The document provides an overview of GSM architecture including:
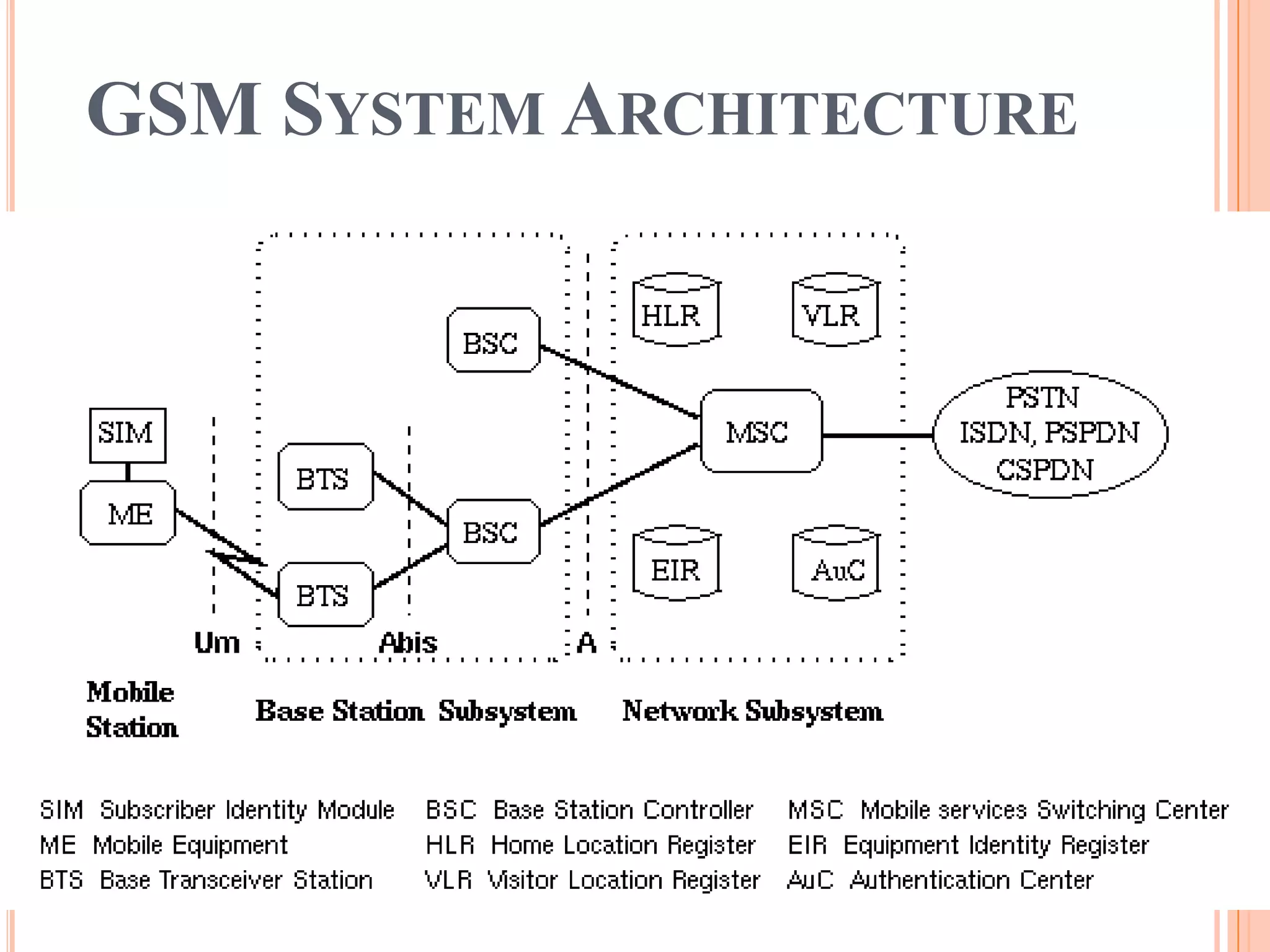
1. GSM uses a cellular network architecture with base stations, base station controllers, mobile switching centers, and databases to manage subscriber identity and location.
