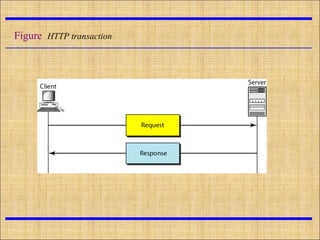
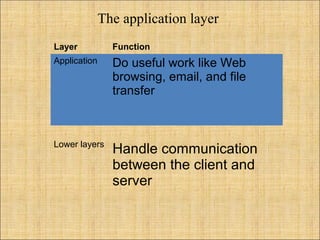
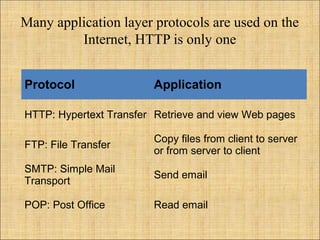
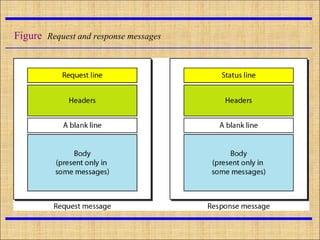
HTTP is the protocol used for communication between web browsers and servers. URIs identify resources, with URLs specifying how to locate resources via protocols, hostnames, directories, and filenames. HTTP uses URLs to retrieve web pages and other resources, with requests containing the method, URL, and headers sent to the server and responses returned with status lines and headers along with the requested content.