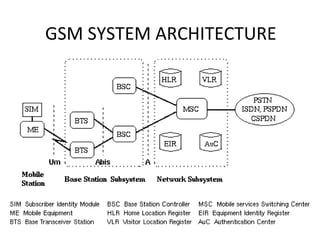
GSM architecture consists of mobile stations, a base station subsystem, and a network switching subsystem. The mobile station includes a mobile equipment and SIM card. The base station subsystem is made up of base transceiver stations that communicate with mobile stations and base station controllers that manage radio resources. The network switching subsystem contains key components like mobile switching centers, home and visitor location registers, and an authentication center that help manage subscriber location and authentication.