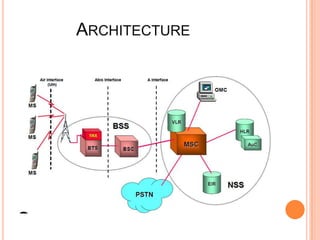
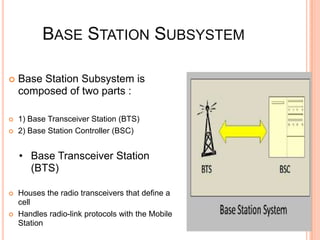
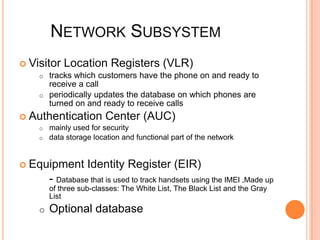
This presentation provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile (GSM) communications. It discusses the architecture of GSM including the mobile station, base station subsystem, and network subsystem. It also covers specifications such as frequency bands and carrier spacing, security features like encryption, and applications like telemetry systems. The presentation concludes by looking at the future of GSM including data rate improvements through technologies like GPRS, EDGE, and the transition to 3G standards.