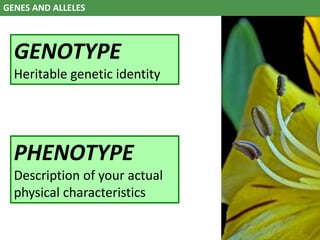
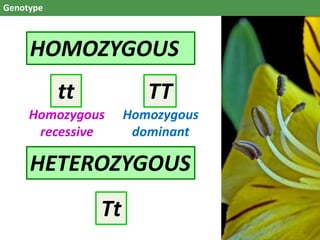
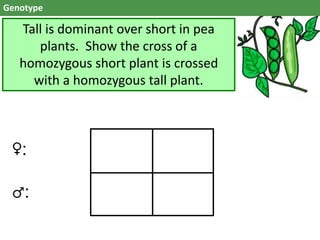
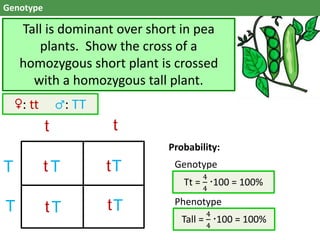
The document discusses genes and alleles, genotypes and phenotypes, dominant and recessive traits, Mendelian and non-Mendelian inheritance patterns. It provides examples of inheritance crosses in pea plants, humans, birds and fish. Key differences are: a gene is a segment of DNA, an allele is a variant of a gene; genotype is the genetic makeup, phenotype is the physical traits; dominant alleles mask recessives but codominant alleles have joint effects. Non-Mendelian patterns like codominance do not follow Mendel's observations.