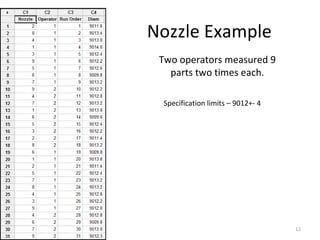
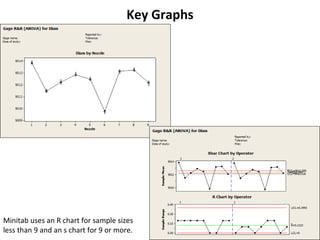
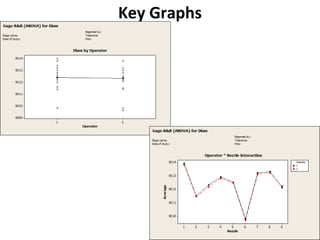
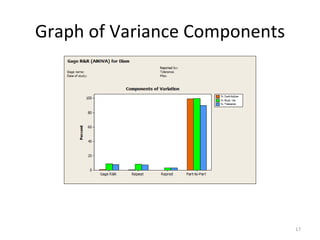
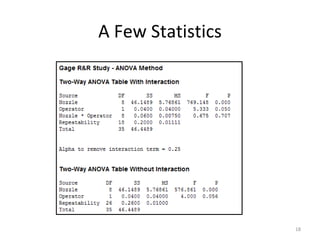
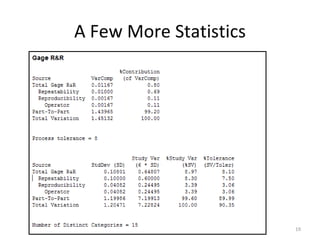
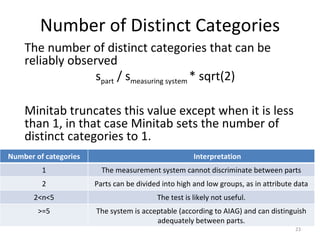
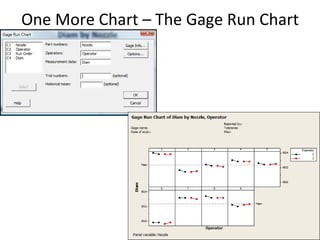
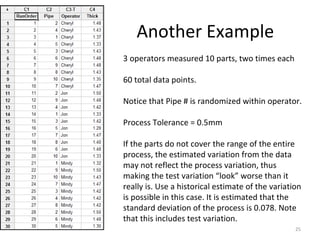
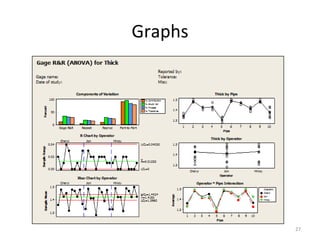
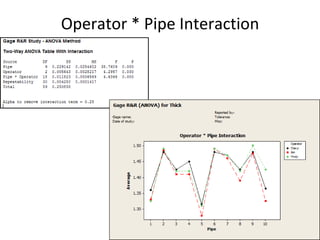
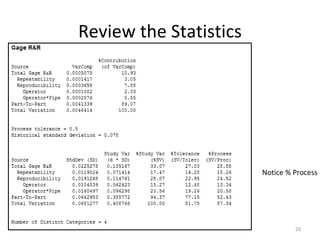
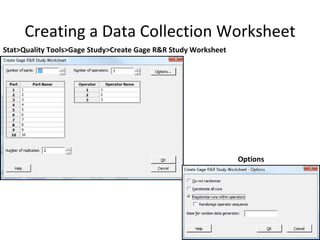
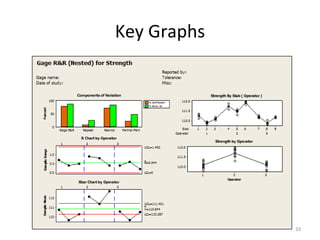
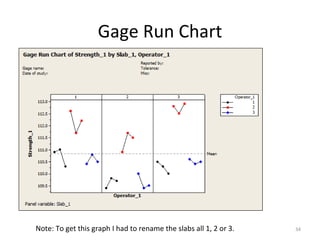
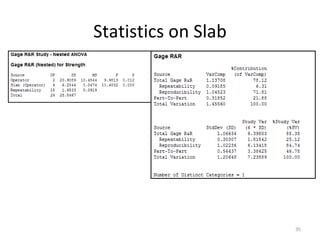
This document discusses variable gage repeatability and reproducibility (R&R) studies in Minitab. It describes how to conduct an R&R study to evaluate measurement systems, including selecting parts, operators, and number of measurements. Key outputs from Minitab like graphs of variance components and statistics like percent tolerance and percent study variation are explained. Guidelines for interpreting R&R results are provided. Examples walking through full R&R studies in Minitab are also included to illustrate the concepts and outputs.