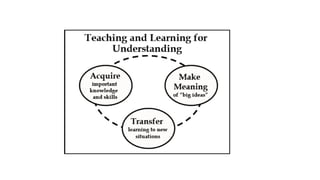
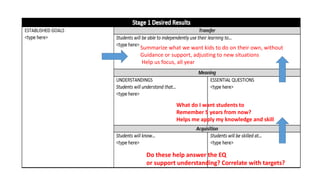
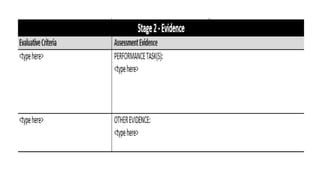
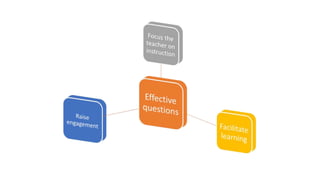
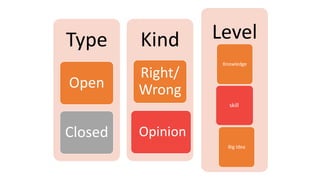
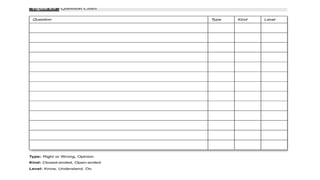
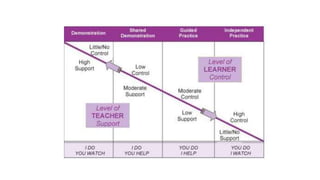
This document discusses strategies for literacy coaching, including setting instructional targets, planning for teaching and learning, unpacking standards, and using high-leverage instructional practices like effective questioning and thinking prompts. It provides examples of how to analyze standards and curriculum, plan learning assessments and activities, and develop student-focused learning goals and evaluation criteria. The document emphasizes using student-centered, evidence-based approaches to help teachers improve literacy instruction.