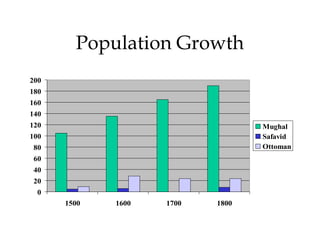
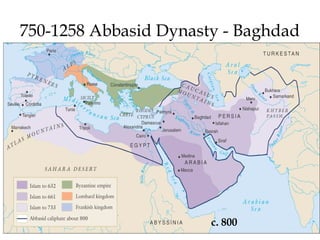
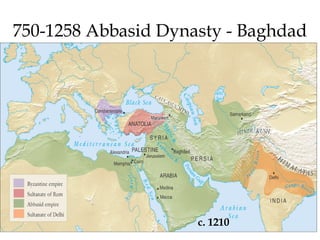
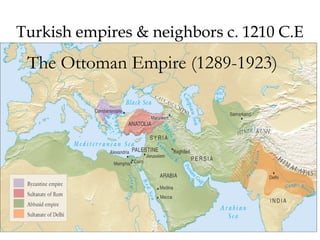
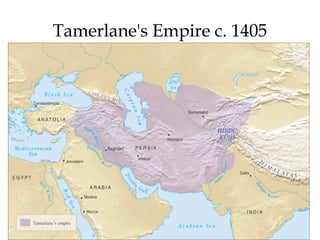
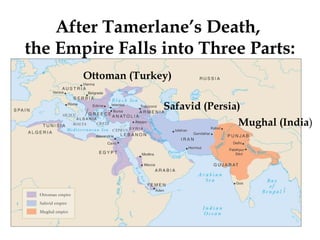
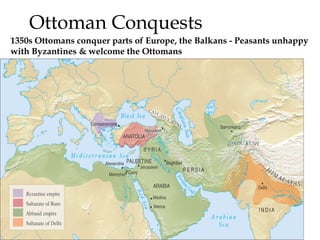
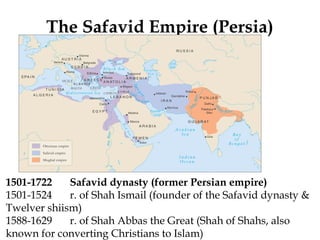
The document provides an overview of three major Islamic empires during the 1500-1800 period: the Ottoman Empire based in Turkey, the Safavid Empire based in Persia, and the Mughal Empire based in South Asia. It discusses the origins and expansion of each empire, key rulers like Suleiman the Magnificent, Shah Abbas, and Akbar, and cultural contributions such as architecture. The empires shared elements of being based on military conquest and steppe Turkish traditions but had religious diversity within their populations.




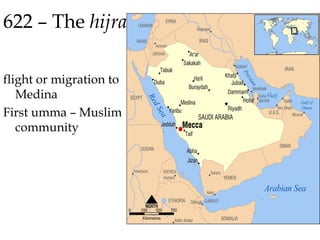






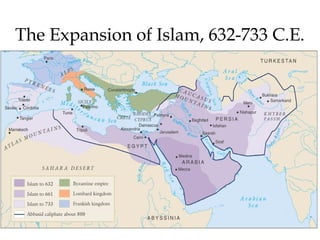
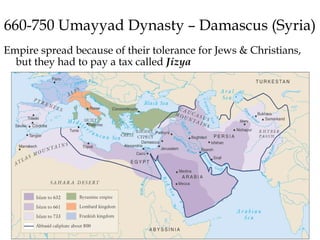




































![The Mughal Empire or South Asia – Pakistan,
India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Bhutan
1526-1858 Mughal dynasty - [moo-guh l] Mo•ghul (mŏŏ-gŭl', mō-) (India)
1498 Portuguese Vasco da Gama arrives at Calicut, Southwest India
1526 Babur (descendant of Tamerland & Genghis Khan) seizes Delhi and
starts the Mughal dynasty
1556-1605 Reign of Akbar
1608 English arrive – Surat, SW India
1628-1657 r. of Emperor Shah Jahan
1639 English build fort at Madras – Southeast India
1648 Shah Jahan builds the Taj Mahal (for his wife)
(English imitation in 1815 – Royal Pavilion @Brighton, after the
British victory over Napoleon at Waterloo)
1659-1707 r. of Aurangzeb
1739 Persians sack Delhi
1757 Battle of Plassey – British East India Company conquer Bengal area
1770s famines lead to 1/3 population loss, under BEIC tax administration
1858 British crown colonizes India](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-islamicempires-modernshorter9-130925000123-phpapp01/85/Lecture-4-islamic-empires-modern-shorter-59-320.jpg)