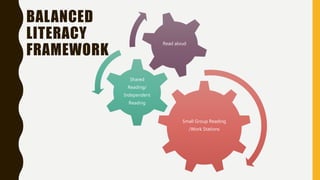
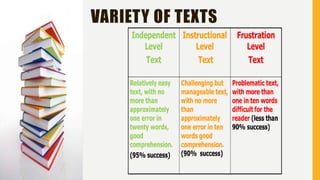
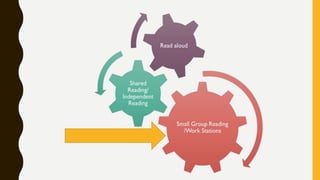
The document discusses big ticket items for effective elementary literacy instruction. It emphasizes that effective teachers matter more than curriculum or programs, and outlines a balanced literacy framework including read aloud, shared reading, small group reading, and independent reading. Key elements of exemplary classrooms include a 50/50 ratio of reading and writing versus other activities, use of various texts, student behaviors like writing to learn and citing evidence from texts, and how teachers teach including more conversational talk and choice in tasks. The document provides coaching questions to guide teachers in these instructional elements.