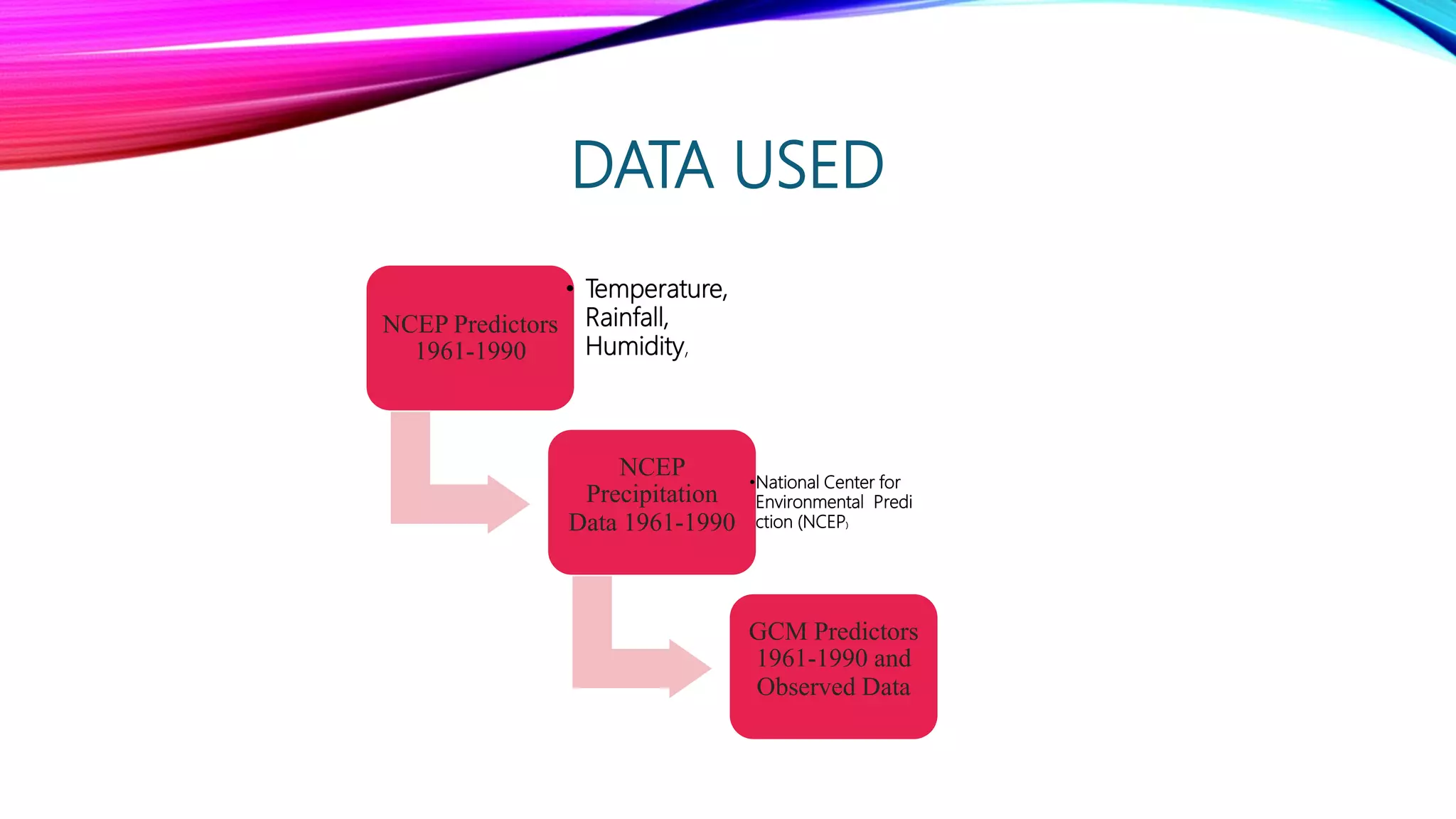
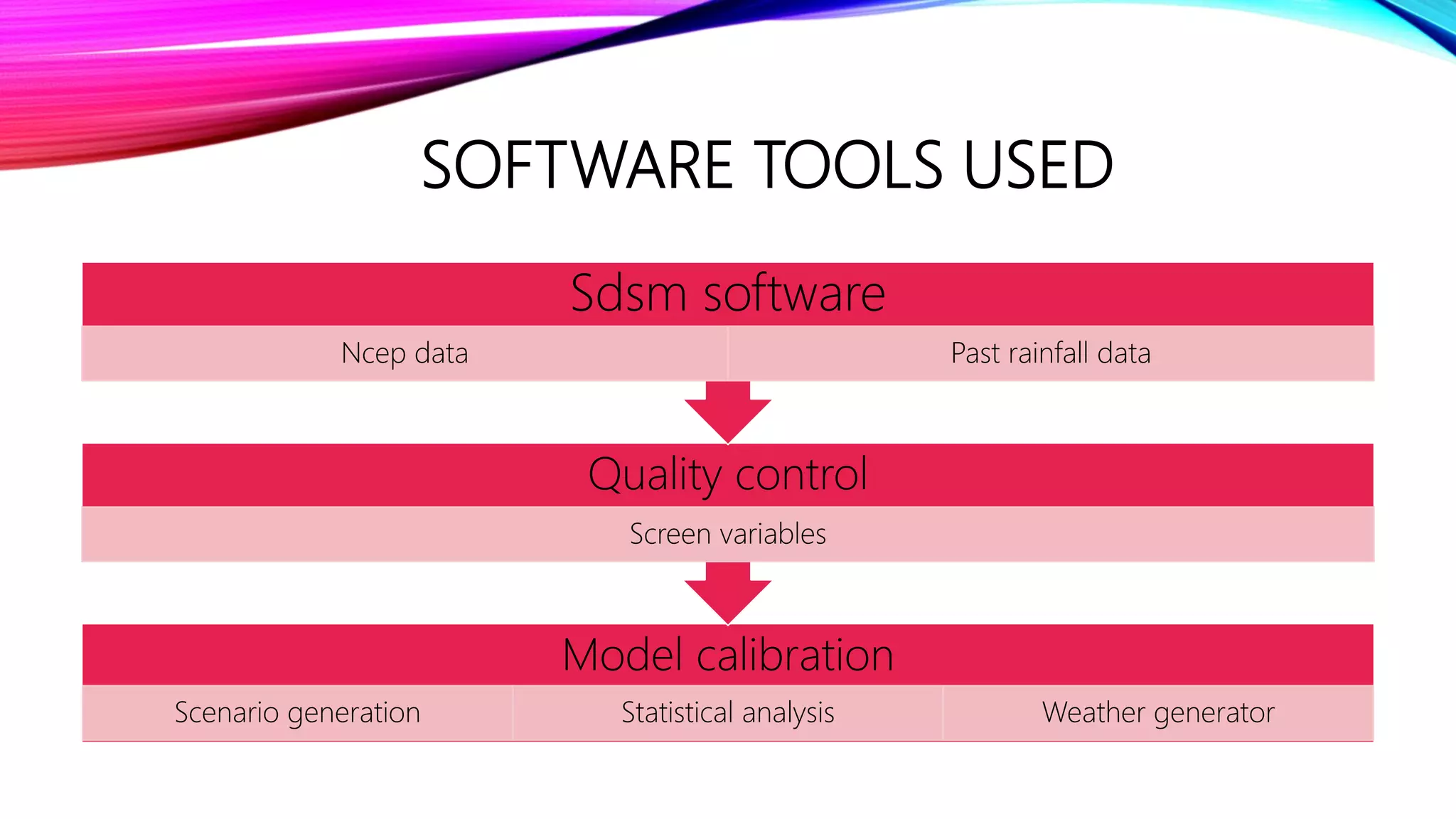
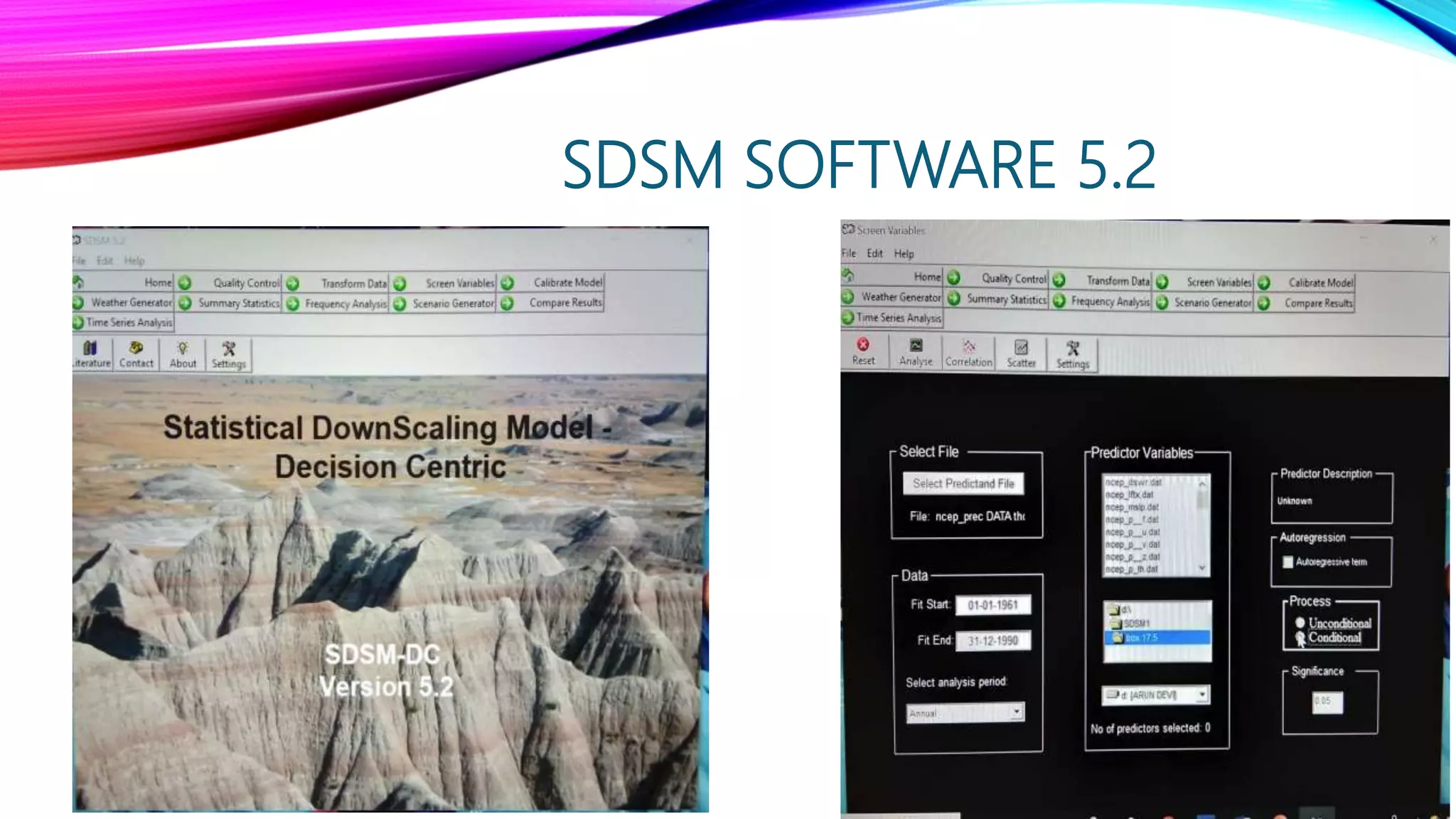
Downscaling is a procedure used to predict future climate changes at local scales from information known at larger scales. There are two main types of downscaling: statistical downscaling uses historical climate data to establish predictor-predictand relationships to project future climate, while dynamical downscaling uses regional climate models with 10-50 km resolution to resolve local atmospheric processes. The document discusses using the Statistical Downscaling Model (SDSM) software version 5.2 along with NCEP predictor data from 1961-1990 and observed rainfall data to statistically downscale climate projections for major Indian cities.