Embed presentation
Downloaded 67 times







![A Symmetric Homomorphic
Encryption Scheme over Integers
Shared key: odd integer p
● To encrypt a bit m:
Choose at random large q, small r (|r| < p/2)
Cipher c = pq + 2r + m [ Ciphertext is close to a multiple of p ]
● To decrypt c:
Message m = (c mod p) mod 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7pyzhvnes3unpugfo4kv-signature-fa17ef08645a3cce9ed98bc960f7e89b419197b8ab9318d2a54057ce7f634710-poli-160709185311/85/Homomorphic-encryption-9-320.jpg)




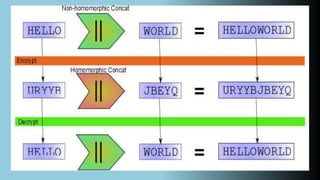
This document provides an overview of homomorphic encryption. It begins by defining homomorphic encryption as a form of encryption that allows specific types of computations to be performed on ciphertext and generate an encrypted result that matches the operations performed on the plaintext when decrypted. It then discusses different types of homomorphic encryption including partially homomorphic (additive or multiplicative), fully homomorphic encryption, and provides examples like RSA, ElGamal, and Paillier. The document concludes by listing some applications of homomorphic encryption such as e-voting, biometric verification, and discusses Paillier encryption specifically.








![A Symmetric Homomorphic
Encryption Scheme over Integers
Shared key: odd integer p
● To encrypt a bit m:
Choose at random large q, small r (|r| < p/2)
Cipher c = pq + 2r + m [ Ciphertext is close to a multiple of p ]
● To decrypt c:
Message m = (c mod p) mod 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7pyzhvnes3unpugfo4kv-signature-fa17ef08645a3cce9ed98bc960f7e89b419197b8ab9318d2a54057ce7f634710-poli-160709185311/85/Homomorphic-encryption-9-320.jpg)



