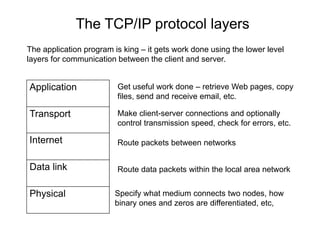
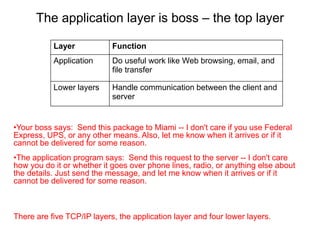
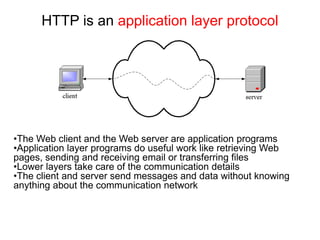
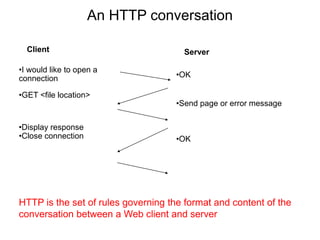
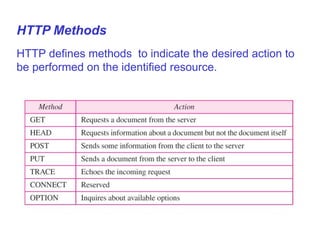
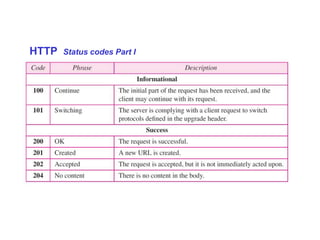
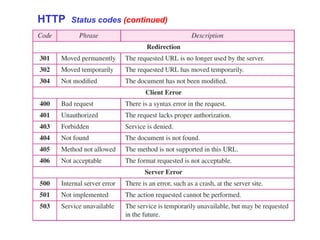
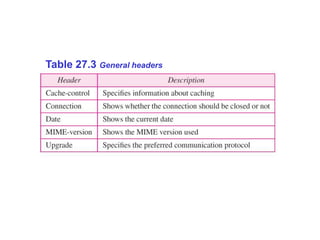
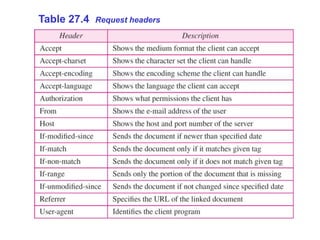
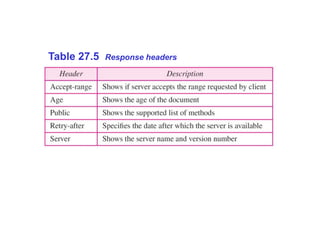
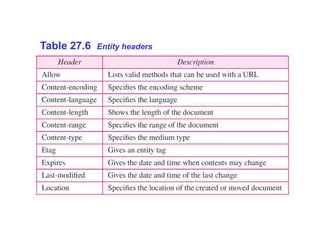
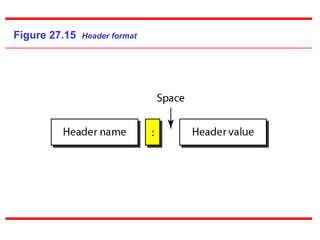
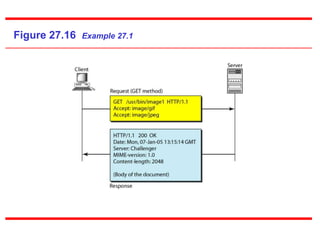
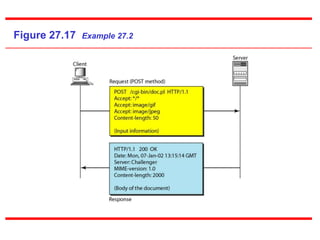
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems and is the foundation for data communication on the World Wide Web. HTTP defines methods like GET and POST to indicate the desired action on a resource and uses status codes in responses. It also uses headers in requests and responses to define parameters of the transaction. HTTP typically uses TCP port 80 to allow a client to open a connection and send requests to a server, which responds with messages that may contain requested resources or error information.