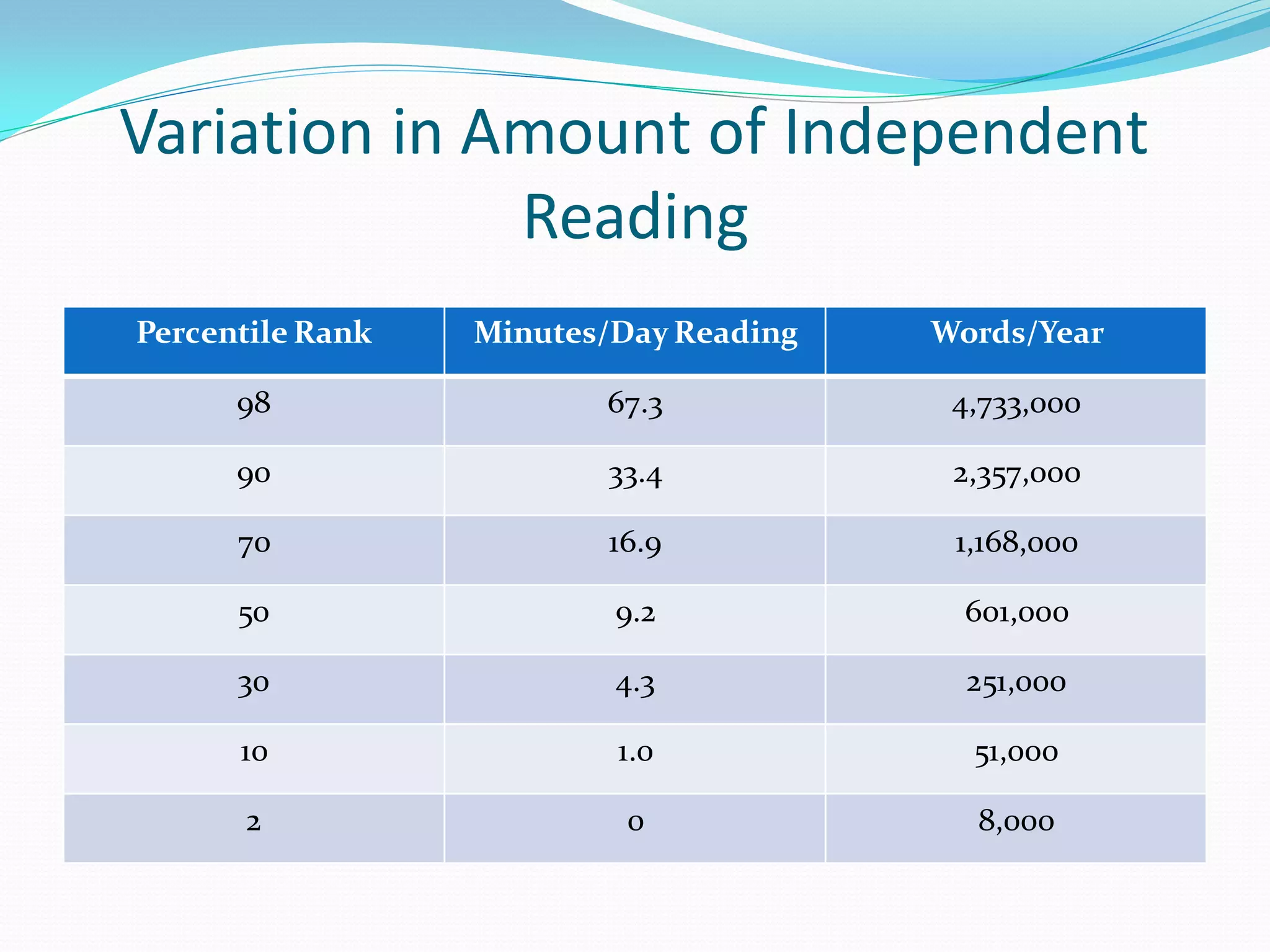
This document provides information and resources for teachers to support reading instruction, including:
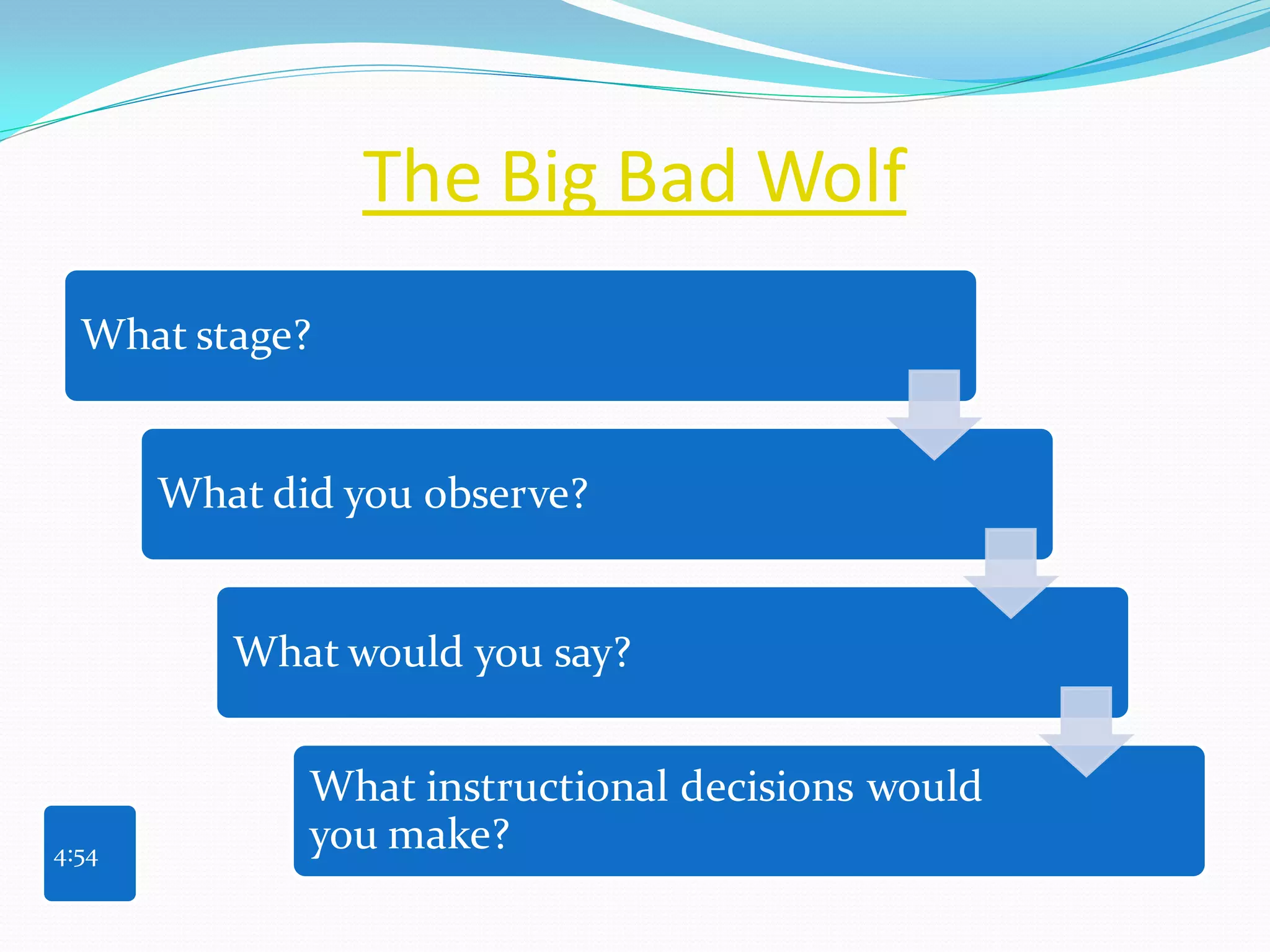
- Descriptions of different reading stages from emergent to advanced to help teachers determine students' reading levels based on observations.
- Suggested next steps include practicing observing students' reading behaviors, discussing observations and instructional decisions with teaching teams, and reflecting on one's own practice through a self-assessment.
- Additional resources are provided, such as videos of children reading at different levels to analyze, guides for reading workshops and self-reflection, and references for further reading. The goal is to help teachers make data-driven decisions to meet students' individual reading needs.