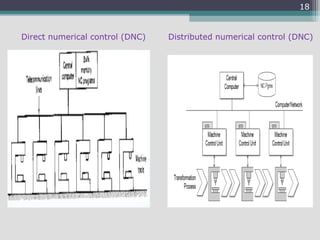
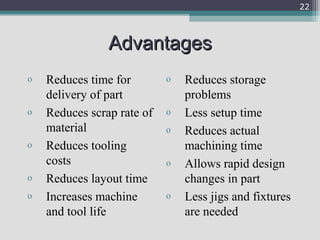
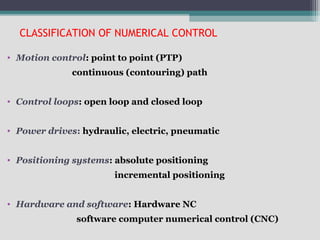
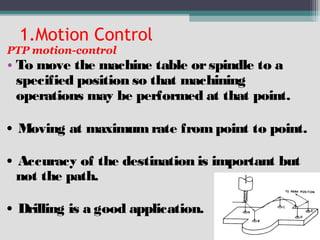
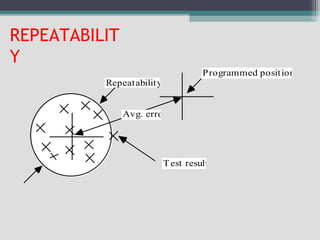
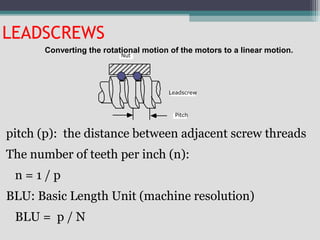
The document provides an overview of numerical control (NC) and computer numerical control (CNC) machines. It discusses:
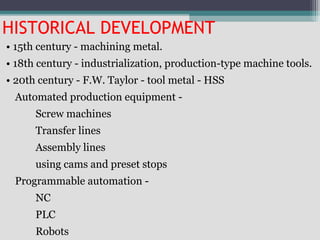
1) The historical development of NC from mechanized production equipment to programmable automation using NC, PLCs, and robots.
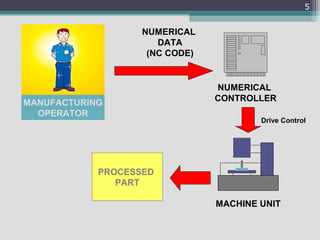
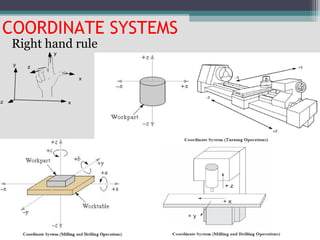
2) The basic definition and components of an NC machine, including the numerical controller, NC code, and interactions between the operator and machine.
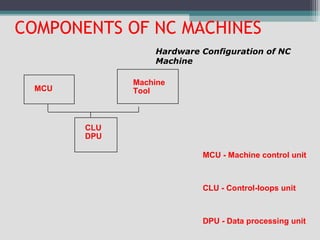
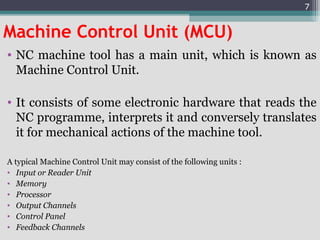
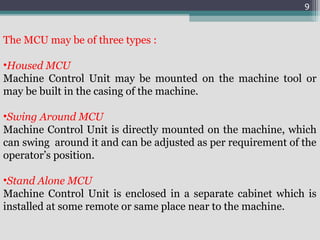
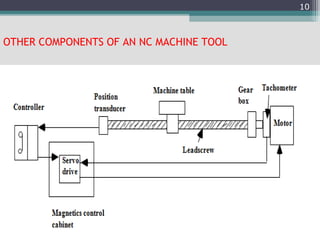
3) The main components of NC machines - the machine control unit, machine tool, and various control units. It also discusses different types of machine control units.
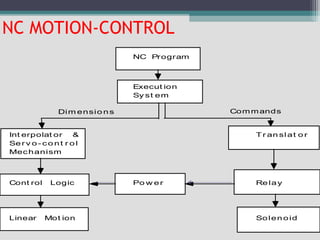
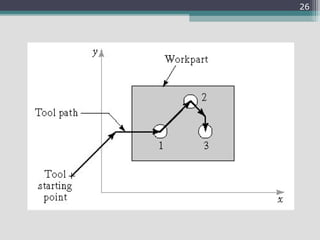
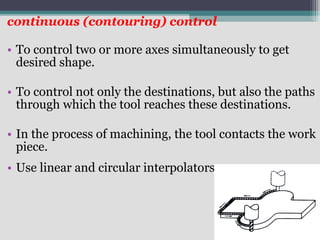
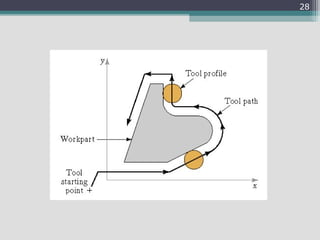
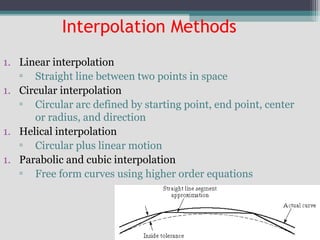
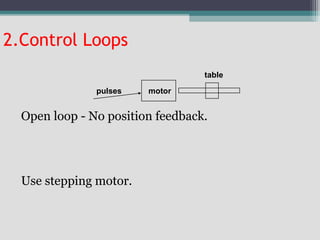
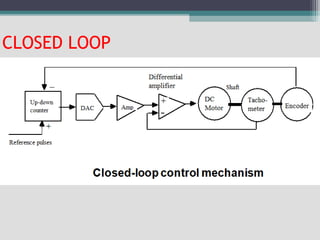
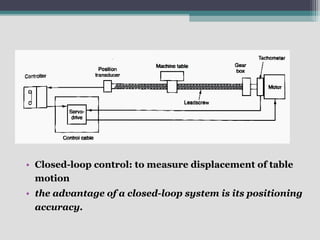
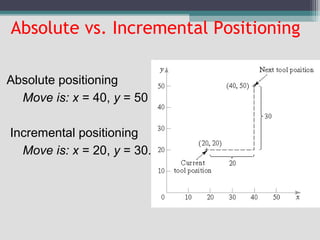
4) Key aspects of NC motion control including point-to-point and continuous path control, open and closed loop systems, and different