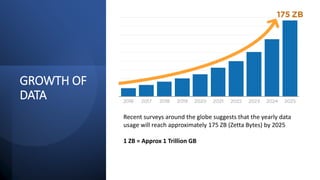
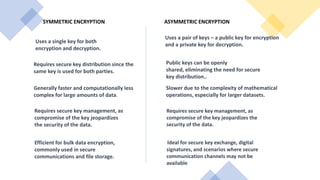
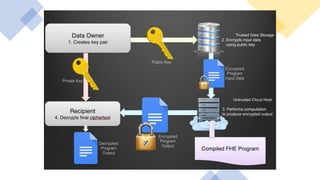
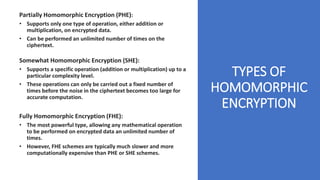
Homomorphic encryption is a cryptographic technique that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it first. It allows a recipient who holds the private key to perform operations on encrypted data and obtain an encrypted result that matches the result of performing the same operations on the plaintext. The key types include partially homomorphic (supports addition or multiplication but not both), somewhat homomorphic (supports a limited number of addition or multiplication operations), and fully homomorphic (supports unlimited addition and multiplication operations). Homomorphic encryption has applications in secure cloud computing, privacy-preserving data analytics, and machine learning. It provides confidentiality during data processing while traditional encryption requires decryption before computations.