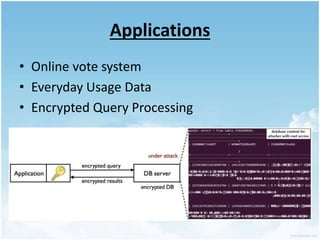
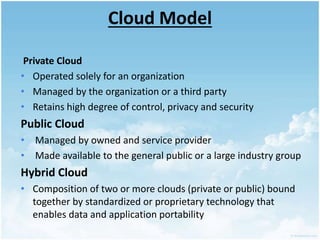
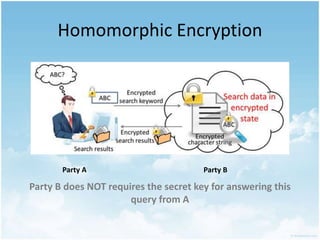
This document discusses homomorphic encryption and its applications in cloud computing. It begins by defining cloud computing and encryption. Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it first. This allows a third party like a cloud provider to process data while maintaining its confidentiality. The document outlines partially homomorphic encryption schemes like RSA that support only some operations, and fully homomorphic encryption that supports any computation. Potential applications of homomorphic encryption include online voting systems, encrypted data analytics, and encrypted database queries. In conclusion, homomorphic encryption enables secure computation on encrypted data and enhances privacy in cloud computing.





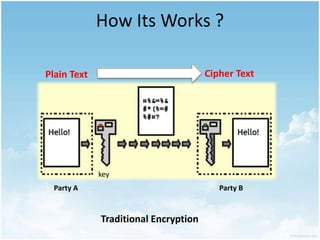




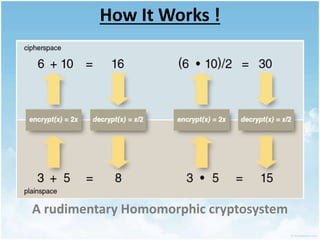
![How It Works !
• Remove Encryption on Summation(Cipher)
= 69 – 10*2
• Suppose I have a file with my phone number
Message = [9, 0, 2, 6, 7, 2, 8, 1, 6, 8]
• And I encrypt it with Caesar cipher* by adding 2 to
each digit, Key = 2
Cipher = [11, 2, 4, 8, 9, 4, 10, 3, 8, 10]
• Want to find the sum of all the numbers in Message.
• Sum up all the elements of Cipher and give the
encrypted result. Summation(Cipher) = 69
• Summation(Message) = 49
• = 49 (Result)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/homomorphicencryptionincloudcomputingfinal-160502185532/85/Homomorphic-encryption-in-cloud-computing-final-14-320.jpg)