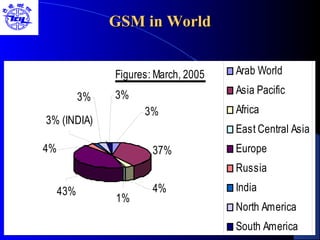
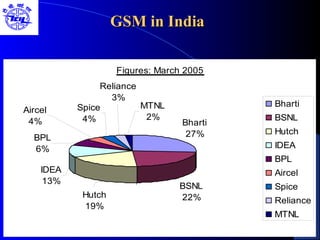
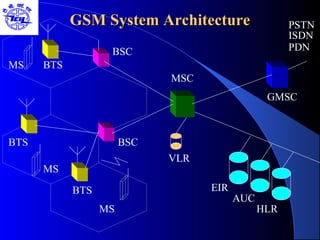
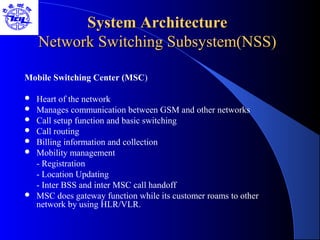
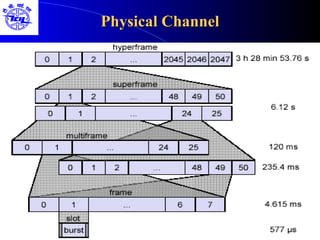
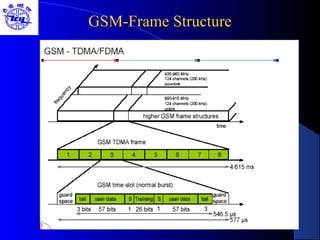
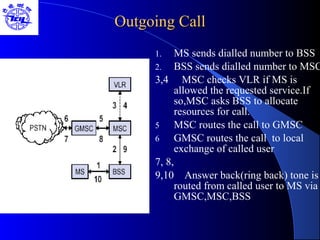
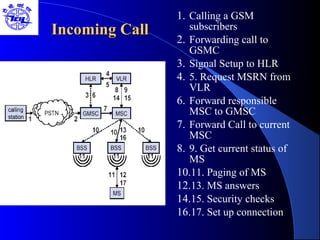
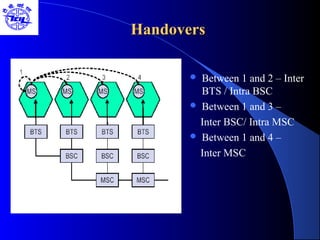
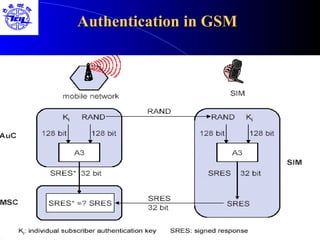
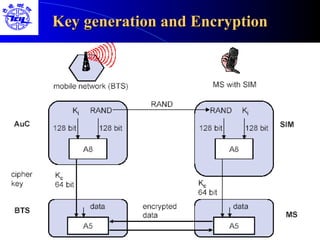
The document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile (GSM) network. It discusses the history and development of GSM, the key components of GSM architecture including the mobile station, base station subsystem, and network switching subsystem. It also describes the technical specifications of GSM such as frequency spectrum, frame structure, channels, and security features. Finally, it discusses the applications and future developments of GSM networks including 2.5G and 3G technologies.