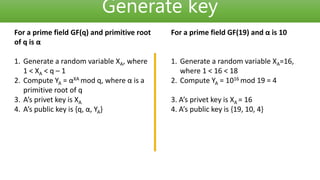
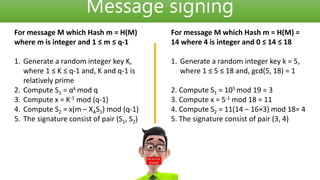
The ElGamal digital signature scheme was described by Tahir Elgamal in 1985. It uses a key pair consisting of a public key and private key, where the private key is used to generate signatures and the public key is used to verify signatures. Signatures provide message authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation by proving the message was signed by the private key holder. The document then proceeds to describe the technical process of generating keys, signing messages, and verifying signatures using ElGamal signatures with an example.