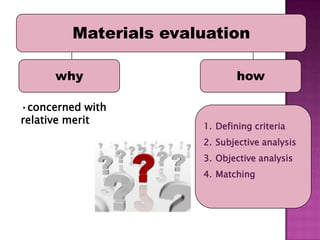
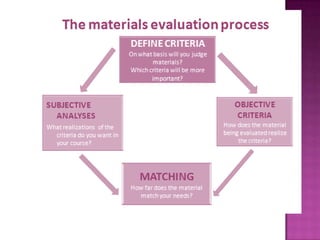
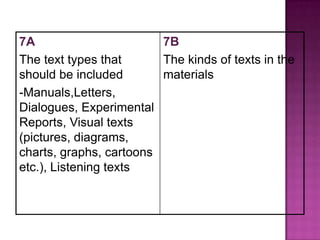
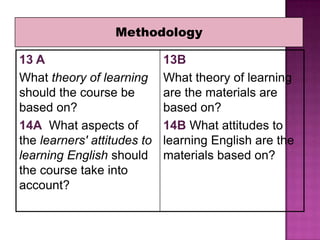
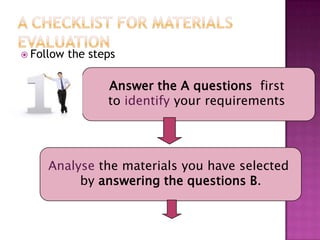
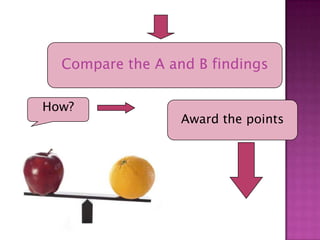
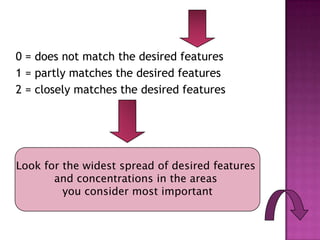
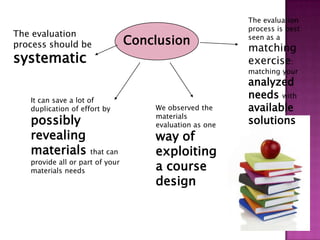
The document discusses the process of materials evaluation, focusing on defining criteria, audience, aims, content organization, methodology, and the necessary exercises and aids for effective course design. It provides a series of questions to identify requirements and analyze materials, emphasizing a systematic approach to matching desired features with available resources. The conclusion highlights the benefits of this evaluation process in optimizing course materials and meeting educational needs.