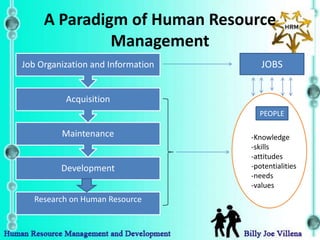
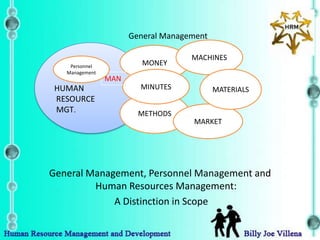
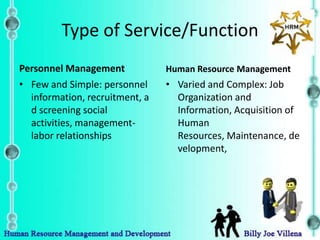
Human resource management is broader in scope than traditional personnel management. It views people as a vital asset and investment rather than just a cost. It involves managing all people in an organization, including top management, middle management, consultants, part-time workers, etc. across both formal and informal settings. The goals of human resource management are to accomplish both organization and individual goals using participatory, flexible and innovative developmental strategies based on a total systems approach respecting the individual and society.