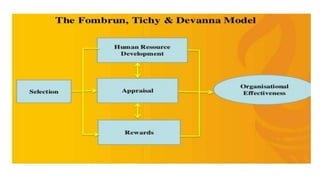
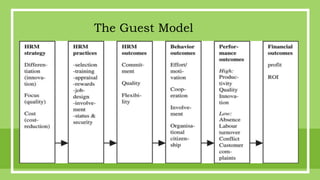
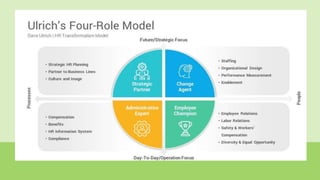
The document outlines various models of human resource management (HRM), including the Harvard Model, Matching Model, Guest Model, Ulrich Model, Storey Model, Best Practice Model, Best Fit Model, and Bath People and Performance Model. Each model presents a unique framework for managing human capital within organizations, focusing on aspects such as stakeholder interests, HR policies, strategic alignment, and employee engagement. The document aims to provide an analytical overview of HRM models, their components, and their relevance to organizational effectiveness.