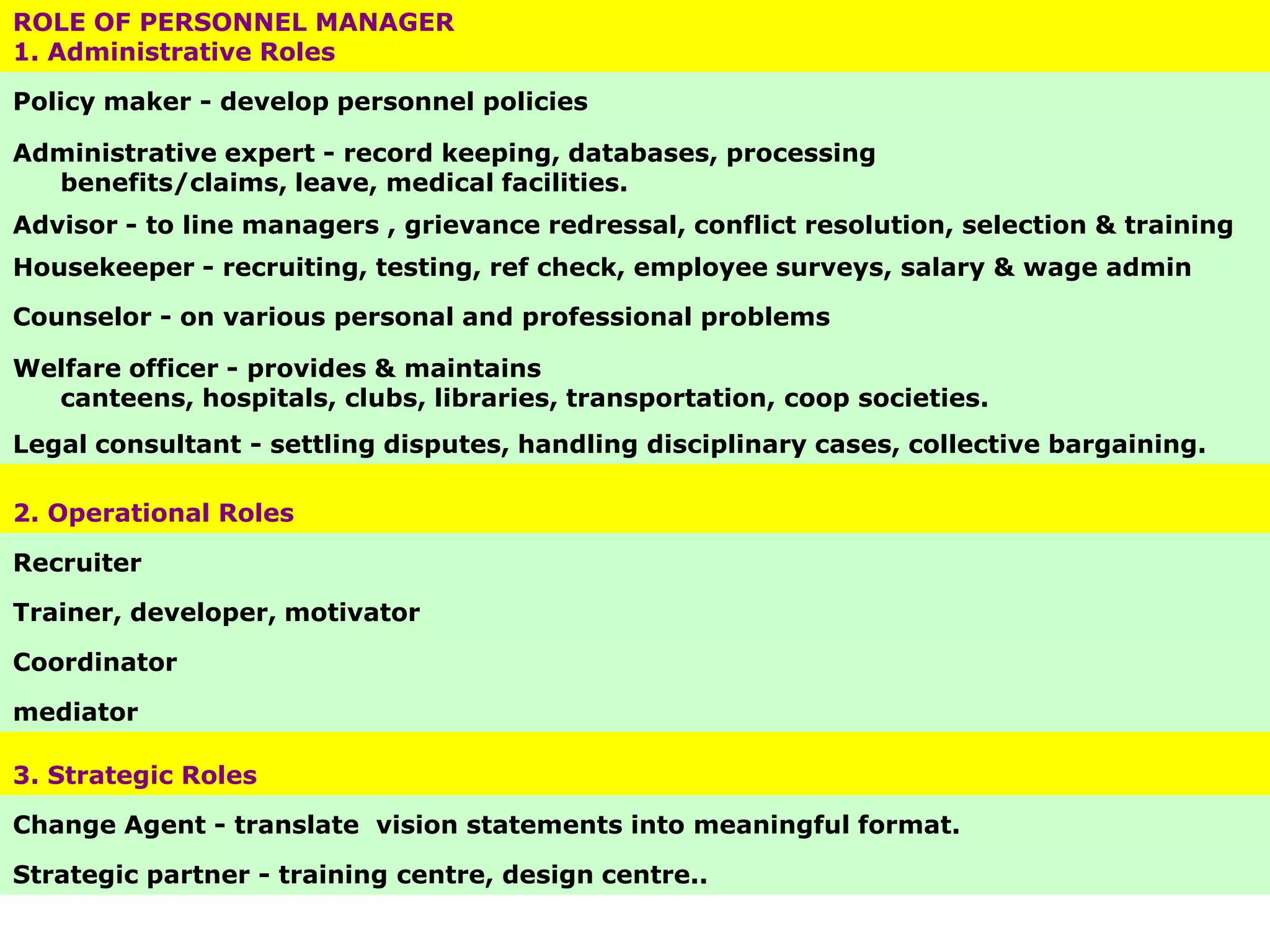
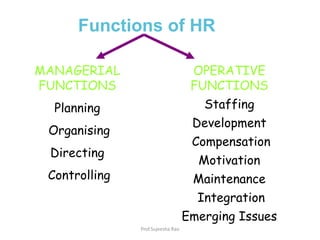
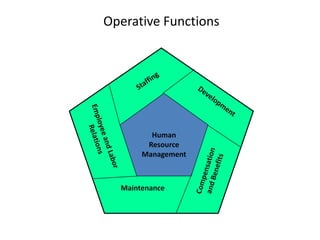
The document outlines the key functions of human resource management (HRM). It discusses both the managerial functions of HRM including planning, organizing, directing, and controlling as well as the operative functions such as staffing, development, compensation, and maintenance. Under operative functions, it provides further details on activities like recruitment, selection, training, performance appraisal, benefits administration, and employee welfare. It also notes emerging issues in HRM like HR audit, HR accounting, and international HRM.