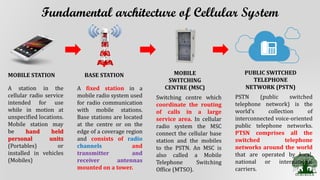
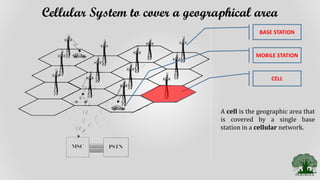
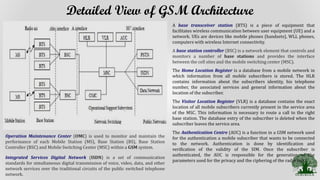
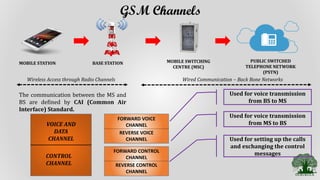
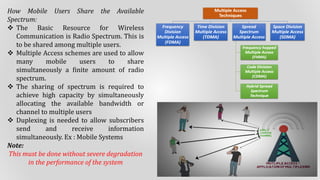
Cellular systems allow mobile users to communicate wirelessly using a network of base stations and switches. A mobile station communicates with the nearest base station, which connects to a mobile switching center. The switching center routes calls between mobile stations and the public switched telephone network. Coverage areas are divided into cells served by individual base stations to allow frequency reuse that improves system capacity.