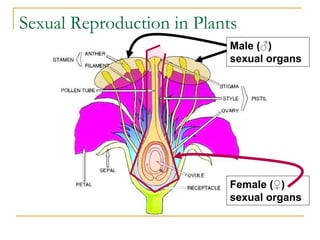
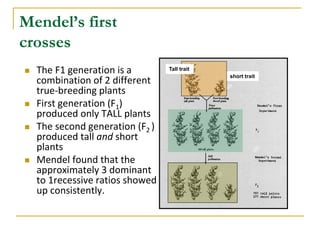
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments crossing true-breeding pea plants that differed in traits like height. In the F1 generation, all offspring exhibited the dominant trait of tall plants. In the F2 generation, approximately 3/4 of offspring were tall (dominant) while 1/4 were short (recessive). Mendel realized each trait was determined by inherited factors, now called genes, that are transmitted from parents to offspring.