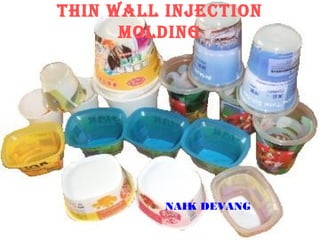
Thin wall injection molding is a process involving parts with wall thicknesses often less than 0.6 mm that allows for lightweight and complex shapes with improved flow characteristics. It is used mainly for packaging and disposable containers, enabling shorter cycle times, higher productivity, and cost savings due to reduced material usage. Key considerations include machine selection, optimized settings, and overcoming limitations such as high material stress and the need for precise control during the molding process.