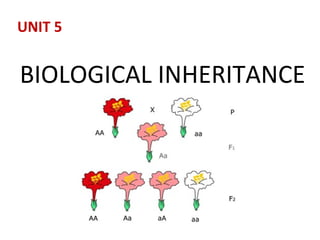
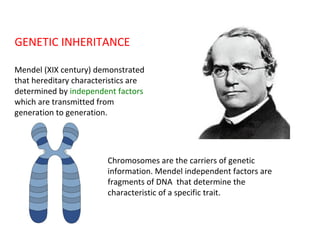
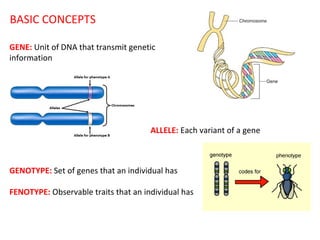
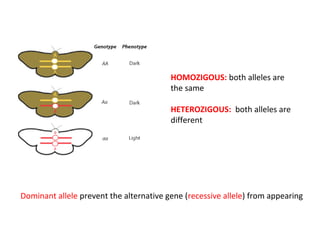
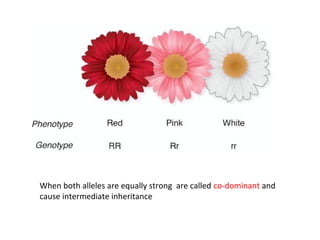
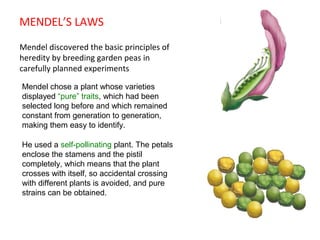
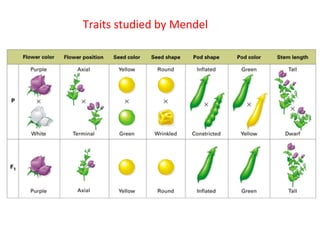
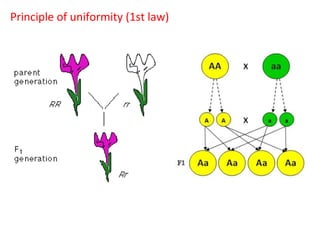
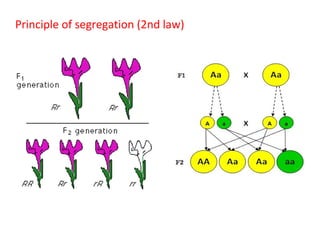
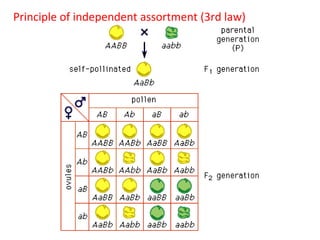
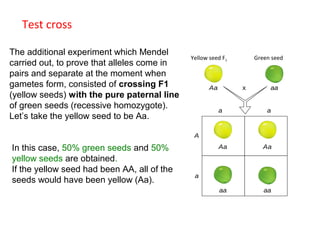
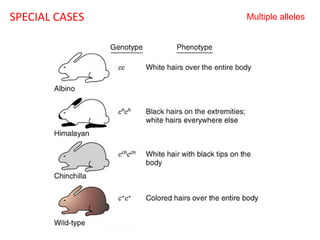
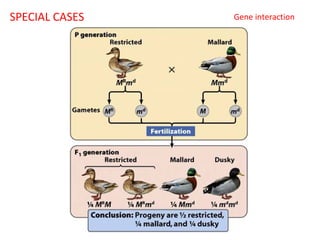
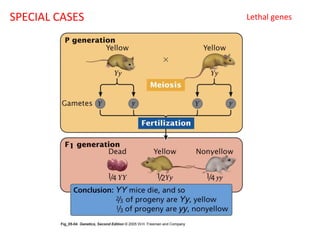
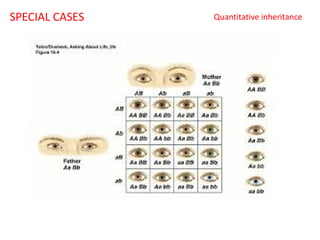
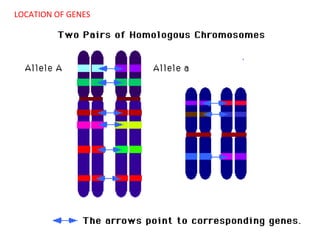
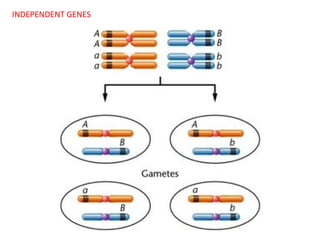
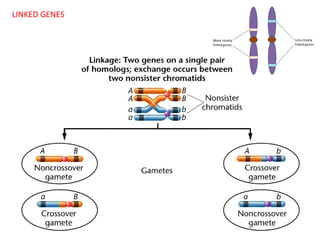
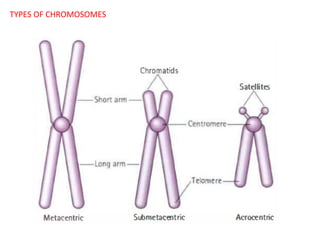
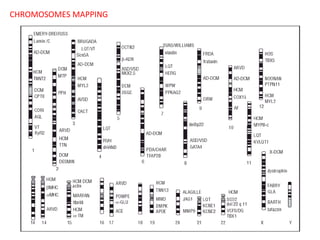
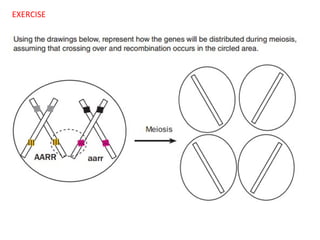
