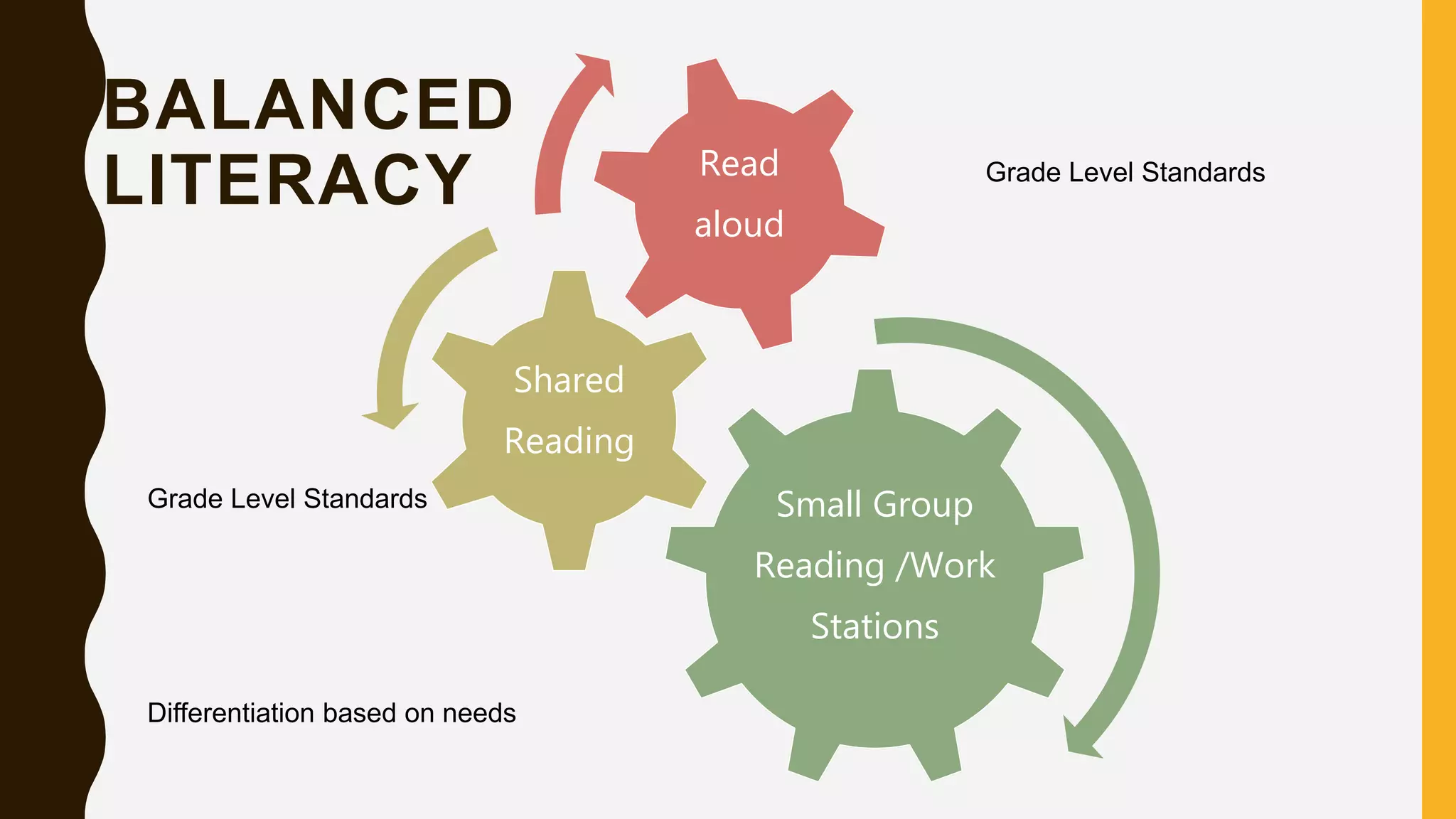
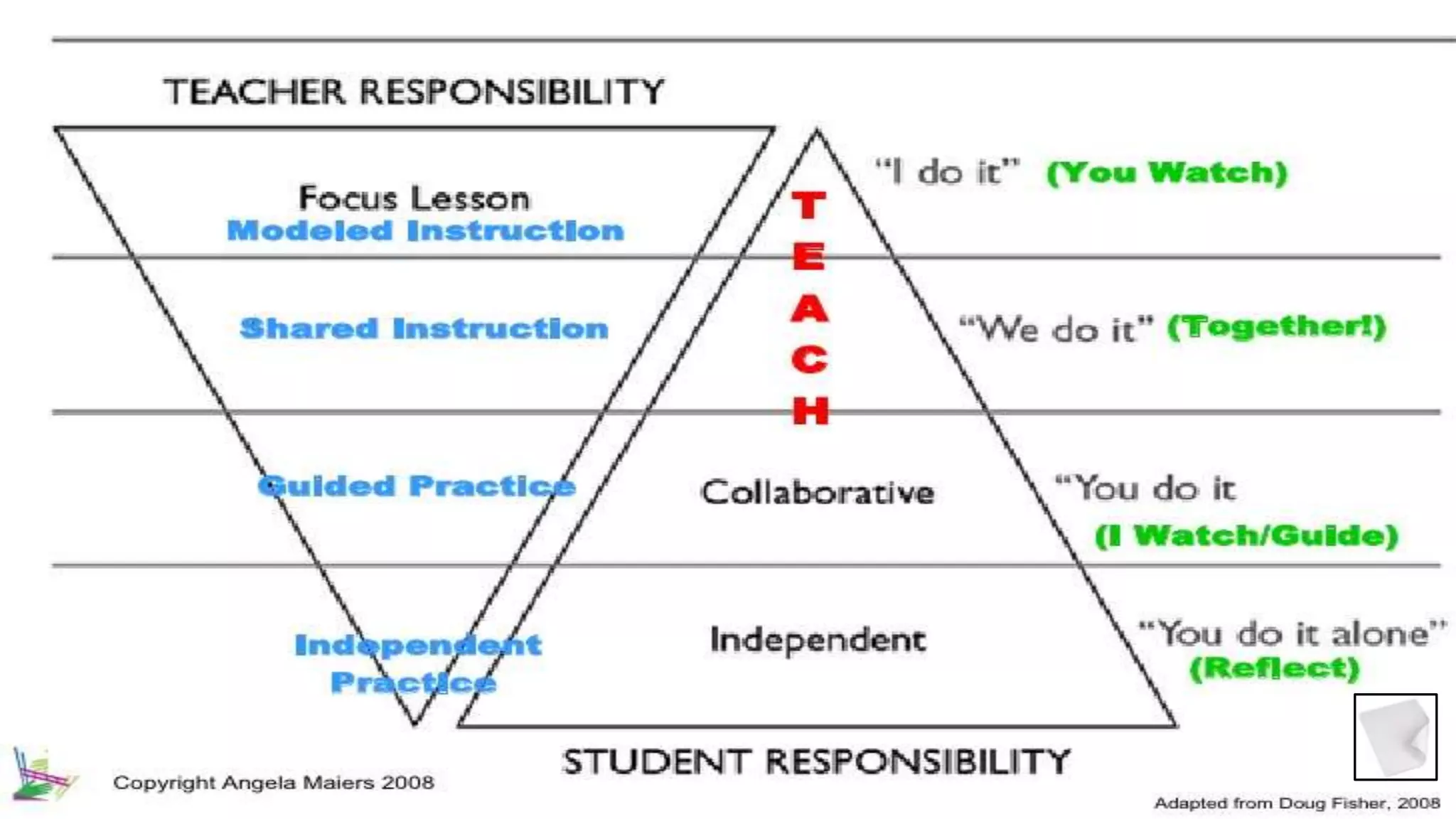
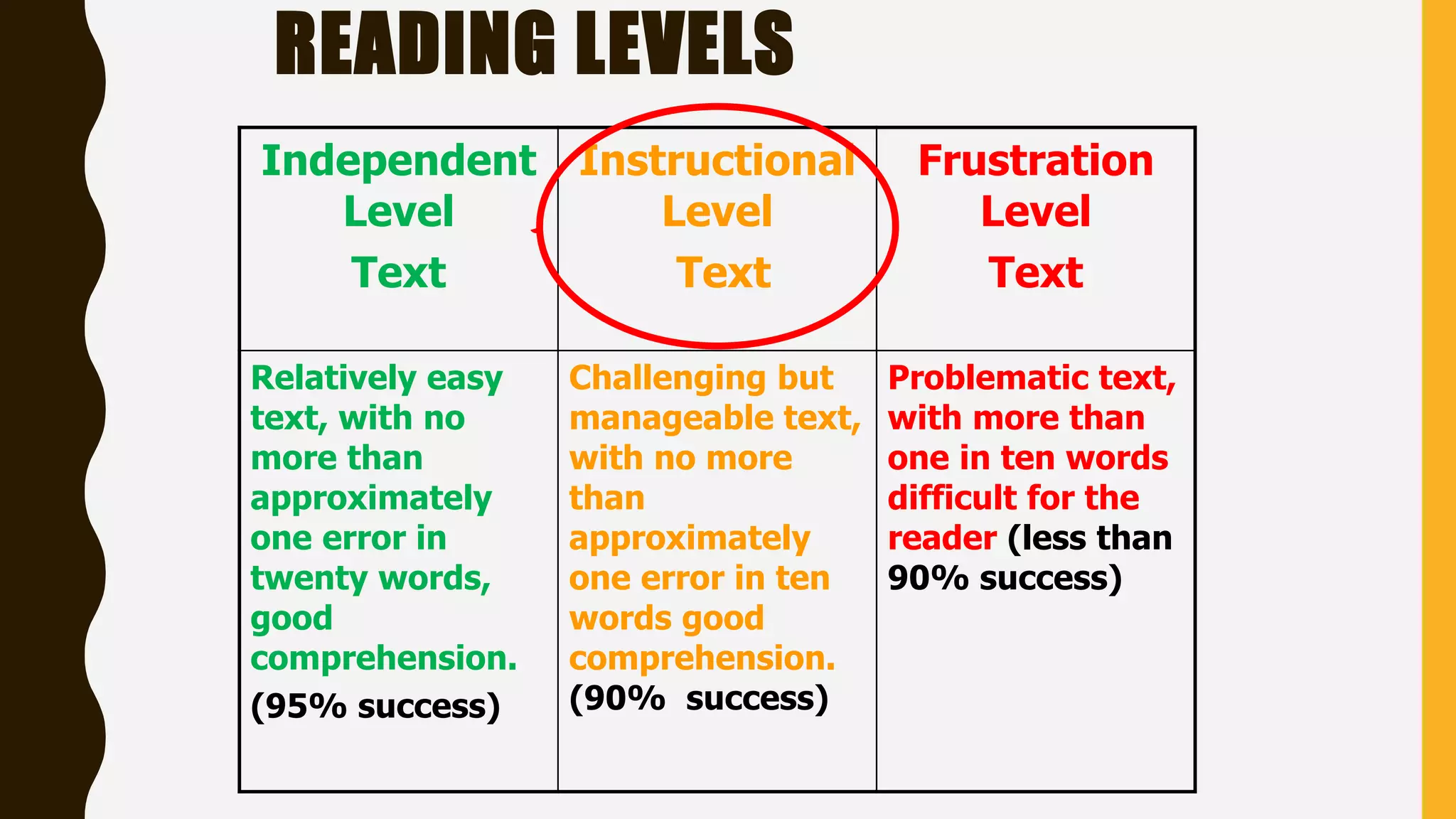
This document provides information about guided reading and implementing small group instruction in the classroom. It discusses what guided reading is, the key components of guided reading lessons, how to group students and select appropriate texts, and how to plan strategic teaching using a guided reading framework. Sample lesson structures and classroom management ideas are also presented to help teachers effectively implement guided reading in their literacy block.