2. The network allows for voice calls and data services including SMS, and provides security through subscriber authentication and encryption.
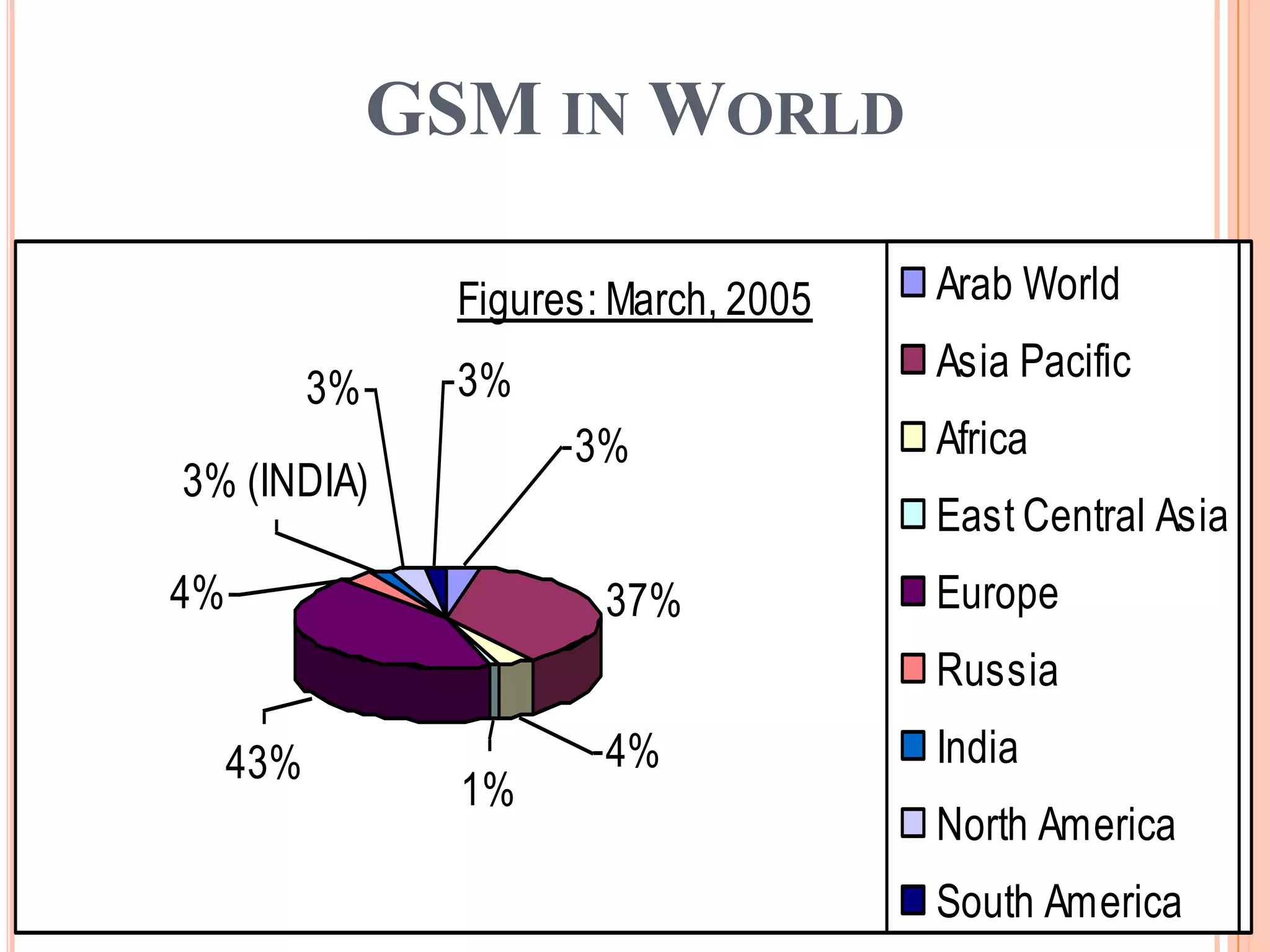
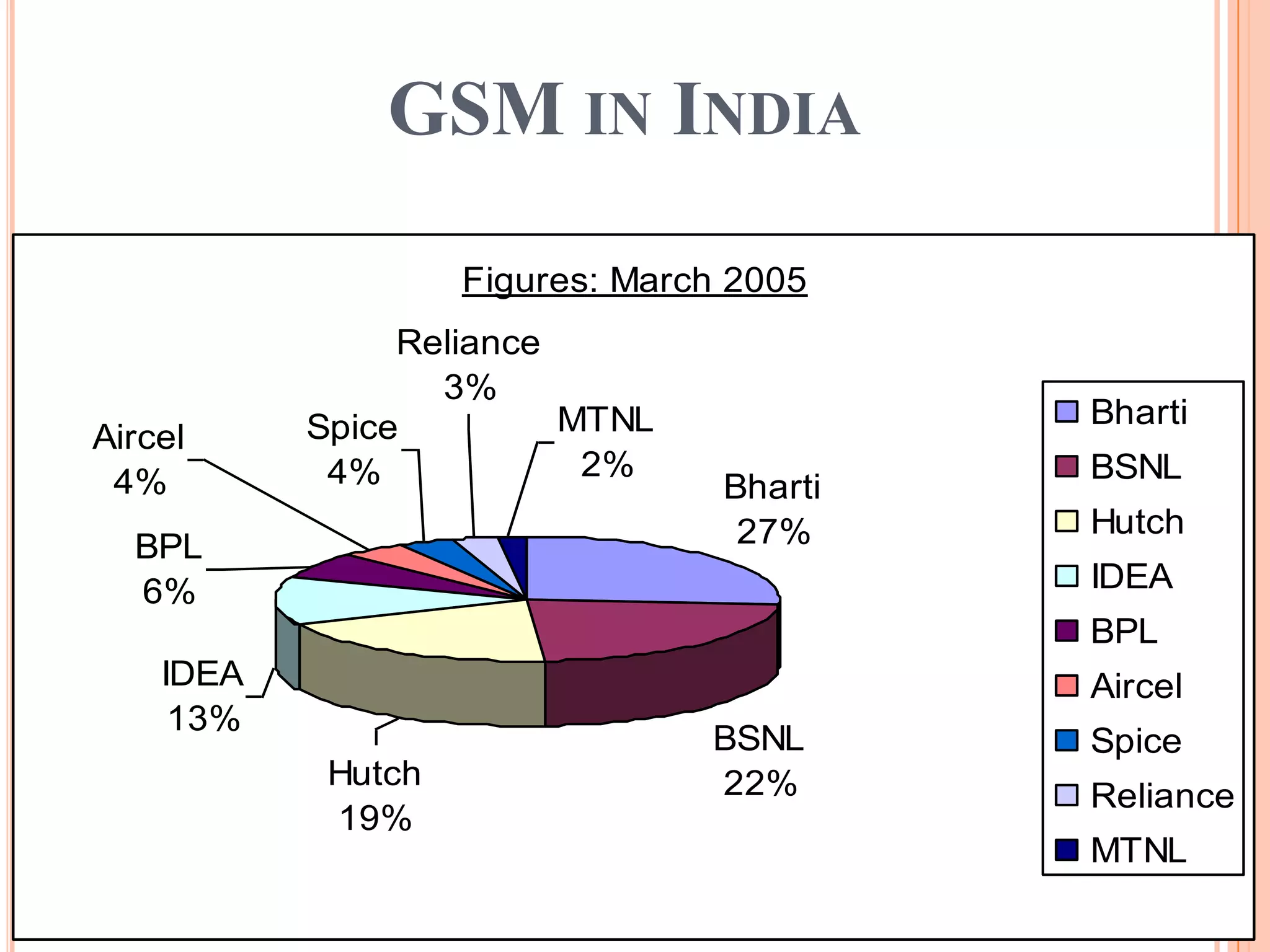
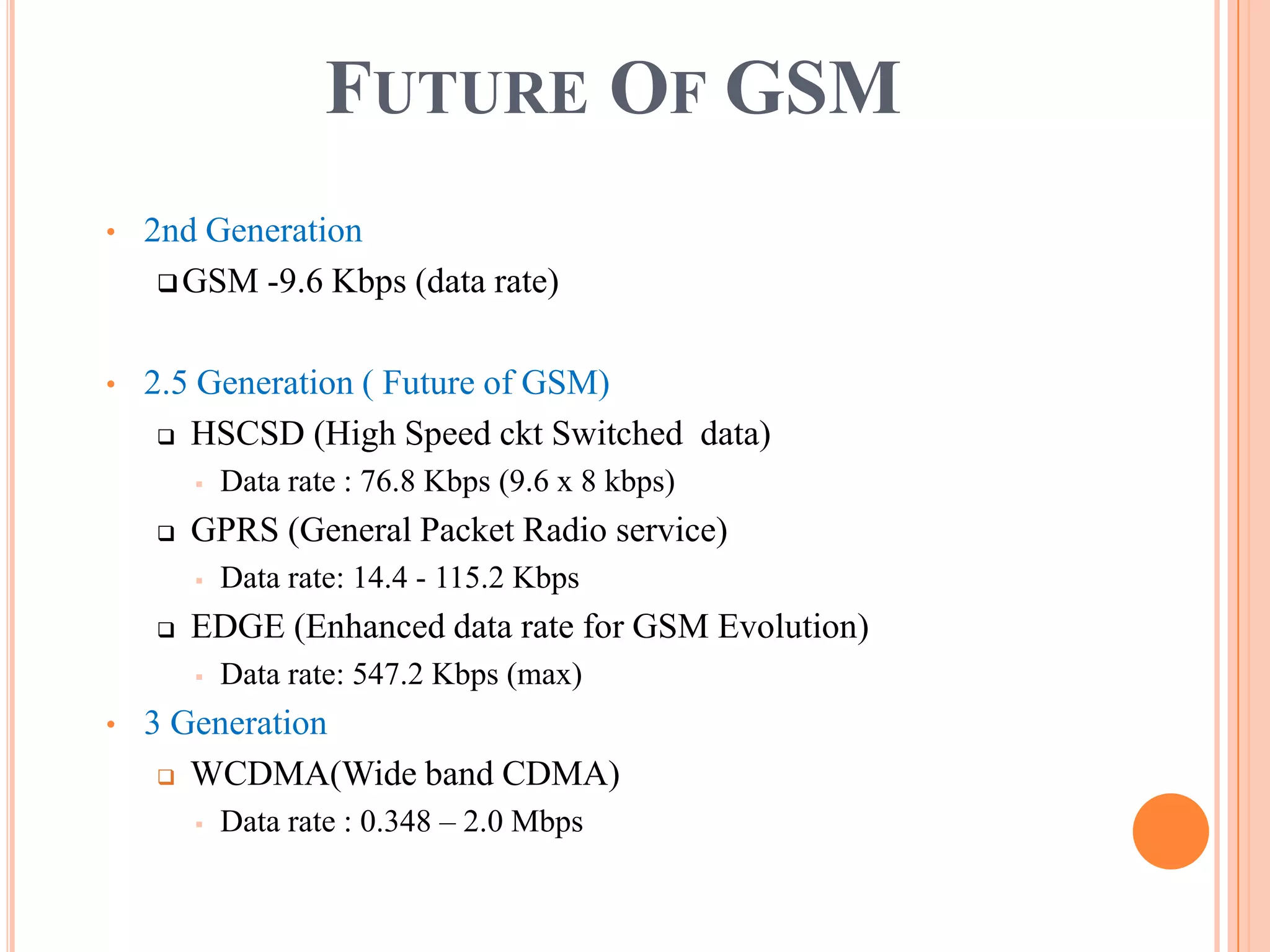
3. GSM is a global standard that enabled international roaming and continues to evolve to support higher data rates through technologies like GPRS, EDGE, and WCDMA.