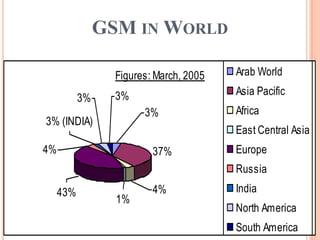
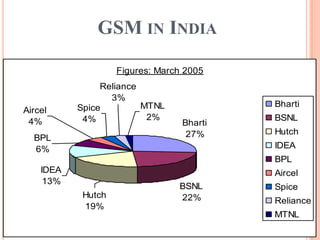
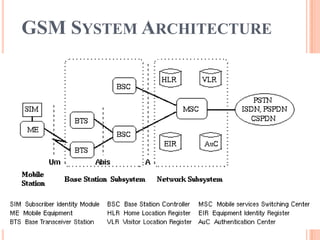
GSM is a second generation cellular standard developed to provide voice and data services using digital modulation. It has a three-part architecture including the mobile station, base station subsystem, and network switching subsystem. The base station subsystem handles radio resources and mobility management, while the network switching subsystem includes registers for subscriber data and authentication. GSM provides services like voice calls, SMS, and data transmission at rates up to 9.6 kbps. It offers security, international roaming, and is being succeeded by 3G technologies providing higher data rates.