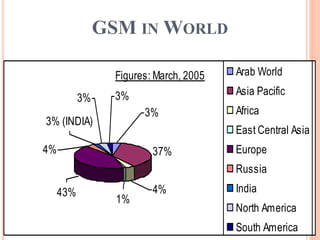
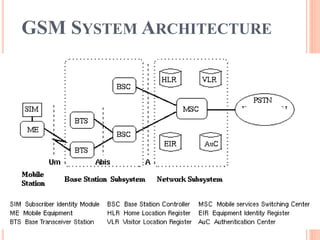
GSM is a second generation cellular standard developed to provide voice and data services using digital modulation. It has a global architecture consisting of mobile stations, base station subsystems, and a network switching subsystem. The network switching subsystem includes components like the mobile switching center, home location register, visitor location register, and others that work together to manage communication and mobility. GSM uses digital encryption and authentication to provide secure communication and prevent fraud. It has been enhanced over time to support additional data capabilities and services.