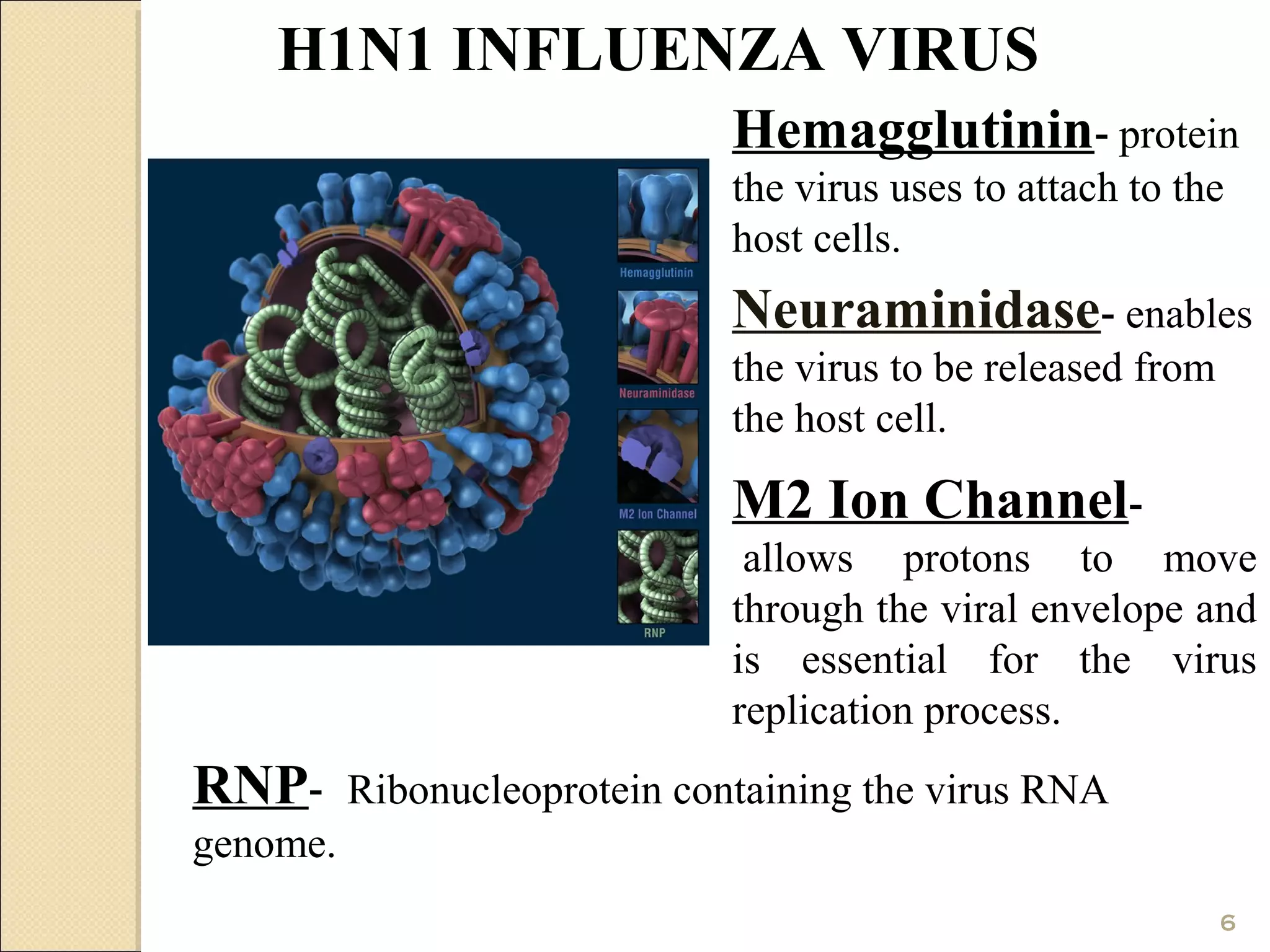
Swine flu, also known as H1N1, is a respiratory disease in pigs that can spread from person to person. The current swine flu virus is contagious and spreading globally. Symptoms are like seasonal flu and include fever, cough, sore throat and body aches. Diagnosis requires lab testing of respiratory samples collected within 5 days of symptoms. There is no vaccine yet for the current virus strain, but antiviral drugs like Tamiflu can treat it. Prevention focuses on hand washing, cough/sneeze etiquette, and avoiding contact with infected individuals.