This document summarizes key information about wireless communication technologies including Wireless Local Loop (WLL), Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), and Bluetooth.
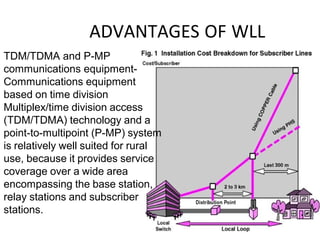
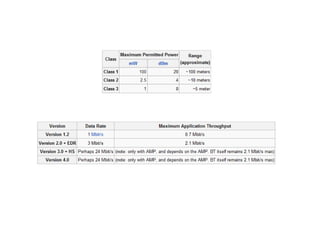
WLL uses radio signals to connect subscribers to telephone networks as an alternative to copper wiring, reducing construction and operating costs. WLAN allows wireless connectivity between devices within a limited area like a home or office, providing installation flexibility and reduced costs compared to wired networks. Bluetooth operates in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz band using frequency-hopping spread spectrum, chopping up and transmitting data across multiple bands to enable short-range wireless communication between devices.