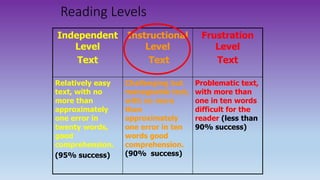
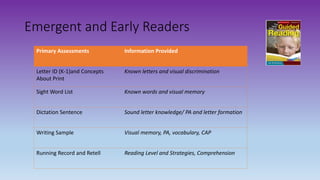
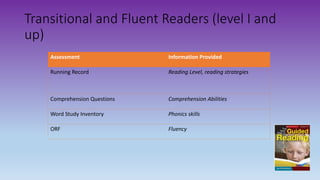
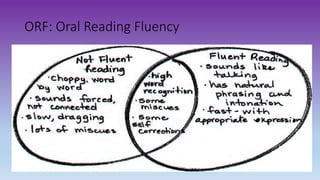
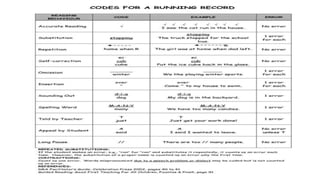
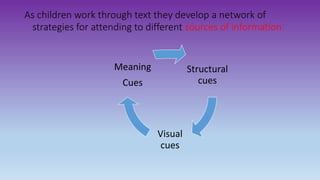
This document discusses how to use data to drive instruction in guided reading. It will teach educators how to use various assessment tools to collect data on students and analyze that data to make instructional decisions. Educators will learn how to group students, select appropriate texts, and plan focused lessons based on what the data shows about students' reading levels and needs. The document emphasizes using formative assessment on an ongoing basis to inform responsive teaching in guided reading.