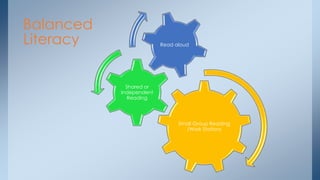
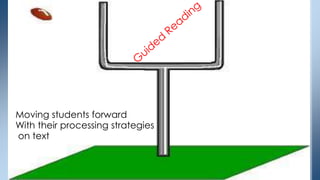
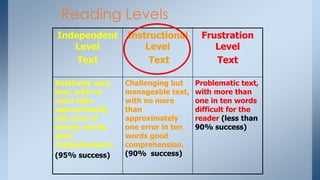
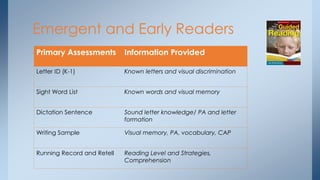
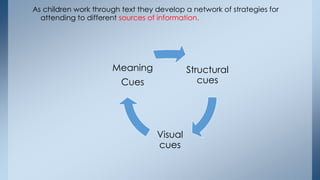
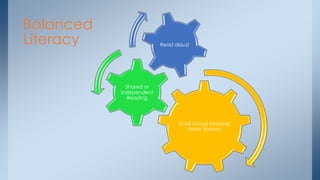
This document discusses strategies for building reading stamina and strength in small group guided reading sessions using complex texts. It describes assessing students and grouping them for guided reading instruction focused on strategic reading actions. Teachers are encouraged to select texts at students' instructional levels and teach comprehension and foundational reading skills through prompting and close reading exercises tailored to students' needs. The goal is to increase students' processing abilities across increasingly challenging texts.