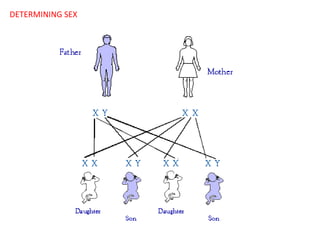
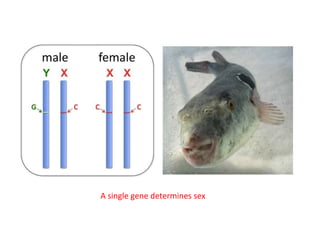
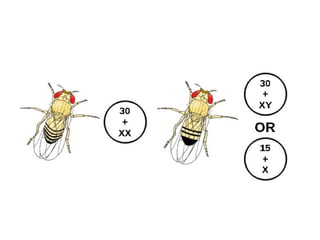
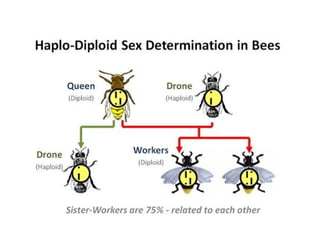
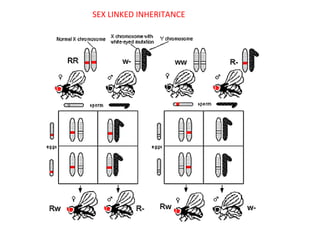
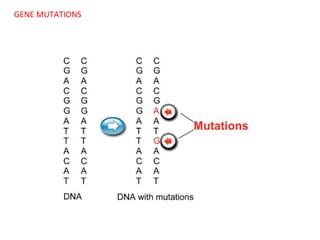
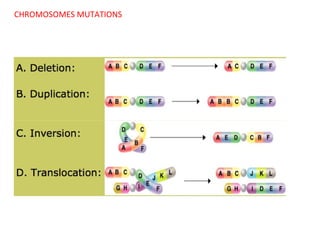
This document summarizes basic concepts of genetic inheritance and Mendel's laws of heredity. It defines key terms like gene, allele, genotype and phenotype. It describes Mendel's experiments with pea plants and his discovery of the principles of uniformity, segregation and independent assortment. The document also discusses Mendel's test crosses and how they proved alleles separate during gamete formation. Finally, it briefly outlines several special inheritance cases as well as the determination of sex and sex-linked inheritance.